Search Results for compounds
Searching compounds for
returned 4373 results.
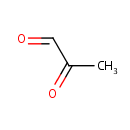
Pyruvaldehyde (PAMDB000281)
IUPAC:
2-oxopropanal
CAS: 78-98-8
Description: Pyruvaldehyde is an organic compound used often as a reagent in organic synthesis, as a flavoring agent, and in tanning. It has been demonstrated as an intermediate in the metabolism of acetone and its derivatives in isolated cell preparations, in various culture media, and in vivo in certain animals.
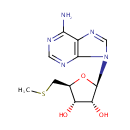
5'-Methylthioadenosine (PAMDB000282)
IUPAC:
(2R,3R,4S,5S)-2-(6-amino-9H-purin-9-yl)-5-[(methylsulfanyl)methyl]oxolane-3,4-diol
CAS: 2457-80-9
Description: 5-Methylthioadenosine is a normal metabolite in Cysteine and methionine metabolism. Spermidine synthase (putrescine aminopropyltransferase)(EC:2.5.1.16) catalyzes the its formation and it is then converted to 5-Methylthio-D-ribose via S-adenosylhomocysteine/5'-methylthioadenosine nucleosidase [EC:3.2.2.9]. (KEGG)
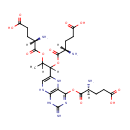
Tetrahydropteroyltri-L-glutamic acid (PAMDB000283)
IUPAC:
(4S)-4-amino-5-[(1-{[(2S)-2-amino-4-carboxybutanoyl]oxy}-1-(4-{[(2S)-2-amino-4-carboxybutanoyl]oxy}-2-imino-1,2,5,8-tetrahydropteridin-6-yl)propan-2-yl)oxy]-5-oxopentanoic acid
CAS: Not Available
Description: Tetrahydropteroyltri-L-glutamic acid is a member of the chemical class known as Biopterins and Derivatives. These are coenzymes containing a 2-amino-pteridine-4-one derivative. tetrahydropteroyltri-L-glutamic acid (CHEBI:17420) is a tetrahydropteroyltri-L-glutamate (CHEBI:26920) tetrahydropteroyltri-L-glutamic acid (CHEBI:17420) is conjugate acid of tetrahydropteroyltri-L-glutamate (CHEBI:58140)
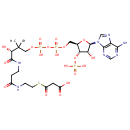
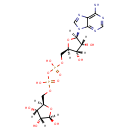
Malonyl-CoA (PAMDB000284)
IUPAC:
3-[(2-{3-[(2R)-3-[({[({[(2R,3S,4R,5R)-5-(6-amino-9H-purin-9-yl)-4-hydroxy-3-(phosphonooxy)oxolan-2-yl]methoxy}(hydroxy)phosphoryl)oxy](hydroxy)phosphoryl}oxy)methyl]-2-hydroxy-3-methylbutanamido]propanamido}ethyl)sulfanyl]-3-oxopropanoic acid
CAS: 524-14-1
Description: Malonyl-CoA is a coenzyme A derivative which plays a key role in fatty acid synthesis in Pseudomonas aeruginosa Fatty acids must be activated with CoA before any chemical modification can be applied. Also fatty acid metabolic intermediates will also exists as CoA derivatives until the CoA is enzymatically cleaved. The fatty acid group is linked to the terminal thiol moiety of CoA
Adenosine diphosphate ribose (PAMDB000285)
IUPAC:
[({[(2R,3S,4R,5R)-5-(6-amino-9H-purin-9-yl)-3,4-dihydroxyoxolan-2-yl]methoxy}(hydroxy)phosphoryl)oxy]({[(2R,3S,4R,5R)-3,4,5-trihydroxyoxolan-2-yl]methoxy})phosphinic acid
CAS: 20762-30-5
Description: Adenosine diphosphate ribose is a member of the chemical class known as Purine Ribonucleoside Diphosphates. These are purine ribobucleotides with diphosphate group linked to the ribose moiety. Adenosine diphosphate ribose is a molecule formed into chains by the enzyme poly ADP ribose polymerase. It binds to and activates the TRPM2 ion channel (WikiPedia)
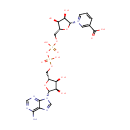
Nicotinic acid adenine dinucleotide (PAMDB000286)
IUPAC:
1-[(2R,3R,4S,5R)-5-[({[({[(2R,3S,4R,5R)-5-(6-amino-9H-purin-9-yl)-3,4-dihydroxyoxolan-2-yl]methoxy}(hydroxy)phosphoryl)oxy](hydroxy)phosphoryl}oxy)methyl]-3,4-dihydroxyoxolan-2-yl]-3-carboxy-1???pyridin-1-ylium
CAS: 6450-77-7
Description: Nicotinic acid adenine dinucleotide phosphate, (NAADP), is a Ca2+-mobilizing second messenger synthesized in response to extracellular stimuli. NAADP binds to and opens Ca2+ channels on intracellular organelles, thereby increasing the intracellular Ca2+ concentration which, in turn, modulates a variety of cellular processes. Structurally, it is a dinucleotide that only differs from the house-keeping enzyme cofactor, NADP by a hydroxyl group (replacing the nicotinamide amino group) and yet this minor modification converts it into the most potent Ca2+-mobilizing second messenger yet described.
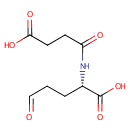
N2-Succinyl-L-glutamic acid 5-semialdehyde (PAMDB000287)
IUPAC:
(2S)-2-(3-carboxypropanamido)-5-oxopentanoic acid
CAS: Not Available
Description: N2-Succinyl-L-glutamic acid 5-semialdehyde is a substrate for Succinate semialdehyde dehydrogenase (mitochondrial) and Ornithine aminotransferase (mitochondrial).
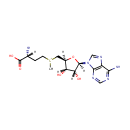
S-Adenosylmethionine (PAMDB000289)
IUPAC:
[(3R)-3-amino-3-carboxypropyl]({[(2S,3S,4R,5R)-5-(6-amino-9H-purin-9-yl)-3,4-dihydroxyoxolan-2-yl]methyl})methylsulfanium
CAS: 29908-03-0
Description: S-Adenosylmethionine is a physiologic methyl radical donor involved in enzymatic transmethylation reactions and present in all living organisms. It is made from adenosine triphosphate (ATP) and methionine by methionine adenosyltransferase (EC 2.5.1.6). Transmethylation, transsulfuration, and aminopropylation are the metabolic pathways that use S-Adenosylmethionine. In bacteria, SAM is bound by the SAM riboswitch, which regulates genes involved in methionine or cysteine biosynthesis. (Wikipedia)
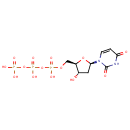
Deoxyuridine triphosphate (PAMDB000290)
IUPAC:
({[({[(2R,3S,5R)-5-(2,4-dioxo-1,2,3,4-tetrahydropyrimidin-1-yl)-3-hydroxyoxolan-2-yl]methoxy}(hydroxy)phosphoryl)oxy](hydroxy)phosphoryl}oxy)phosphonic acid
CAS: 1173-82-6
Description: Deoxyuridine triphosphate is an intermediate in the metabolism of Pyrimidine. It is a substrate for Inosine triphosphate pyrophosphatase, Uridine-cytidine kinase 1, Nucleoside diphosphate kinase 3, Nucleoside diphosphate kinase B, Nucleoside diphosphate kinase 6, Nucleoside diphosphate kinase homolog 5, Nucleoside diphosphate kinase A and Nucleoside diphosphate kinase 7.
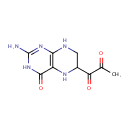
Dyspropterin (PAMDB000292)
IUPAC:
1-(2-amino-4-oxo-3,4,5,6,7,8-hexahydropteridin-6-yl)propane-1,2-dione
CAS: 89687-39-8
Description: Dyspropterin, an intermediate formed from dihydroneopterin triphosphate in the biosynthetic pathway of tetrahydrobiopterin.