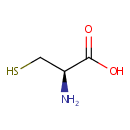
L-Cysteine (PAMDB000152)
| Record Information | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Version | 1.0 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Update Date | 1/22/2018 11:54:54 AM | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Metabolite ID | PAMDB000152 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Identification | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Name: | L-Cysteine | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Description: | Cysteine is a naturally occurring, sulfur-containing amino acid that is found in most proteins, although only in small quantities. Cysteine is unique amongst the twenty natural amino acids as it contains a thiol group. Thiol groups can undergo oxidation/reduction (redox) reactions; when cysteine is oxidized it can form cystine, which is two cysteine residues joined by a disulfide bond. This reaction is reversible: as reduction of this disulphide bond regenerates two cysteine molecules. The disulphide bonds of cystine are crucial to defining the structures of many proteins. Cysteine is often involved in electron-transfer reactions, and help the enzyme catalyze its reaction. Cysteine is also part of the antioxidant glutathione. Oxidation of cysteine can produce a disulfide bond with another thiol, or further oxidation can produce sulphfinic or sulfonic acids. The cysteine thiol group is also a nucleophile and can undergo addition and substitution reactions. Thiol groups become much more reactive when they are ionized, and cysteine residues in proteins have pKa values close to neutrality, so are often in their reactive thiolate form in the cell. The thiol group also has a high affinity for heavy metals and proteins containing cysteine will bind metals such as mercury, lead and cadmium tightly.Due to this ability to undergo redox reactions, cysteine has antioxidant properties. Cysteine is important in energy metabolism. (http://www.dcnutrition.com/AminoAcids/) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Structure | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Synonyms: |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Chemical Formula: | C3H7NO2S | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Average Molecular Weight: | 121.158 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Monoisotopic Molecular Weight: | 121.019749163 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| InChI Key: | XUJNEKJLAYXESH-REOHCLBHSA-N | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| InChI: | InChI=1S/C3H7NO2S/c4-2(1-7)3(5)6/h2,7H,1,4H2,(H,5,6)/t2-/m0/s1 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| CAS number: | 52-90-4 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| IUPAC Name: | (2R)-2-amino-3-sulfanylpropanoic acid | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Traditional IUPAC Name: | L-cysteine | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| SMILES: | N[C@@H](CS)C(O)=O | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Chemical Taxonomy | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Taxonomy Description | This compound belongs to the class of organic compounds known as l-alpha-amino acids. These are alpha amino acids which have the L-configuration of the alpha-carbon atom. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Kingdom | Organic compounds | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Super Class | Organic acids and derivatives | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Class | Carboxylic acids and derivatives | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Sub Class | Amino acids, peptides, and analogues | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Direct Parent | L-alpha-amino acids | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Alternative Parents | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Substituents |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Molecular Framework | Aliphatic acyclic compounds | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| External Descriptors |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Physical Properties | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| State: | Solid | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Charge: | 0 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Melting point: | 220 °C | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Experimental Properties: |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Predicted Properties |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Biological Properties | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Cellular Locations: | Cytoplasm | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Reactions: | Cysteinylglycine + Water > L-Cysteine + Glycine Adenosine triphosphate + L-Cysteine + Water > ADP + Hydrogen ion + Phosphate + L-Cysteine Adenosine triphosphate + L-Cysteine + Water > ADP + Hydrogen ion + Phosphate + L-Cysteine L-Cysteine + SufSE sulfur acceptor complex > L-Alanine + SufSE with bound sulfur O-Acetylserine + Hydrogen sulfide <> Acetic acid + L-Cysteine + Hydrogen ion L-Cysteine + Water > Hydrogen sulfide + Ammonium + Pyruvic acid Adenosine triphosphate + L-Cysteine + tRNA(Cys) + tRNA(Cys) <> Adenosine monophosphate + L-Cysteinyl-tRNA(Cys) + Pyrophosphate + L-Cysteinyl-tRNA(Cys) L-Cysteine + IscS sulfur acceptor protein > L-Alanine + IscS with bound sulfur Adenosine triphosphate + L-Cysteine + L-Glutamate <> ADP + gamma-Glutamylcysteine + Hydrogen ion + Phosphate D-4'-Phosphopantothenate + Cytidine triphosphate + L-Cysteine > 4-Phosphopantothenoylcysteine + Cytidine monophosphate + Hydrogen ion + Pyrophosphate L-Cysteine + O-Succinyl-L-homoserine <> L-Cystathionine + Hydrogen ion + Succinic acid L-Cysteine + Water <> Hydrogen sulfide + Pyruvic acid + Ammonia Adenosine triphosphate + L-Glutamate + L-Cysteine <> ADP + Phosphate + gamma-Glutamylcysteine O-Acetylserine + Hydrogen sulfide <> L-Cysteine + Acetic acid Cystathionine + Succinic acid <> O-Succinyl-L-homoserine + L-Cysteine O-Succinyl-L-homoserine + L-Cysteine <> L-Cystathionine + Succinic acid Adenosine triphosphate + L-Cysteine + tRNA(Cys) <> Adenosine monophosphate + Pyrophosphate + L-Cysteinyl-tRNA(Cys) Adenosine triphosphate + D-4'-Phosphopantothenate + L-Cysteine <> Adenosine monophosphate + Pyrophosphate + 4-Phosphopantothenoylcysteine Cytidine triphosphate + D-4'-Phosphopantothenate + L-Cysteine <> Cytidine monophosphate + Pyrophosphate + 4-Phosphopantothenoylcysteine O-Acetylserine + Thiosulfate + Thioredoxin + Hydrogen ion <> L-Cysteine + Sulfite + Thioredoxin disulfide + Acetic acid [Enzyme]-cysteine + L-Cysteine <> [Enzyme]-S-sulfanylcysteine + L-Alanine Oxoglutaric acid + L-Cysteine > L-Glutamate + 3-Mercaptopyruvic acid More...L-Cysteine + Water > Pyruvic acid + Ammonia + Hydrogen sulfide + Hydrogen ion L-Cysteine + a sulfur acceptor + Hydrogen ion L-Alanine + <i>S</i>-sulfanyl-[acceptor] -->-->L-Cysteine + L-Cysteine-Desulfurases > L-Alanine + Persulfurated-L-cysteine-desulfurases Adenosine triphosphate + L-Glutamate + L-Cysteine > ADP + Inorganic phosphate + gamma-Glutamylcysteine L-Cysteine + acceptor > L-Alanine + S-sulfanyl-acceptor L-Cysteine + 'activated' tRNA > L-Serine + tRNA containing a thionucleotide L-Cysteine + an [L-cysteine desulfurase] L-cysteine persulfide > an [L-cysteine desulfurase] L-cysteine persulfide + L-Alanine + L-Alanine L-Cysteine + tRNA(Cys) + Adenosine triphosphate + Hydrogen ion > Pyrophosphate + Adenosine monophosphate + L-cysteinyl-tRNA(Cys) O-Acetylserine > Hydrogen ion + Acetic acid + L-Cysteine L-Cysteine > Hydrogen ion + Hydrogen sulfide + 2-Aminoacrylic acid Cytidine triphosphate + D-4'-Phosphopantothenate + L-Cysteine + D-4'-Phosphopantothenate > Cytidine monophosphate + Pyrophosphate + 4-Phosphopantothenoylcysteine + Cytidine monophosphate D-4'-Phosphopantothenate + Cytidine triphosphate + L-Cysteine + D-4'-Phosphopantothenate > Cytidine monophosphate + Pyrophosphate + Hydrogen ion + 4-Phosphopantothenoylcysteine + Cytidine monophosphate L-Glutamic acid + Adenosine triphosphate + L-Cysteine + L-Glutamate > Adenosine diphosphate + Phosphate + Hydrogen ion + gamma-Glutamylcysteine + ADP | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Pathways: |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Spectra | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Spectra: | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| References | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| References: |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Synthesis Reference: | Kumagai, Hidehiko; Tanaka, Hideyuki; Sejima, Shunsuke; Yamada, Hideaki. Elimination and replacement reactions of b-chloro-L-alanine by cysteine desulfhydrase from Aerobacter aerogenes. Agricultural and Biological Chemistry (1977), 41(10), 2071-5. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Material Safety Data Sheet (MSDS) | Download (PDF) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Links | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| External Links: |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Enzymes
- General function:
- Involved in proteolysis
- Specific function:
- Aminopeptidase N is involved in the degradation of intracellular peptides generated by protein breakdown during normal growth as well as in response to nutrient starvation
- Gene Name:
- pepN
- Locus Tag:
- PA3083
- Molecular weight:
- 100 kDa
Reactions
| Release of an N-terminal amino acid, Xaa-|-Yaa- from a peptide, amide or arylamide. Xaa is preferably Ala, but may be most amino acids including Pro (slow action). When a terminal hydrophobic residue is followed by a prolyl residue, the two may be released as an intact Xaa-Pro dipeptide. |
- General function:
- Involved in metabolic process
- Specific function:
- Catalyzes the removal of elemental sulfur and selenium atoms from cysteine and selenocysteine to produce alanine. Functions as a sulfur delivery protein for NAD, biotin and Fe-S cluster synthesis. Transfers sulfur on 'Cys-456' of thiI in a transpersulfidation reaction. Transfers sulfur on 'Cys-19' of tusA in a transpersulfidation reaction. Functions also as a selenium delivery protein in the pathway for the biosynthesis of selenophosphate
- Gene Name:
- iscS
- Locus Tag:
- PA3814
- Molecular weight:
- 44.7 kDa
Reactions
| L-cysteine + acceptor = L-alanine + S-sulfanyl-acceptor. |
- General function:
- Involved in glutamate-cysteine ligase activity
- Specific function:
- ATP + L-glutamate + L-cysteine = ADP + phosphate + gamma-L-glutamyl-L-cysteine
- Gene Name:
- gshA
- Locus Tag:
- PA5203
- Molecular weight:
- 59.2 kDa
Reactions
| ATP + L-glutamate + L-cysteine = ADP + phosphate + gamma-L-glutamyl-L-cysteine. |
- General function:
- Involved in cysteine biosynthetic process from serine
- Specific function:
- O(3)-acetyl-L-serine + H(2)S = L-cysteine + acetate
- Gene Name:
- cysK
- Locus Tag:
- PA2709
- Molecular weight:
- 34.3 kDa
Reactions
| O(3)-acetyl-L-serine + H(2)S = L-cysteine + acetate. |
| 3-chloro-L-alanine + thioglycolate = S-carboxymethyl-L-cysteine + chloride. |
- General function:
- Involved in phosphopantothenate--cysteine ligase activity
- Specific function:
- Catalyzes two steps in the biosynthesis of coenzyme A. In the first step cysteine is conjugated to 4'-phosphopantothenate to form 4-phosphopantothenoylcysteine, in the latter compound is decarboxylated to form 4'-phosphopantotheine
- Gene Name:
- coaBC
- Locus Tag:
- PA5320
- Molecular weight:
- 43.1 kDa
Reactions
| N-((R)-4'-phosphopantothenoyl)-L-cysteine = pantotheine 4'-phosphate + CO(2). |
| CTP + (R)-4'-phosphopantothenate + L-cysteine = CMP + diphosphate + N-((R)-4'-phosphopantothenoyl)-L-cysteine. |
- General function:
- Involved in cysteine biosynthetic process from serine
- Specific function:
- Two cysteine synthase enzymes are found. Both catalyze the same reaction. Cysteine synthase B can also use thiosulfate in place of sulfide to give cysteine thiosulfonate as a product
- Gene Name:
- cysM
- Locus Tag:
- PA0932
- Molecular weight:
- 32.4 kDa
Reactions
| O(3)-acetyl-L-serine + H(2)S = L-cysteine + acetate. |
- General function:
- Involved in cysteine-tRNA ligase activity
- Specific function:
- ATP + L-cysteine + tRNA(Cys) = AMP + diphosphate + L-cysteinyl-tRNA(Cys)
- Gene Name:
- cysS
- Locus Tag:
- PA1795
- Molecular weight:
- 51.2 kDa
Reactions
| ATP + L-cysteine + tRNA(Cys) = AMP + diphosphate + L-cysteinyl-tRNA(Cys). |
- General function:
- Involved in aminopeptidase activity
- Specific function:
- Presumably involved in the processing and regular turnover of intracellular proteins. Catalyzes the removal of unsubstituted N-terminal amino acids from various peptides. Required for plasmid ColE1 site-specific recombination but not in its aminopeptidase activity. Could act as a structural component of the putative nucleoprotein complex in which the Xer recombination reaction takes place
- Gene Name:
- pepA
- Locus Tag:
- PA3831
- Molecular weight:
- 52.3 kDa
Reactions
| Release of an N-terminal amino acid, Xaa-|-Yaa-, in which Xaa is preferably Leu, but may be other amino acids including Pro although not Arg or Lys, and Yaa may be Pro. Amino acid amides and methyl esters are also readily hydrolyzed, but rates on arylamides are exceedingly low. |
| Release of an N-terminal amino acid, preferentially leucine, but not glutamic or aspartic acids. |
- General function:
- Involved in RNA binding
- Specific function:
- Catalyzes the ATP-dependent transfer of a sulfur to tRNA to produce 4-thiouridine in position 8 of tRNAs, which functions as a near-UV photosensor. Also catalyzes the transfer of sulfur to the sulfur carrier protein ThiS, forming ThiS-thiocarboxylate. This is a step in the synthesis of thiazole, in the thiamine biosynthesis pathway. The sulfur is donated as persulfide by iscS
- Gene Name:
- thiI
- Locus Tag:
- PA5118
- Molecular weight:
- 54.8 kDa
Reactions
| L-cysteine + 'activated' tRNA = L-serine + tRNA containing a thionucleotide. |
| [IscS]-SSH + [ThiS]-COAMP = [IscS]-SH + [ThiS]-COSH + AMP. |
Transporters
- General function:
- Involved in proteolysis
- Specific function:
- Aminopeptidase N is involved in the degradation of intracellular peptides generated by protein breakdown during normal growth as well as in response to nutrient starvation
- Gene Name:
- pepN
- Locus Tag:
- PA3083
- Molecular weight:
- 100 kDa
Reactions
| Release of an N-terminal amino acid, Xaa-|-Yaa- from a peptide, amide or arylamide. Xaa is preferably Ala, but may be most amino acids including Pro (slow action). When a terminal hydrophobic residue is followed by a prolyl residue, the two may be released as an intact Xaa-Pro dipeptide. |
- General function:
- Involved in nucleotide binding
- Specific function:
- Probably part of a binding-protein-dependent transport system yecCS for an amino acid. Probably responsible for energy coupling to the transport system
- Gene Name:
- yecC
- Locus Tag:
- PA5152
- Molecular weight:
- 28.4 kDa