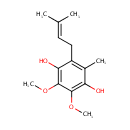
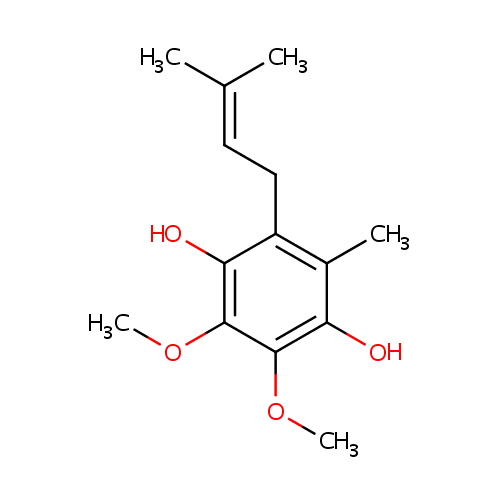
Ubiquinol-1 (PAMDB001968)
| Record Information | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Version | 1.0 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Update Date | 1/22/2018 11:54:54 AM | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Metabolite ID | PAMDB001968 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Identification | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Name: | Ubiquinol-1 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Description: | Ubiquinol-1 is a member of the chemical class known as Polyprenylbenzoquinols. They are reduced forms of polyprenylbenzoquinines (ubiquinones). These are compounds containing a polyisoprene chain attached to a quinol at the second ring position. Ubiquiol-1 has just 1 isoprene unit. Normally in Pseudomonas aeruginosa the active form of Ubiquinol has 8 isoprene units (Ubiquinol-8) and in humans it normally has 10. Ubiquinol-1 is a ??ailed??or incomplete version of Ubiquinol 8 that arises from conjugation by a shortened prenyl tail via 4-hydroxybenzoate polyprenyltransferase. Coenzyme Q(n) exists in three redox states, fully oxidized (ubiquinone), partially reduced (semiquinones or ubisemiquinones), and fully reduced (ubiquinols). The redox functions of ubiquinol in cellular energy production and antioxidant protection are based on the ability to exchange two electrons in a redox cycle between ubiquinol (reduced) and the ubiquinone (oxidized) form. Ubiquionols are important in cellular respiration. They are fat-soluble and therefore mobile in cellular membranes; they play a unique role in the electron transport chain (ETC). In the inner bacterial membrane, electrons from NADH and succinate pass through the ETC to the oxygen, which is then reduced to water. The transfer of electrons through ETC results in the pumping of H+ across the membrane creating a proton gradient across the membrane, which is used by ATP synthase (located on the membrane) to generate ATP. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Structure | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Synonyms: |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Chemical Formula: | C14H20O4 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Average Molecular Weight: | 252.3062 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Monoisotopic Molecular Weight: | 252.136159128 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| InChI Key: | TVLSKGDBUQMDPR-UHFFFAOYSA-N | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| InChI: | InChI=1S/C14H20O4/c1-8(2)6-7-10-9(3)11(15)13(17-4)14(18-5)12(10)16/h6,15-16H,7H2,1-5H3 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| CAS number: | Not Available | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| IUPAC Name: | 2,3-dimethoxy-5-methyl-6-(3-methylbut-2-en-1-yl)benzene-1,4-diol | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Traditional IUPAC Name: | 2,3-dimethoxy-5-methyl-6-(3-methylbut-2-en-1-yl)benzene-1,4-diol | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| SMILES: | COC1=C(O)C(C)=C(CC=C(C)C)C(O)=C1OC | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Chemical Taxonomy | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Taxonomy Description | This compound belongs to the class of organic compounds known as prenylated hydroquinones. These are quinones with a structure characterized by the hydroquinone ring substituted by an prenyl side-chain. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Kingdom | Organic compounds | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Super Class | Lipids and lipid-like molecules | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Class | Prenol lipids | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Sub Class | Quinone and hydroquinone lipids | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Direct Parent | Prenylated hydroquinones | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Alternative Parents | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Substituents |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Molecular Framework | Aromatic homomonocyclic compounds | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| External Descriptors |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Physical Properties | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| State: | Not Available | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Charge: | 0 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Melting point: | Not Available | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Experimental Properties: |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Predicted Properties |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Biological Properties | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Cellular Locations: | Membrane | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Reactions: | D-Glucose + Ubiquinone-10 > Gluconolactone + Ubiquinol-1 Pyruvic acid + Ubiquinone-10 + Water > Acetic acid + Carbon dioxide + Ubiquinol-1 Succinic acid + Ubiquinone-1 > Ubiquinol-1 + Fumaric acid L-Proline + Ubiquinone-1 + L-Proline > Hydrogen ion + Ubiquinol-1 + 1-Pyrroline-5-carboxylic acid + L-D-1-Pyrroline-5-carboxylic acid Glycerol 3-phosphate + Ubiquinone-1 > Dihydroxyacetone phosphate + Ubiquinol-1 4,5-Dihydroorotic acid + Ubiquinone-1 + 4,5-Dihydroorotic acid > Ubiquinol-1 + Orotic acid 2 Ubiquinol-1 + Oxygen + 4 Hydrogen ion >2 Ubiquinone-1 +2 Water +4 Hydrogen ion NADH + 5 Hydrogen ion + Ubiquinone-1 > Hydrogen ion + NAD + Ubiquinol-1 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Pathways: | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Spectra | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Spectra: |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| References | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| References: |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Synthesis Reference: | Not Available | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Material Safety Data Sheet (MSDS) | Not Available | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Links | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| External Links: |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Enzymes
- General function:
- Involved in magnesium ion binding
- Specific function:
- Pyruvate + ferricytochrome b1 + H(2)O = acetate + CO(2) + ferrocytochrome b1
- Gene Name:
- poxB
- Locus Tag:
- PA5297
- Molecular weight:
- 62.3 kDa
Reactions
| Pyruvate + ubiquinone + H(2)O = acetate + CO(2) + ubiquinol. |
- General function:
- Involved in electron carrier activity
- Specific function:
- Two distinct, membrane-bound, FAD-containing enzymes are responsible for the catalysis of fumarate and succinate interconversion; the fumarate reductase is used in anaerobic growth, and the succinate dehydrogenase is used in aerobic growth
- Gene Name:
- sdhB
- Locus Tag:
- PA1584
- Molecular weight:
- 26.2 kDa
Reactions
| Succinate + acceptor = fumarate + reduced acceptor. |
- General function:
- Involved in oxidoreductase activity
- Specific function:
- Oxidizes proline to glutamate for use as a carbon and nitrogen source and also function as a transcriptional repressor of the put operon
- Gene Name:
- putA
- Locus Tag:
- PA0782
- Molecular weight:
- 115.6 kDa
Reactions
| L-proline + acceptor = (S)-1-pyrroline-5-carboxylate + reduced acceptor. |
| (S)-1-pyrroline-5-carboxylate + NAD(P)(+) + 2 H(2)O = L-glutamate + NAD(P)H. |
- General function:
- Involved in oxidation-reduction process
- Specific function:
- sn-glycerol 3-phosphate + NAD(P)(+) = glycerone phosphate + NAD(P)H
- Gene Name:
- gpsA
- Locus Tag:
- PA1614
- Molecular weight:
- 36.8 kDa
Reactions
| sn-glycerol 3-phosphate + NAD(P)(+) = glycerone phosphate + NAD(P)H. |
- General function:
- Involved in catalytic activity
- Specific function:
- (S)-dihydroorotate + a quinone = orotate + a quinol
- Gene Name:
- pyrD
- Locus Tag:
- PA3050
- Molecular weight:
- 36.1 kDa
Reactions
| (S)-dihydroorotate + a quinone = orotate + a quinol. |
- General function:
- Involved in electron carrier activity
- Specific function:
- Two distinct, membrane-bound, FAD-containing enzymes are responsible for the catalysis of fumarate and succinate interconversion; the fumarate reductase is used in anaerobic growth, and the succinate dehydrogenase is used in aerobic growth
- Gene Name:
- sdhA
- Locus Tag:
- PA1583
- Molecular weight:
- 63.5 kDa
Reactions
| Succinate + acceptor = fumarate + reduced acceptor. |
- General function:
- Involved in succinate dehydrogenase activity
- Specific function:
- Membrane-anchoring subunit of succinate dehydrogenase (SDH)
- Gene Name:
- sdhD
- Locus Tag:
- PA1582
- Molecular weight:
- 13.7 kDa
- General function:
- Involved in oxidoreductase activity, acting on NADH or NADPH
- Specific function:
- NDH-1 shuttles electrons from NADH, via FMN and iron- sulfur (Fe-S) centers, to quinones in the respiratory chain. The immediate electron acceptor for the enzyme in this species is believed to be ubiquinone. Couples the redox reaction to proton translocation (for every two electrons transferred, four hydrogen ions are translocated across the cytoplasmic membrane), and thus conserves the redox energy in a proton gradient
- Gene Name:
- nuoA
- Locus Tag:
- PA2637
- Molecular weight:
- 15 kDa
Reactions
| NADH + quinone = NAD(+) + quinol. |
- General function:
- Involved in NADH dehydrogenase (ubiquinone) activity
- Specific function:
- NDH-1 shuttles electrons from NADH, via FMN and iron- sulfur (Fe-S) centers, to quinones in the respiratory chain. The immediate electron acceptor for the enzyme in this species is ubiquinone. Couples the redox reaction to proton translocation (for every two electrons transferred, four hydrogen ions are translocated across the cytoplasmic membrane), and thus conserves the redox energy in a proton gradient
- Gene Name:
- nuoB
- Locus Tag:
- PA2638
- Molecular weight:
- 25.4 kDa
Reactions
| NADH + quinone = NAD(+) + quinol. |
- General function:
- Involved in oxidoreductase activity
- Specific function:
- NDH-1 shuttles electrons from NADH, via FMN and iron- sulfur (Fe-S) centers, to quinones in the respiratory chain. The immediate electron acceptor for the enzyme in this species is believed to be ubiquinone. Couples the redox reaction to proton translocation (for every two electrons transferred, four hydrogen ions are translocated across the cytoplasmic membrane), and thus conserves the redox energy in a proton gradient
- Gene Name:
- nuoE
- Locus Tag:
- PA2640
- Molecular weight:
- 18.1 kDa
Reactions
| NADH + quinone = NAD(+) + quinol. |
- General function:
- Involved in oxidation-reduction process
- Specific function:
- NDH-1 shuttles electrons from NADH, via FMN and iron- sulfur (Fe-S) centers, to quinones in the respiratory chain. The immediate electron acceptor for the enzyme in this species is believed to be ubiquinone. Couples the redox reaction to proton translocation (for every two electrons transferred, four hydrogen ions are translocated across the cytoplasmic membrane), and thus conserves the redox energy in a proton gradient. This subunit may bind ubiquinone
- Gene Name:
- nuoH
- Locus Tag:
- PA2643
- Molecular weight:
- 36.7 kDa
Reactions
| NADH + quinone = NAD(+) + quinol. |
- General function:
- Involved in electron carrier activity
- Specific function:
- NDH-1 shuttles electrons from NADH, via FMN and iron- sulfur (Fe-S) centers, to quinones in the respiratory chain. The immediate electron acceptor for the enzyme in this species is believed to be ubiquinone. Couples the redox reaction to proton translocation (for every two electrons transferred, four hydrogen ions are translocated across the cytoplasmic membrane), and thus conserves the redox energy in a proton gradient
- Gene Name:
- nuoI
- Locus Tag:
- PA2644
- Molecular weight:
- 20.6 kDa
Reactions
| NADH + quinone = NAD(+) + quinol. |
- General function:
- Involved in NADH dehydrogenase (ubiquinone) activity
- Specific function:
- NDH-1 shuttles electrons from NADH, via FMN and iron- sulfur (Fe-S) centers, to quinones in the respiratory chain. The immediate electron acceptor for the enzyme in this species is believed to be ubiquinone. Couples the redox reaction to proton translocation (for every two electrons transferred, four hydrogen ions are translocated across the cytoplasmic membrane), and thus conserves the redox energy in a proton gradient
- Gene Name:
- nuoJ
- Locus Tag:
- PA2645
- Molecular weight:
- 17.6 kDa
Reactions
| NADH + quinone = NAD(+) + quinol. |
- General function:
- Involved in oxidoreductase activity, acting on NADH or NADPH
- Specific function:
- There are 2 NADH dehydrogenases in Pseudomonas aeruginosa, however only this complex is able to use dNADH (reduced nicotinamide hypoxanthine dinucleotide, deamino-NADH) and dNADH-DB (dimethoxy- 5-methyl-6-decyl-1,4-benzoquinone) as substrates
- Gene Name:
- nuoK
- Locus Tag:
- PA2646
- Molecular weight:
- 11 kDa
Reactions
| NADH + quinone = NAD(+) + quinol. |
- General function:
- Involved in NADH dehydrogenase (ubiquinone) activity
- Specific function:
- NDH-1 shuttles electrons from NADH, via FMN and iron- sulfur (Fe-S) centers, to quinones in the respiratory chain. The immediate electron acceptor for the enzyme in this species is believed to be ubiquinone. Couples the redox reaction to proton translocation (for every two electrons transferred, four hydrogen ions are translocated across the cytoplasmic membrane), and thus conserves the redox energy in a proton gradient
- Gene Name:
- nuoM
- Locus Tag:
- PA2648
- Molecular weight:
- 55.7 kDa
Reactions
| NADH + quinone = NAD(+) + quinol. |
- General function:
- Involved in NADH dehydrogenase (ubiquinone) activity
- Specific function:
- NDH-1 shuttles electrons from NADH, via FMN and iron- sulfur (Fe-S) centers, to quinones in the respiratory chain. The immediate electron acceptor for the enzyme in this species is believed to be ubiquinone. Couples the redox reaction to proton translocation (for every two electrons transferred, four hydrogen ions are translocated across the cytoplasmic membrane), and thus conserves the redox energy in a proton gradient
- Gene Name:
- nuoN
- Locus Tag:
- PA2649
- Molecular weight:
- 51.7 kDa
Reactions
| NADH + quinone = NAD(+) + quinol. |
- General function:
- Involved in oxidoreductase activity, acting on CH-OH group of donors
- Specific function:
- GDH is probably involved in energy conservation rather than in sugar metabolism
- Gene Name:
- gcd
- Locus Tag:
- PA2290
- Molecular weight:
- 86.2 kDa
Reactions
| D-glucose + ubiquinone = D-glucono-1,5-lactone + ubiquinol. |
- General function:
- Involved in NADH dehydrogenase (ubiquinone) activity
- Specific function:
- NDH-1 shuttles electrons from NADH, via FMN and iron- sulfur (Fe-S) centers, to quinones in the respiratory chain. The immediate electron acceptor for the enzyme in this species is believed to be ubiquinone. Couples the redox reaction to proton translocation (for every two electrons transferred, four hydrogen ions are translocated across the cytoplasmic membrane), and thus conserves the redox energy in a proton gradient
- Gene Name:
- nuoF
- Locus Tag:
- PA2641
- Molecular weight:
- 48.7 kDa
Reactions
| NADH + quinone = NAD(+) + quinol. |
- General function:
- Involved in oxidoreductase activity, acting on NADH or NADPH
- Specific function:
- NDH-1 shuttles electrons from NADH, via FMN and iron- sulfur (Fe-S) centers, to quinones in the respiratory chain. The immediate electron acceptor for the enzyme in this species is believed to be ubiquinone. Couples the redox reaction to proton translocation (for every two electrons transferred, four hydrogen ions are translocated across the cytoplasmic membrane), and thus conserves the redox energy in a proton gradient
- Gene Name:
- nuoC
- Locus Tag:
- PA2639
- Molecular weight:
- 68.3 kDa
Reactions
| NADH + quinone = NAD(+) + quinol. |
- General function:
- Involved in electron carrier activity
- Specific function:
- NDH-1 shuttles electrons from NADH, via FMN and iron- sulfur (Fe-S) centers, to quinones in the respiratory chain. The immediate electron acceptor for the enzyme in this species is believed to be ubiquinone. Couples the redox reaction to proton translocation (for every two electrons transferred, four hydrogen ions are translocated across the cytoplasmic membrane), and thus conserves the redox energy in a proton gradient
- Gene Name:
- nuoG
- Locus Tag:
- PA2642
- Molecular weight:
- 99 kDa
Reactions
| NADH + quinone = NAD(+) + quinol. |
- General function:
- Involved in NADH dehydrogenase (ubiquinone) activity
- Specific function:
- NDH-1 shuttles electrons from NADH, via FMN and iron- sulfur (Fe-S) centers, to quinones in the respiratory chain. The immediate electron acceptor for the enzyme in this species is believed to be ubiquinone. Couples the redox reaction to proton translocation (for every two electrons transferred, four hydrogen ions are translocated across the cytoplasmic membrane), and thus conserves the redox energy in a proton gradient
- Gene Name:
- nuoL
- Locus Tag:
- PA2647
- Molecular weight:
- 66.2 kDa
Reactions
| NADH + quinone = NAD(+) + quinol. |
- General function:
- Involved in succinate dehydrogenase activity
- Specific function:
- Membrane-anchoring subunit of succinate dehydrogenase (SDH)
- Gene Name:
- sdhC
- Locus Tag:
- PA1581
- Molecular weight:
- 13.7 kDa
- General function:
- Involved in cytochrome bo3 ubiquinol oxidase activity
- Specific function:
- Cytochrome o terminal oxidase complex is the component of the aerobic respiratory chain of Pseudomonas aeruginosa that predominates when cells are grown at high aeration
- Gene Name:
- cyoA
- Locus Tag:
- PA1317
- Molecular weight:
- 36.6 kDa
Reactions
| Ubiquinol-8 + O(2) = Ubiquinone-8 + H(2)O. |
- General function:
- Involved in cytochrome o ubiquinol oxidase activity
- Specific function:
- Cytochrome o terminal oxidase complex is the component of the aerobic respiratory chain of Pseudomonas aeruginosa that predominates when cells are grown at high aeration
- Gene Name:
- cyoD
- Locus Tag:
- PA1320
- Molecular weight:
- 12.1 kDa
- General function:
- Involved in cytochrome-c oxidase activity
- Specific function:
- Cytochrome o terminal oxidase complex is the component of the aerobic respiratory chain of Pseudomonas aeruginosa that predominates when cells are grown at high aeration. This ubiquinol oxidase shows proton pump activity across the membrane in addition to the electron transfer
- Gene Name:
- cyoB
- Locus Tag:
- PA1318
- Molecular weight:
- 73.9 kDa
Reactions
| Ubiquinol-8 + O(2) = Ubiquinone-8 + H(2)O. |
- General function:
- Involved in heme-copper terminal oxidase activity
- Specific function:
- Cytochrome o terminal oxidase complex is the component of the aerobic respiratory chain of Pseudomonas aeruginosa that predominates when cells are grown at high aeration
- Gene Name:
- cyoC
- Locus Tag:
- PA1319
- Molecular weight:
- 22.8 kDa
Reactions
| Ubiquinol-8 + O(2) = Ubiquinone-8 + H(2)O. |