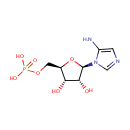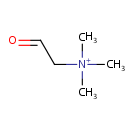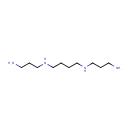
Search Results for compounds
Searching compounds for
returned 4373 results.
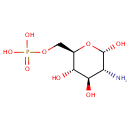
5-Aminoimidazole ribonucleotide (PAMDB000306)
IUPAC:
{[(2R,3S,4R,5R)-5-(5-amino-1H-imidazol-1-yl)-3,4-dihydroxyoxolan-2-yl]methoxy}phosphonic acid
CAS: 25635-88-5
Description: 5-aminoimidazole ribonucleotide (AIR), is an intermediate of purine nucleotide biosynthesis, the precursor to 4-amino-2-methyl-5-hydroxymethylpyrimidine (HMP), the first product of the pyrimidine biosynthesis in a reaction mediated by the enzyme HMP-P kinase (ThiD). HMP is a precursor of thiamin phosphate (TMP), and subsequently to thiamin pyrophosphate (TPP), an essential cofactor in all living systems that plays a central role in metabolism. 5-Aminoimidazole ribonucleotide is a substrate for Scaffold attachment factor B2, Multifunctional protein ADE2, Serine/threonine-protein kinase Chk1, Vinexin, Trifunctional purine biosynthetic protein adenosine-3, Antileukoproteinase 1 and Scaffold attachment factor B.
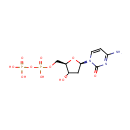
dCDP (PAMDB000307)
IUPAC:
[({[(2R,3S,5R)-5-(4-amino-2-oxo-1,2-dihydropyrimidin-1-yl)-3-hydroxyoxolan-2-yl]methoxy}(hydroxy)phosphoryl)oxy]phosphonic acid
CAS: 800-73-7
Description: dCDP or Deoxycytidine 5'-diphosphate (dCDP) is a nucleoside diphosphate. It is related to the common nucleic acid CTP, or cytidine triphosphate, with the -OH (hydroxyl) group on the 2' carbon on the nucleotide's pentose removed (hence the deoxy- part of the name), and with one fewer phosphoryl group than CTP .dCDP is a product and competitive inhibitor of ribonucleoside-diphosphate reductase (EC 1.17.4.1) from Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Structural studies indicate the base is in anti conformation and the sugar in S-type puckering, when bound either to the complete enzyme complex or to the large protein subunit alone. [PMID: 8019775] Ribonucleoside-diphosphate reductase is very tightly controlled by a variety of allosteric effectors. The enzyme has different regions of it that act differently on allosteric regulators. At the activity site, dATP is a general inhibitor for all substrates and ATP is an activator. Binding of nucleotides at the specificity site further controls the activity of the enzyme towards different substrates in order to maintain an appropriate balance of all deoxynucleotides for DNA synthesis. The dNDPs produced by the enzyme are then phosphorylated to dNTPs by kinases.
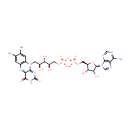
FAD (PAMDB000308)
IUPAC:
[({[(2R,3S,4R,5R)-5-(6-amino-9H-purin-9-yl)-3,4-dihydroxyoxolan-2-yl]methoxy}(hydroxy)phosphoryl)oxy]({[(2R,3S,4S)-5-{7,8-dimethyl-2,4-dioxo-2H,3H,4H,10H-benzo[g]pteridin-10-yl}-2,3,4-trihydroxypentyl]oxy})phosphinic acid
CAS: 146-14-5
Description: Flavine Adenine Dinucleotide (FAD) is a condensation product of riboflavin and adenosine diphosphate. FAD is a redox cofactor involved in several important reactions in metabolism. It can exist in two different redox states, (FAD and FADH2) which it converts between by accepting or donating electrons. It is a coenzyme of various aerobic dehydrogenases, e.g., D-amino acid oxidase and L-amino acid oxidase. (Lehninger, Principles of Biochemistry, 1982, p972)
Betaine aldehyde (PAMDB000309)
IUPAC:
trimethyl(2-oxoethyl)azanium
CAS: 7418-61-3
Description: Betaine aldehyde is an intermediate in the metabolism of glycine, serine and threonine. Betaine aldehyde dehydrogenase facilitates the conversion of betaine aldehyde to betaine. (PMID: 12467448, 7646513)
Glucosamine 6-phosphate (PAMDB000310)
IUPAC:
{[(2R,3S,4R,5R,6S)-5-amino-3,4,6-trihydroxyoxan-2-yl]methoxy}phosphonic acid
CAS: 3616-42-0
Description: Glucosamine 6-phosphate is normally produced via the de novo glucosamine synthesis by the enzyme fructose-6-phosphate amidotransferase and the modulation of this pathway by glutamine. Glutamine-fructose-6-phosphate amidotransferase (GFAT) catalyzes the first committed step in the pathway for biosynthesis of hexosamines. A member of the N-terminal nucleophile class of amidotransferases, GFAT transfers the amino group from the L-glutamine amide to D-fructose 6-phosphate, producing glutamic acid and glucosamine 6-phosphate. (PMID 11270676, 11842094)
Spermine (PAMDB000311)
IUPAC:
(3-aminopropyl)({4-[(3-aminopropyl)amino]butyl})amine
CAS: 71-44-3
Description: Spermine is a biogenic polyamine formed from spermidine. It is found in a wide variety of organisms and tissues and is an essential growth factor in some bacteria. It is found as a polycation at all pH values. Spermine is associated with nucleic acids, particularly in viruses, and is thought to stabilize the helical structure.
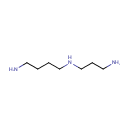
Spermidine (PAMDB000312)
IUPAC:
(4-aminobutyl)(3-aminopropyl)amine
CAS: 124-20-9
Description: Spermidine is a polyamine formed from putrescine. It is found in almost all tissues in association with nucleic acids. It is found as a cation at all pH values, and is thought to help stabilize some membranes and nucleic acid structures. It is a precursor of spermine.
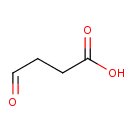
Succinic acid semialdehyde (PAMDB000313)
IUPAC:
4-oxobutanoic acid
CAS: 692-29-5
Description: Succinic acid semialdehyde is an intermediate in the catabolism of gamma-aminobutyrate (PMID 16435183). Succinate semialdehyde dehydrogenase is an enzyme that catalyses the reaction of succinate semialdehyde and NAD+ to form succinate and NADH.
Coproporphyrinogen III (PAMDB000314)
IUPAC:
3-[10,14,19-tris(2-carboxyethyl)-5,9,15,20-tetramethyl-21,22,23,24-tetraazapentacyclo[16.2.1.1?,??1????.1??,???tetracosa-1(20),3,5,8,10,13,15,18-octaen-4-yl]propanoic acid
CAS: 2624-63-7
Description: In the metabolism of porphyrin, the enzyme uroporphyrinogen III decarboxylase generates coproporphyrinogen III from uroporphyrinogen III, and coproporphyrinogen III oxidase converts it into protoporphyrinogen IX. (Wikipedia)
Maltotriose (PAMDB000315)
IUPAC:
(2R,3R,4S,5S,6R)-2-{[(2R,3S,4R,5R,6R)-4,5-dihydroxy-2-(hydroxymethyl)-6-{[(2R,3S,4R,5R)-4,5,6-trihydroxy-2-(hydroxymethyl)oxan-3-yl]oxy}oxan-3-yl]oxy}-6-(hydroxymethyl)oxane-3,4,5-triol
CAS: 1109-28-0
Description: Maltotriose is a member of the chemical class known as Trihexoses. These are trisaccharides containing three hexose carbohydrates. In Pseudomonas aeruginosa, maltotriose is an intermediate involved in degradation of glycogen to glucose. (Ecocyc)