Search Results for compounds
Searching compounds for
returned 4373 results.
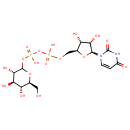
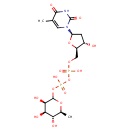
UDP-Glucose (PAMDB000651)
IUPAC:
[({[(2S,3R,4S,5S)-5-(2,4-dioxo-1,2,3,4-tetrahydropyrimidin-1-yl)-3,4-dihydroxyoxolan-2-yl]methoxy}(hydroxy)phosphoryl)oxy]({[(3S,4R,5R,6S)-3,4,5-trihydroxy-6-(hydroxymethyl)oxan-2-yl]oxy})phosphinic acid
CAS: 133-89-1
Description: UDP-glucose is key intermediate in carbohydrate metabolism. Serves as a precursor of glycogen, can be metabolized into UDPgalactose and UDPglucuronic acid which can then be incorporated into polysaccharides as galactose and glucuronic acid. Also serves as a precursor of lipopolysaccharides.
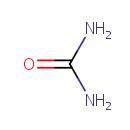
Urea (PAMDB000652)
IUPAC:
urea
CAS: 57-13-6
Description: Urea is the principal end product of protein catabolism. Urea is formed in a cyclic pathway known simply as the urea cycle. In this cycle, amino groups donated by ammonia and L-aspartate are converted to urea. Urea is essentially a waste product; it has no physiological function.
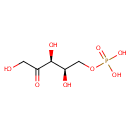
Xylulose 5-phosphate (PAMDB000653)
IUPAC:
{[(2R,3S)-2,3,5-trihydroxy-4-oxopentyl]oxy}phosphonic acid
CAS: 4212-65-1
Description: Xylulose 5-phosphate (Xu-5-P) is a metabolite of the hexose monophosphate pathway that activates protein phosphatase 2A to mediate the acute effects of carbohydrate feeding on the glycolytic pathway, as well as the coordinate long-term control of the enzymes required for fatty acid and triglyceride synthesis. Xu-5-P is the signal for the coordinated control of lipogenesis. Feeding carbohydrates to cells causes levels of glucose, Glucose-6-phosphate (Glc-6-P), and Fructose-6-phosphate (Fru-6-P) to rise. Elevation of Fru-6-P leads to elevation of Xu-5-P in reactions catalyzed by the near-equilibrium isomerases of the nonoxidative portion of the hexose monophosphate pathway (ribulose 5-phosphate (Ru5P) epimerase [EC 5.1.3.1], ribose 5-phosphate (Rib5P) isomerase [EC 5.3.1.6], transaldolase [EC 2.2.1.2], and transketolase [EC 2.2.1.1]). The elevation of Xu-5-P is the coordinating signal that both acutely activates phosphofructokinase [PFK; EC 2.7.1.11] in glycolysis and will increase transcription of the genes for the enzymes of lipogenesis, the hexose monophosphate shunt, and glycolysis, all of which are required for the de novo synthesis of fat. (PMID 12721358)
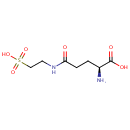
5-L-Glutamyl-taurine (PAMDB000654)
IUPAC:
(2S)-2-amino-4-[(2-sulfoethyl)carbamoyl]butanoic acid
CAS: Not Available
Description: 5-L-Glutamyl-taurine is an intermediate in taurine and hypotaurine metabolism. 5-L-Glutamyl-taurine is produced from Taurine via the enzyme gamma-glutamyltranspeptidase (EC 2.3.2.2).
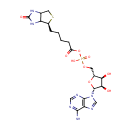
Biotinyl-5'-AMP (PAMDB000655)
IUPAC:
{[(2R,3S,4R,5R)-5-(6-amino-9H-purin-9-yl)-3,4-dihydroxyoxolan-2-yl]methoxy}({5-[(4S)-2-oxo-hexahydro-1H-thieno[3,4-d]imidazolidin-4-yl]pentanoyl}oxy)phosphinic acid
CAS: 4130-20-5
Description: 5'-biotinyl-AMP (B-AMP) is the active form of biotin. Biotin is essential to maintain metabolic homeostasis and as regulator of gene expression. The vitamin biotin plays an essential role in gluconeogenesis, fatty acid synthesis, and carbohydrate metabolism because of its role as cofactor of five carboxylases; pyruvate carboxylase (PC), propionyl-CoA carboxylase (PCC), methylcrotonyl-CoA carboxylase, and two forms of acetyl-CoA carboxylase (ACC-1 and ACC-2). Carboxylase biotinylation is catalyzed by the enzyme holocarboxylase synthetase (HCS) through a reaction that involves the transformation of biotin into B-AMP and its subsequent attachment to a specific lysine residue in the carboxylases. B-AMP is also required to activate a signal transduction cascade that includes a soluble guanylate cyclase (sGC) and cGMP-dependent protein kinase (PKG). The regulatory role of biotin in the biotin cycle seems to be limited to the expression of proteins involved in the transport and utilization of exogenous vitamin while having no effect on biotinidase mRNA levels, enzyme responsible for biotin recycling during carboxylase turnover.
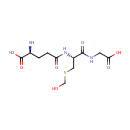
S-(Hydroxymethyl)glutathione (PAMDB000659)
IUPAC:
(2S)-2-amino-4-{[(1R)-1-[(carboxymethyl)carbamoyl]-2-[(hydroxymethyl)sulfanyl]ethyl]carbamoyl}butanoic acid
CAS: 32260-87-0
Description: S-Hydroxymethylglutathione is a critical component of the binding site for activating fatty acids in glutathione-dependent formaldehyde dehydrogenase activity. (OMIM 103710)
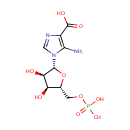
5-Amino-1-(5-phospho-D-ribosyl)imidazole-4-carboxylate (PAMDB000663)
IUPAC:
5-amino-1-[(2R,3R,4S,5R)-3,4-dihydroxy-5-[(phosphonooxy)methyl]oxolan-2-yl]-1H-imidazole-4-carboxylic acid
CAS: Not Available
Description: 5-amino-1-(5-phospho-D-ribosyl) imidazole-4-carboxylate is an intermediate in purine metabolism. 5-amino-1-(5-phospho-D-ribosyl) imidazole-4-carboxylate is converted from aminoimidazole ribotide via phosphoribosylaminoimidazole carboxylase [EC: 4.1.1.21].
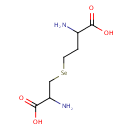
Selenocystathionine (PAMDB000666)
IUPAC:
2-amino-4-[(2-amino-2-carboxyethyl)selanyl]butanoic acid
CAS: 2196-58-9
Description: Selenocystathionine is formed from selenohomocysteine by the enzyme cystathionine beta-synthase (EC 4.2.1.22), as a by-product of cystathionine synthesis. It is an intermediate in selenoamine acid metabolism.
Deoxythymidine diphosphate-L-rhamnose (PAMDB000667)
IUPAC:
{[hydroxy({[(2R,3S,5R)-3-hydroxy-5-(5-methyl-2,4-dioxo-1,2,3,4-tetrahydropyrimidin-1-yl)oxolan-2-yl]methoxy})phosphoryl]oxy}({[(3R,4R,5R,6S)-3,4,5-trihydroxy-6-methyloxan-2-yl]oxy})phosphinic acid
CAS: 2147-59-3
Description: Deoxythymidine diphosphate (dTDP)-L-rhamnose is the precursor of L-rhamnose, a saccharide required for the virulence of some pathogenic bacteria. In gram negative bacteria such as Salmonella enterica, Vibrio cholerae or Pseudomonas aeruginosa 075:K5, L-rhamnose is an important residue in the O-antigen of lipopolysaccharides, which are essential for resistance to serum killing and for colonization. dTDP-L-rhamnose is synthesized from glucose-1-phosphate and deoxythymidine triphosphate (dTTP) via a pathway involving four distinct enzymes. Whereas common sugars such as glucose, fructose and mannose are all D-configured, bacteria commonly utilize the L-configured carbohydrates in pharmacologically active compounds and in their cell-wall structures. The enzymes involved in dTDP-L-rhamnose synthesis are potential targets for the design of new therapeutic agents against bacteria. (PMID 10802738, 12773151)
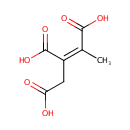
Cis-2-Methylaconitate (PAMDB000668)
IUPAC:
(1Z)-1-methylprop-1-ene-1,2,3-tricarboxylic acid
CAS: 6061-93-4
Description: cis-2-Methylaconitate is produced due to the dehydration of 2-methylcitrate in 2-methylcitric acid cycle. The cycle is catalyzed by a cofactor-less (PrpD) enzyme or by an aconitase-like (AcnD) enzyme.