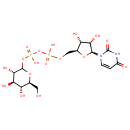
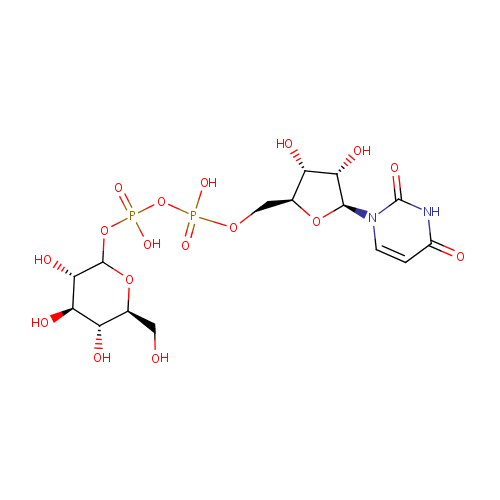
UDP-Glucose (PAMDB000651)
| Record Information | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Version | 1.0 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Update Date | 1/22/2018 11:54:54 AM | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Metabolite ID | PAMDB000651 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Identification | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Name: | UDP-Glucose | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Description: | UDP-glucose is key intermediate in carbohydrate metabolism. Serves as a precursor of glycogen, can be metabolized into UDPgalactose and UDPglucuronic acid which can then be incorporated into polysaccharides as galactose and glucuronic acid. Also serves as a precursor of lipopolysaccharides. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Structure | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Synonyms: |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Chemical Formula: | C15H24N2O17P2 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Average Molecular Weight: | 566.3018 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Monoisotopic Molecular Weight: | 566.055020376 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| InChI Key: | HSCJRCZFDFQWRP-LPTOLDDLSA-N | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| InChI: | InChI=1S/C15H24N2O17P2/c18-3-5-8(20)10(22)12(24)14(32-5)33-36(28,29)34-35(26,27)30-4-6-9(21)11(23)13(31-6)17-2-1-7(19)16-15(17)25/h1-2,5-6,8-14,18,20-24H,3-4H2,(H,26,27)(H,28,29)(H,16,19,25)/t5-,6-,8-,9-,10+,11-,12-,13-,14?/m0/s1 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| CAS number: | 133-89-1 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| IUPAC Name: | [({[(2S,3R,4S,5S)-5-(2,4-dioxo-1,2,3,4-tetrahydropyrimidin-1-yl)-3,4-dihydroxyoxolan-2-yl]methoxy}(hydroxy)phosphoryl)oxy]({[(3S,4R,5R,6S)-3,4,5-trihydroxy-6-(hydroxymethyl)oxan-2-yl]oxy})phosphinic acid | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Traditional IUPAC Name: | {[(2S,3R,4S,5S)-5-(2,4-dioxo-3H-pyrimidin-1-yl)-3,4-dihydroxyoxolan-2-yl]methoxy(hydroxy)phosphoryl}oxy[(3S,4R,5R,6S)-3,4,5-trihydroxy-6-(hydroxymethyl)oxan-2-yl]oxyphosphinic acid | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| SMILES: | OC[C@@H]1OC(OP(O)(=O)OP(O)(=O)OC[C@@H]2O[C@@H]([C@@H](O)[C@H]2O)N2C=CC(=O)NC2=O)[C@@H](O)[C@H](O)[C@H]1O | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Chemical Taxonomy | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Taxonomy Description | This compound belongs to the class of organic compounds known as pyrimidine nucleotide sugars. These are pyrimidine nucleotides bound to a saccharide derivative through the terminal phosphate group. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Kingdom | Organic compounds | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Super Class | Nucleosides, nucleotides, and analogues | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Class | Pyrimidine nucleotides | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Sub Class | Pyrimidine nucleotide sugars | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Direct Parent | Pyrimidine nucleotide sugars | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Alternative Parents |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Substituents |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Molecular Framework | Aromatic heteromonocyclic compounds | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| External Descriptors | Not Available | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Physical Properties | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| State: | Solid | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Charge: | -2 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Melting point: | Not Available | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Experimental Properties: |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Predicted Properties |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Biological Properties | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Cellular Locations: | Cytoplasm | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Reactions: | Water + UDP-Glucose > Glucose 1-phosphate +2 Hydrogen ion + Uridine 5'-monophosphate Galactose 1-phosphate + UDP-Glucose <> Glucose 1-phosphate + Uridine diphosphategalactose UDP-Glucose <> Uridine diphosphategalactose Glucose 1-phosphate + Hydrogen ion + Uridine triphosphate <> Pyrophosphate + UDP-Glucose Glucose 6-phosphate + UDP-Glucose > Hydrogen ion + Trehalose 6-phosphate + Uridine 5'-diphosphate Water + 2 NAD + UDP-Glucose <>3 Hydrogen ion +2 NADH + Uridine diphosphate glucuronic acid + UDP-Glucuronic acid O-Acetyl-rhamanosyl-N-acetylglucosamyl-undecaprenyl diphosphate + UDP-Glucose > Glucosyl-O-acetyl-rhamanosyl-N-acetylglucosamyl-undecaprenyl diphosphate + Hydrogen ion + Uridine 5'-diphosphate glucosyl-galactosyl-glucosyl-inner core oligosaccharide lipid A + UDP-Glucose > glucosyl-glucosyl-galactosyl-glucosyl-inner core oligosaccharide lipid A + Hydrogen ion + Uridine 5'-diphosphate galactosyl-glucosyl-inner core oligosaccharide lipid A + UDP-Glucose > glucosyl-galactosyl-glucosyl-inner core oligosaccharide lipid A + Hydrogen ion + Uridine 5'-diphosphate glucosyl-inner core oligosaccharide lipid A + UDP-Glucose > galactosyl-glucosyl-inner core oligosaccharide lipid A + Hydrogen ion + Uridine 5'-diphosphate inner core oligosaccharide lipid A (E coli) + UDP-Glucose > glucosyl-inner core oligosaccharide lipid A + Hydrogen ion + Uridine 5'-diphosphate UDP-Glucose + Water + 2 NAD <> Uridine diphosphate glucuronic acid +2 NADH +2 Hydrogen ion UDP-Glucose + Water <> Uridine 5'-monophosphate + Glucose 1-phosphate Uridine triphosphate + Glucose 1-phosphate <> Pyrophosphate + UDP-Glucose UDP-Glucose + LPS (1-O-antigen) <> Uridine 5'-diphosphate + D-Glucosyllipopolysaccharide UDP-Glucose + Glucose 6-phosphate <> Uridine 5'-diphosphate + Trehalose 6-phosphate UDP-Glucose + Cellulose <> Uridine 5'-diphosphate + Cellulose GDP-L-Fucose + UDP-Glucose + Uridine diphosphate glucuronic acid + Uridine diphosphategalactose colanic acid UDP-Glucose + a lipopolysaccharide D-glucosyl-lipopolysaccharide + Uridine 5'-diphosphate UDP-Glucose + Heptosyl2-KDO2-lipid A > Hydrogen ion + Glucosyl-heptosyl2-KDO2-lipid A + Uridine 5'-diphosphate UDP-Glucose + Galactosyl-glucosyl-heptosyl3-KDO2-lipid A-bisphosphate > Hydrogen ion + Galactosyl-glucosyl2-heptosyl3-KDO2-lipid A-bisphosphate + Uridine 5'-diphosphate UDP-Glucose + Galactosyl-glucosyl2-heptosyl3-KDO2-lipid A-bisphosphate > Hydrogen ion + Galactosyl-glucosyl3-heptosyl3-KDO2-lipid A-bisphosphate + Uridine 5'-diphosphate More...UDP-Glucose + α-D-glucose 6-phosphate > Hydrogen ion + Uridine 5'-diphosphate + Trehalose 6-phosphate UDP-Glucose + (1,4-beta-D-glucosyl)(n) > Uridine 5'-diphosphate + (1,4-beta-D-glucosyl)(n+1) UDP-Glucose + LPS (1-O-antigen) > Uridine 5'-diphosphate + D-glucosyl-lipopolysaccharide UDP-Glucose + 2 NAD + Water > UDP-Glucuronic acid +2 NADH UDP-Glucose <> Uridine 5'-diphosphate UDP-Glucose + Di-trans,poly-cis-undecaprenyl phosphate <> Uridine 5'-monophosphate + alpha-D-Glucopyranosyl-diphospho-ditrans,octacis-undecaprenol Glucose 1-phosphate + Uridine triphosphate + Hydrogen ion + Uridine triphosphate > Pyrophosphate + UDP-Glucose β-D-glucose 1-phosphate + Uridine triphosphate + Hydrogen ion + Uridine triphosphate > UDP-Glucose + Pyrophosphate Alpha-D-glucose 1-phosphate + Uridine triphosphate + Hydrogen ion + Uridine triphosphate > Pyrophosphate + UDP-Glucose UDP-Glucose > Uridine diphosphategalactose + Uridine diphosphategalactose Galactose 1-phosphate + UDP-Glucose + Galactose 1-phosphate > Uridine diphosphategalactose + Glucose 1-phosphate + Uridine diphosphategalactose Alpha-D-glucose 1-phosphate + UDP-galactose > UDP-Glucose + Galactose 1-phosphate + Galactose 1-phosphate (heptosyl)2-Kdo2-lipid A + UDP-Glucose > Uridine 5'-diphosphate + Hydrogen ion + glucosyl-(heptosyl)2-Kdo2-lipid A galactosyl-glucosyl-(heptosyl)3-Kdo2-lipid A-bisphosphate + UDP-Glucose > Uridine 5'-diphosphate + Hydrogen ion + galactosyl-(glucosyl)2-(heptosyl)3-Kdo2-lipid A-bisphosphate galactosyl-(glucosyl)2-(heptosyl)3-Kdo2-lipid A-bisphosphate + UDP-Glucose > Uridine 5'-diphosphate + Hydrogen ion + galactosyl-(glucosyl)3-(heptosyl)3-Kdo2-lipid A-bisphosphate UDP-Glucose + 2 NAD + Water > UDP-Glucuronic acid +2 NADH +3 Hydrogen ion UDP-Glucose + Alpha-D-glucose 6-phosphate > Uridine 5'-diphosphate + Trehalose 6-phosphate + Hydrogen ion + Uridine 5'-diphosphate UDP-Glucose + D-Fructose + D-Fructose <> Sucrose + Phosphate | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Pathways: |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Spectra | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Spectra: |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| References | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| References: |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Synthesis Reference: | Burma, D. P.; Mortimer, D. C. Biosynthesis of uridine diphosphate glucose and sucrose in sugar-beet leaf. Archives of Biochemistry and Biophysics (1956), 62 16-28. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Material Safety Data Sheet (MSDS) | Download (PDF) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Links | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| External Links: |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Enzymes
- General function:
- Involved in catalytic activity
- Specific function:
- UDP-glucose = UDP-galactose
- Gene Name:
- galE
- Locus Tag:
- PA1384
- Molecular weight:
- 36.4 kDa
Reactions
| UDP-glucose = UDP-galactose. |
- General function:
- Involved in UTP:glucose-1-phosphate uridylyltransferase activity
- Specific function:
- May play a role in stationary phase survival
- Gene Name:
- galU
- Locus Tag:
- PA2023
- Molecular weight:
- 31.2 kDa
Reactions
| UTP + alpha-D-glucose 1-phosphate = diphosphate + UDP-glucose. |
- General function:
- Involved in nucleoside-triphosphate diphosphatase activity
- Specific function:
- Specific function unknown
- Gene Name:
- mazG
- Locus Tag:
- PA0935
- Molecular weight:
- 31.2 kDa
Reactions
| ATP + H(2)O = AMP + diphosphate. |
- General function:
- Involved in biosynthetic process
- Specific function:
- Involved in the addition of the first glucose residue to the lipopolysaccharide core
- Gene Name:
- rfaG
- Locus Tag:
- PA5010
- Molecular weight:
- 42.2 kDa