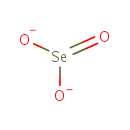
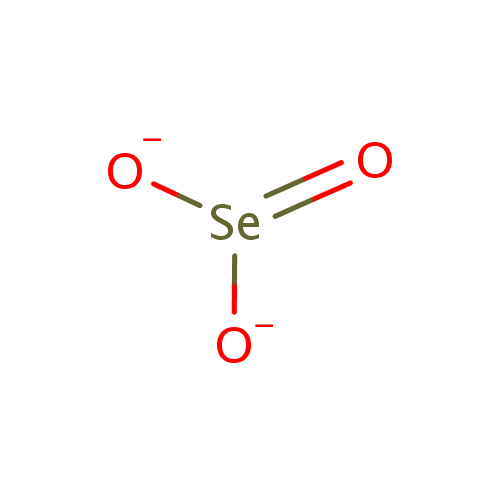
Selenite (PAMDB001752)
| Record Information | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Version | 1.0 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Update Date | 1/22/2018 11:54:54 AM | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Metabolite ID | PAMDB001752 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Identification | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Name: | Selenite | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Description: | The selenite anion is a selenium oxoanion with the chemical formula SeO32−. A selenite (compound) is a compound that contains this ion. In slightly acid conditions, the hydrogenselenite ion, HSeO3−, is formed; in more acidic conditions selenous acid, H2SeO3, exists. Most selenite salts can be formed by heating the relevant metal oxide with selenium dioxide, e.g.:Na2O + SeO2 → Na2SeO3. Selenite is an inorganic form of selenium which may also be useful in cancer chemotherapy.(Wikipedia) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Structure | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Synonyms: |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Chemical Formula: | O3Se | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Average Molecular Weight: | 126.96 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Monoisotopic Molecular Weight: | 127.901265694 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| InChI Key: | MCAHWIHFGHIESP-UHFFFAOYSA-L | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| InChI: | InChI=1S/H2O3Se/c1-4(2)3/h(H2,1,2,3)/p-2 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| CAS number: | 14124-67-5 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| IUPAC Name: | selenite | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Traditional IUPAC Name: | selenite | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| SMILES: | [O-][Se]([O-])=O | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Chemical Taxonomy | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Taxonomy Description | This compound belongs to the class of inorganic compounds known as non-metal selenites. These are inorganic non-metallic compoundscontaining a selenite as its largest oxoanion. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Kingdom | Inorganic compounds | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Super Class | Mixed metal/non-metal compounds | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Class | Other mixed metal/non-metal oxoanionic compounds | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Sub Class | Non-metal selenites | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Direct Parent | Non-metal selenites | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Alternative Parents | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Substituents |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Molecular Framework | Acyclic compounds | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| External Descriptors |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Physical Properties | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| State: | Solid | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Charge: | 0 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Melting point: | Not Available | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Experimental Properties: |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Predicted Properties |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Biological Properties | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Cellular Locations: | Cytoplasm | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Reactions: | Menaquinol 8 + Selenocystathionine > Water + Menaquinone 8 + Selenite Hydrogen selenide + 3 NADP + 3 Water <> Selenite +3 NADPH +5 Hydrogen ion Selenite + Glutathione + Hydrogen ion > Selenodiglutathione + Glutathione disulfide + Water Selenite + Water + an oxidized electron acceptor < selenate + a reduced electron acceptor Selenite + Water + Adenosine triphosphate > Selenite + ADP + Phosphate + Hydrogen ion Selenite + Water + Adenosine triphosphate > Selenite + ADP + Phosphate + Hydrogen ion Selenite + Water + Acceptor <> Selenate + Reduced acceptor Selenate + 2 Hydrogen ion + 2 Electron > Selenite + Water | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Pathways: |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Spectra | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Spectra: |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| References | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| References: | Not Available | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Synthesis Reference: | Not Available | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Material Safety Data Sheet (MSDS) | Not Available | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Links | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| External Links: |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Enzymes
- General function:
- Involved in oxidoreductase activity
- Specific function:
- The nitrate reductase enzyme complex allows Pseudomonas aeruginosa to use nitrate as an electron acceptor during anaerobic growth. The alpha chain is the actual site of nitrate reduction
- Gene Name:
- narG
- Locus Tag:
- PA3875
- Molecular weight:
- 141 kDa
Reactions
| Nitrite + acceptor = nitrate + reduced acceptor. |
- General function:
- Involved in oxidation-reduction process
- Specific function:
- Thioredoxin + NADP(+) = thioredoxin disulfide + NADPH
- Gene Name:
- trxB
- Locus Tag:
- PA2616
- Molecular weight:
- 33.8 kDa
Reactions
| Thioredoxin + NADP(+) = thioredoxin disulfide + NADPH. |
- General function:
- Involved in iron-sulfur cluster binding
- Specific function:
- The nitrate reductase enzyme complex allows Pseudomonas aeruginosa to use nitrate as an electron acceptor during anaerobic growth. The beta chain is an electron transfer unit containing four cysteine clusters involved in the formation of iron-sulfur centers. Electrons are transferred from the gamma chain to the molybdenum cofactor of the alpha subunit
- Gene Name:
- narH
- Locus Tag:
- PA3874
- Molecular weight:
- 58.1 kDa
Reactions
| Nitrite + acceptor = nitrate + reduced acceptor. |
- General function:
- Involved in nitrate reductase activity
- Specific function:
- The nitrate reductase enzyme complex allows Pseudomonas aeruginosa to use nitrate as an electron acceptor during anaerobic growth. The gamma chain is a membrane-embedded heme-iron unit resembling cytochrome b, which transfers electrons from quinones to the beta subunit
- Gene Name:
- narI
- Locus Tag:
- PA3872
- Molecular weight:
- 25 kDa
Reactions
| Nitrite + acceptor = nitrate + reduced acceptor. |
- General function:
- Involved in nucleotide binding
- Specific function:
- Part of the ABC transporter complex cysAWTP involved in sulfate/thiosulfate import. Responsible for energy coupling to the transport system
- Gene Name:
- cysA
- Locus Tag:
- PA0280
- Molecular weight:
- 36.8 kDa
Reactions
| ATP + H(2)O + sulfate(Out) = ADP + phosphate + sulfate(In). |
- General function:
- Involved in oxidoreductase activity
- Specific function:
- Catalytic subunit of the periplasmic nitrate reductase (NAP). Only expressed at high levels during aerobic growth. NapAB complex receives electrons from the membrane-anchored tetraheme protein napC, thus allowing electron flow between membrane and periplasm. Essential function for nitrate assimilation and may have a role in anaerobic metabolism
- Gene Name:
- napA
- Locus Tag:
- PA1174
- Molecular weight:
- 92.9 kDa
Reactions
| Nitrite + acceptor = nitrate + reduced acceptor. |
- General function:
- Involved in transporter activity
- Specific function:
- Part of the ABC transporter complex cysAWTP (TC 3.A.1.6.1) involved in sulfate/thiosulfate import. Probably responsible for the translocation of the substrate across the membrane
- Gene Name:
- cysW
- Locus Tag:
- PA0281
- Molecular weight:
- 31.3 kDa
- General function:
- Involved in transporter activity
- Specific function:
- Part of the ABC transporter complex cysAWTP (TC 3.A.1.6.1) involved in sulfate/thiosulfate import. This protein specifically binds thiosulfate and is involved in its transmembrane transport
- Gene Name:
- cysP
- Locus Tag:
- PA1493
- Molecular weight:
- 36.5 kDa
- General function:
- Energy production and conversion
- Specific function:
- Small subunit of the periplasmic nitrate reductase (NAP). Only expressed at high levels during aerobic growth. NapAB complex receives electrons from the membrane-anchored tetraheme napC protein, thus allowing electron flow between membrane and periplasm. Essential function for nitrate assimilation and may have a role in anaerobic metabolism
- Gene Name:
- napB
- Locus Tag:
- PA1173
- Molecular weight:
- 17.9 kDa
- General function:
- Involved in unfolded protein binding
- Specific function:
- Chaperone required for proper molybdenum cofactor insertion and final assembly of the membrane-bound respiratory nitrate reductase 1. Required for the insertion of the molybdenum into the apo-NarG subunit, maybe by keeping NarG in an appropriate competent-open conformation for the molybdenum cofactor insertion to occur. NarJ maintains the apoNarGH complex in a soluble state. Upon insertion of the molybdenum cofactor, NarJ seems to dissociate from the activated soluble NarGH complex, before its association with the NarI subunit on the membrane
- Gene Name:
- narJ
- Locus Tag:
- PA3873
- Molecular weight:
- 27.3 kDa
Transporters
- General function:
- Involved in nucleotide binding
- Specific function:
- Part of the ABC transporter complex cysAWTP involved in sulfate/thiosulfate import. Responsible for energy coupling to the transport system
- Gene Name:
- cysA
- Locus Tag:
- PA0280
- Molecular weight:
- 36.8 kDa
Reactions
| ATP + H(2)O + sulfate(Out) = ADP + phosphate + sulfate(In). |
- General function:
- Involved in transporter activity
- Specific function:
- Part of the ABC transporter complex cysAWTP (TC 3.A.1.6.1) involved in sulfate/thiosulfate import. Probably responsible for the translocation of the substrate across the membrane
- Gene Name:
- cysW
- Locus Tag:
- PA0281
- Molecular weight:
- 31.3 kDa
- General function:
- Involved in transporter activity
- Specific function:
- Part of the ABC transporter complex cysAWTP (TC 3.A.1.6.1) involved in sulfate/thiosulfate import. This protein specifically binds thiosulfate and is involved in its transmembrane transport
- Gene Name:
- cysP
- Locus Tag:
- PA1493
- Molecular weight:
- 36.5 kDa