|
Record Information |
|---|
| Version |
1.0 |
|---|
| Update Date |
1/22/2018 11:54:54 AM |
|---|
|
Metabolite ID | PAMDB001129 |
|---|
|
Identification |
|---|
| Name: |
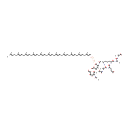
N-Acetylmuramoyl-L-alanyl-D-glutamyl-L-lysyl-D-alanyl-D-alanine-diphosphoundecaprenyl-N-acetylglucosamine |
|---|
| Description: | N-acetylmuramoyl-L-alanyl-D-glutamyl-L-lysyl-D-alanyl-D-alanine-diphosphoundecaprenyl-N-acetylglucosamine is an intermediate in peptidoglycan synthesis. It is a substrate for the enzyme undecaprenyldiphospho-muramoylpentapeptide beta-N-acetylglucosaminyltransferase (murG). Peptidoglycan can be described as a fisherman's net that encloses bacteria. The mesh of the net is made of two segments of parallel, somewhat inextensible glycan threads, held together by two small elastic peptide crosslinks allowing the net to expand or shrink. The glycan moiety of the peptidoglycan is very uniform among all bacteria, and is made up of alternating β-1,4-linked N-acetylglucosamine and N-acetyl muramate residues, with an average chain lengthof 10 to 65 disaccharide units (depending on the organism). The peptidoglycan synthesis pathway starts in the cytoplasm, where in six steps the peptidoglycan precursor a UDP-N-acetylmuramoyl-pentapeptide is synthesized. This precursor is then attached to the memberane acceptor all-trans-undecaprenyl phosphate, generating a N-acetylmuramoyl-pentapeptide-diphosphoundecaprenol, also known as lipid I. Another transferase then adds UDP-N-acetyl-α-D-glucosamine, yielding the complete monomeric unit a lipid II, also known as lipid II. This final lipid intermediate is transferred by an as yet unknown mechanism through the membrane. The peptidoglycan monomers are then polymerized on the outside surface by glycosyltransferases, which form the linear glycan chains, and transpeptidases, which catalyze the formation of peptide crosslinks. Peptide crosslinks form between different parts of the peptides depending on the organism. For example, in Mycobacteria and in Pseudomonas aeruginosa most links form between the carboxyl group of the penultimate D-alanine (residue 4) of one peptide to the amino group at the D-center of meso-diaminopimelate (residue 3) of an adjacent peptide of a second glycan chain (as in Pseudomonas aeruginosa). The crosslinking reaction is catalyzed by transpeptidases and involves the cleavage of the D-alanyl-D-alanine bond of the donor peptide, providing the energy to drive the reaction. As a result, the peptides in the peptidoglycan polymers are one or two amino acids shorter than the peptides in the monomers. |
|---|
|
Structure |
|
|---|
| Synonyms: | - N-acetyl-muramoyl-(pentapeptide)-N-acetylglucosamine-diphosphoundecaprenol
- N-acetylmuramoyl-L-alanyl-D-glutamyl-meso-2,6-diaminoheptane-D-alanyl-D-alanine-diphosphoundecaprenyl-N-acetylglucosamine
- Diphosphoundecaprenyl-[GlcNAc-MurNAc-pentapeptide]n
- Diphosphoundecaprenyl-[GlcNAc-MurNAc-pentapeptide]N
- GlcNAc-(1->4)-MurNAc-pentapeptide-diphosphoundecaprenol
- Lipid II
- Lipid intermediate II
- Lipid intermediic acid II
- N-Acetyl-muramoyl-(pentapeptide)-N-acetylglucosamine-diphosphoundecaprenol
- N-Acetylmuramoyl-L-alanyl-D-glutamyl-meso-2,6-diaminoheptane-D-alanyl-D-alanine-diphosphoundecaprenyl-N-acetylglucosamine
- Undecaprenyl-diphospho-N-acetylmuramoyl-(N-acetylglucosamine)-L-ala-D-glu-meso-2,6-diaminopimeloyl-D-ala-D-ala
- Undecaprenyl-pyrophosphoryl-MurNAc-(pentapeptide)-N-acetylglucosamine
- Undecaprenyl-pyrophosphoryl-MurNAc-(pentapeptide)-N-acetylglucosamine
|
|---|
|
Chemical Formula: |
C94H156N8O26P2 |
|---|
| Average Molecular Weight: |
1876.23 |
|---|
| Monoisotopic Molecular
Weight: |
1875.060600228 |
|---|
| InChI Key: |
MYJUVRULDQURQG-OCYHILAXSA-N |
|---|
| InChI: | InChI=1S/C94H156N8O26P2/c1-59(2)31-21-32-60(3)33-22-34-61(4)35-23-36-62(5)37-24-38-63(6)39-25-40-64(7)41-26-42-65(8)43-27-44-66(9)45-28-46-67(10)47-29-48-68(11)49-30-50-69(12)54-56-122-129(118,119)128-130(120,121)127-94-82(100-75(18)106)86(85(79(58-104)125-94)126-93-81(99-74(17)105)84(110)83(109)78(57-103)124-93)123-73(16)89(113)96-71(14)88(112)101-77(52-53-80(107)108)91(115)102-76(51-19-20-55-95)90(114)97-70(13)87(111)98-72(15)92(116)117/h31,33,35,37,39,41,43,45,47,49,54,70-73,76-79,81-86,93-94,103-104,109-110H,19-30,32,34,36,38,40,42,44,46,48,50-53,55-58,95H2,1-18H3,(H,96,113)(H,97,114)(H,98,111)(H,99,105)(H,100,106)(H,101,112)(H,102,115)(H,107,108)(H,116,117)(H,118,119)(H,120,121)/t70-,71+,72-,73-,76+,77-,78-,79-,81-,82-,83-,84-,85-,86-,93-,94-/m1/s1 |
|---|
| CAS
number: |
Not Available |
|---|
| IUPAC Name: | (4R)-4-{[(1S)-5-amino-1-{[(1R)-1-{[(1R)-1-carboxyethyl]-C-hydroxycarbonimidoyl}ethyl]-C-hydroxycarbonimidoyl}pentyl]-C-hydroxycarbonimidoyl}-4-{[(2S)-2-{[(2R)-2-{[(2R,3S,4R,5R,6R)-3-{[(2R,3R,4R,5S,6R)-4,5-dihydroxy-3-[(1-hydroxyethylidene)amino]-6-(hydroxymethyl)oxan-2-yl]oxy}-6-{[hydroxy({hydroxy[(3,7,11,15,19,23,27,31,35,39,43-undecamethyltetratetraconta-2,6,10,14,18,22,26,30,34,38,42-undecaen-1-yl)oxy]phosphoryl}oxy)phosphoryl]oxy}-5-[(1-hydroxyethylidene)amino]-2-(hydroxymethyl)oxan-4-yl]oxy}-1-hydroxypropylidene]amino}-1-hydroxypropylidene]amino}butanoic acid |
|---|
|
Traditional IUPAC Name: |
(4R)-4-{[(1S)-5-amino-1-{[(1R)-1-{[(1R)-1-carboxyethyl]-C-hydroxycarbonimidoyl}ethyl]-C-hydroxycarbonimidoyl}pentyl]-C-hydroxycarbonimidoyl}-4-{[(2S)-2-{[(2R)-2-{[(2R,3S,4R,5R,6R)-3-{[(2R,3R,4R,5S,6R)-4,5-dihydroxy-3-[(1-hydroxyethylidene)amino]-6-(hydroxymethyl)oxan-2-yl]oxy}-6-({hydroxy[hydroxy(3,7,11,15,19,23,27,31,35,39,43-undecamethyltetratetraconta-2,6,10,14,18,22,26,30,34,38,42-undecaen-1-yl)oxyphosphoryl]oxyphosphoryl}oxy)-5-[(1-hydroxyethylidene)amino]-2-(hydroxymethyl)oxan-4-yl]oxy}-1-hydroxypropylidene]amino}-1-hydroxypropylidene]amino}butanoic acid |
|---|
| SMILES: | [H][C@](C)(O[C@@]1([H])[C@]([H])(O[C@@]2([H])O[C@]([H])(CO)[C@@]([H])(O)[C@]([H])(O)[C@@]2([H])N=C(C)O)[C@@]([H])(CO)O[C@]([H])(OP(O)(=O)OP(O)(=O)OCC=C(C)CCC=C(C)CCC=C(C)CCC=C(C)CCC=C(C)CCC=C(C)CCC=C(C)CCC=C(C)CCC=C(C)CCC=C(C)CCC=C(C)C)[C@]1([H])N=C(C)O)C(O)=N[C@@]([H])(C)C(O)=N[C@]([H])(CCC(O)=O)C(O)=N[C@@]([H])(CCCCN)C(O)=N[C@]([H])(C)C(O)=N[C@]([H])(C)C(O)=O |
|---|
|
Chemical Taxonomy |
|---|
|
Taxonomy Description | This compound belongs to the class of organic compounds known as polyprenyl phospho carbohydrates. These are polyprenyl phosphates with a carbohydrate moiety attached to it. |
|---|
|
Kingdom |
Organic compounds |
|---|
| Super Class | Lipids and lipid-like molecules |
|---|
|
Class |
Prenol lipids |
|---|
| Sub Class | Polyprenols |
|---|
|
Direct Parent |
Polyprenyl phospho carbohydrates |
|---|
| Alternative Parents |
|
|---|
| Substituents |
- Polyterpenoid
- Bactoprenol diphosphate
- Polyprenyl phospho carbohydrate
- Alpha peptide
- N-acyl-alpha-hexosamine
- Disaccharide phosphate
- N-acyl-aliphatic-alpha amino acid
- N-acyl-alpha amino acid or derivatives
- N-acyl-alpha-amino acid
- Glucosamine
- Amino sugar
- O-glycosyl compound
- Glycosyl compound
- Disaccharide
- Organic pyrophosphate
- Isoprenoid phosphate
- Alpha-amino acid or derivatives
- Monoalkyl phosphate
- Amino saccharide
- Alkyl phosphate
- Phosphoric acid ester
- Oxane
- Organic phosphoric acid derivative
- Organic phosphate
- Dicarboxylic acid or derivatives
- Saccharide
- Secondary alcohol
- 1,2-diol
- Oxacycle
- Organoheterocyclic compound
- Organic 1,3-dipolar compound
- Propargyl-type 1,3-dipolar organic compound
- Ether
- Dialkyl ether
- Carboxylic acid
- Carboxylic acid derivative
- Carboximidic acid derivative
- Carboximidic acid
- Acetal
- Hydrocarbon derivative
- Primary amine
- Primary alcohol
- Organooxygen compound
- Organonitrogen compound
- Primary aliphatic amine
- Carbonyl group
- Amine
- Alcohol
- Aliphatic heteromonocyclic compound
|
|---|
| Molecular Framework |
Aliphatic heteromonocyclic compounds |
|---|
| External Descriptors |
Not Available |
|---|
|
Physical Properties |
|---|
| State: |
Not Available |
|---|
| Charge: | -4 |
|---|
|
Melting point: |
Not Available |
|---|
| Experimental Properties: |
|
|---|
| Predicted Properties |
|
|---|
|
Biological Properties |
|---|
| Cellular Locations: |
Membrane |
|---|
| Reactions: | |
|---|
|
Pathways: |
Not Available |
|---|
|
Spectra |
|---|
| Spectra: |
|
|---|
|
References |
|---|
| References: |
- Barneoud-Arnoulet, A., Barreteau, H., Touze, T., Mengin-Lecreulx, D., Lloubes, R., Duche, D. (2010). "Toxicity of the colicin M catalytic domain exported to the periplasm is FkpA independent." J Bacteriol 192:5212-5219. Pubmed: 20675494
- Gerard, F., Brooks, M. A., Barreteau, H., Touze, T., Graille, M., Bouhss, A., Blanot, D., van Tilbeurgh, H., Mengin-Lecreulx, D. (2011). "X-ray structure and site-directed mutagenesis analysis of the Escherichia coli colicin M immunity protein." J Bacteriol 193:205-214. Pubmed: 21037007
- Keseler, I. M., Collado-Vides, J., Santos-Zavaleta, A., Peralta-Gil, M., Gama-Castro, S., Muniz-Rascado, L., Bonavides-Martinez, C., Paley, S., Krummenacker, M., Altman, T., Kaipa, P., Spaulding, A., Pacheco, J., Latendresse, M., Fulcher, C., Sarker, M., Shearer, A. G., Mackie, A., Paulsen, I., Gunsalus, R. P., Karp, P. D. (2011). "EcoCyc: a comprehensive database of Escherichia coli biology." Nucleic Acids Res 39:D583-D590. Pubmed: 21097882
- van der Werf, M. J., Overkamp, K. M., Muilwijk, B., Coulier, L., Hankemeier, T. (2007). "Microbial metabolomics: toward a platform with full metabolome coverage." Anal Biochem 370:17-25. Pubmed: 17765195
- Winder, C. L., Dunn, W. B., Schuler, S., Broadhurst, D., Jarvis, R., Stephens, G. M., Goodacre, R. (2008). "Global metabolic profiling of Escherichia coli cultures: an evaluation of methods for quenching and extraction of intracellular metabolites." Anal Chem 80:2939-2948. Pubmed: 18331064
|
|---|
| Synthesis Reference: |
Not Available |
|---|
| Material Safety Data Sheet (MSDS) |
Not Available |
|---|
|
Links |
|---|
| External Links: |
| Resource | Link |
|---|
| CHEBI ID | Not Available | | HMDB ID | Not Available | | Pubchem Compound ID | 25203452 | | Kegg ID | Not Available | | ChemSpider ID | Not Available | | Wikipedia ID | Not Available | | BioCyc ID | C6 | | EcoCyc ID | C6 |
|
|---|