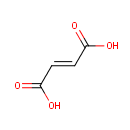
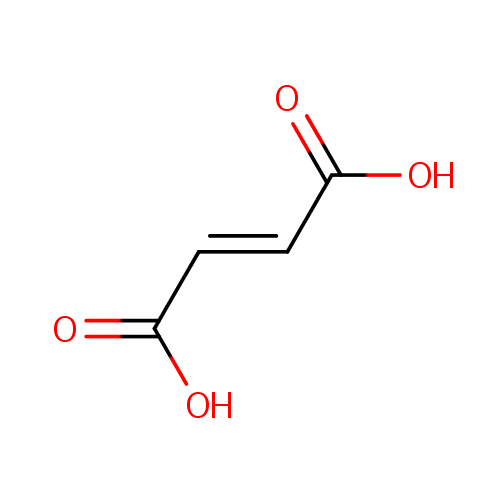
Fumaric acid (PAMDB000073)
| Record Information | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Version | 1.0 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Update Date | 1/22/2018 11:54:54 AM | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Metabolite ID | PAMDB000073 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Identification | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Name: | Fumaric acid | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Description: | A precursor to L-malate in the Krebs tricarboxylic acid cycle. It is formed by the oxidation of succinate by succinate dehydrogenase. Fumarate is converted by fumarase to malate. A fumarate is a salt or ester of the organic compound fumaric acid, a dicarboxylic acid. (wikipedia) | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Structure | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Synonyms: |
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Chemical Formula: | C4H4O4 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Average Molecular Weight: | 116.0722 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Monoisotopic Molecular Weight: | 116.010958616 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| InChI Key: | VZCYOOQTPOCHFL-OWOJBTEDSA-N | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| InChI: | InChI=1S/C4H4O4/c5-3(6)1-2-4(7)8/h1-2H,(H,5,6)(H,7,8)/b2-1+ | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| CAS number: | 110-17-8 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| IUPAC Name: | (2E)-but-2-enedioic acid | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Traditional IUPAC Name: | fumaric acid | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| SMILES: | OC(=O)\C=C\C(O)=O | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Chemical Taxonomy | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Taxonomy Description | This compound belongs to the class of organic compounds known as dicarboxylic acids and derivatives. These are organic compounds containing exactly two carboxylic acid groups. | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Kingdom | Organic compounds | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Super Class | Organic acids and derivatives | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Class | Carboxylic acids and derivatives | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Sub Class | Dicarboxylic acids and derivatives | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Direct Parent | Dicarboxylic acids and derivatives | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Alternative Parents | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Substituents |
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Molecular Framework | Aliphatic acyclic compounds | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| External Descriptors |
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Physical Properties | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| State: | Solid | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Charge: | -2 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Melting point: | 549 °C | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Experimental Properties: |
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Predicted Properties |
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Biological Properties | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Cellular Locations: | Cytoplasm | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Reactions: | Ubiquinone-8 + Succinic acid > Fumaric acid + Ubiquinol-8 Fumaric acid + Water <> L-Malic acid Fumaric acid + Menaquinol 8 > Menaquinone 8 + Succinic acid 2-Demethylmenaquinol 8 + Fumaric acid > 2-Demethylmenaquinone 8 + Succinic acid Water + 2-Hydroxy-6-ketononatrienedioate > Fumaric acid + Hydrogen ion + 2-Hydroxy-2,4-pentadienoate SAICAR <> Phosphoribosyl formamidocarboxamide + Fumaric acid Adenylsuccinic acid <> Adenosine monophosphate + Fumaric acid L-Aspartic acid + Fumaric acid > Hydrogen ion + Iminoaspartic acid + Succinic acid 3 Fumaric acid + Protoporphyrinogen IX > Protoporphyrin IX +3 Succinic acid Argininosuccinic acid <> L-Arginine + Fumaric acid L-Aspartic acid > Fumaric acid + Ammonium Succinic acid + FAD <> FADH2 + Fumaric acid Succinic acid + Acceptor <> Fumaric acid + Reduced acceptor L-Aspartic acid <> Fumaric acid + Ammonia 4,5-Dihydroorotic acid + Fumaric acid <> Orotic acid + Succinic acid SAICAR <> Fumaric acid + AICAR 2-Hydroxy-6-ketononatrienedioate + Water <> 2-Hydroxy-2,4-pentadienoate + Fumaric acid adenylo-succinate > Fumaric acid + Adenosine monophosphate L-arginino-succinate <> L-Arginine + Fumaric acid L-Aspartic acid <> Hydrogen ion + Fumaric acid + Ammonia Fumaric acid + a menaquinol > a menaquinone + Succinic acid More...a ubiquinone + Succinic acid <> a ubiquinol + Fumaric acid Succinic acid + Quinone <> Fumaric acid + Hydroquinone 2-Hydroxy-6-ketononadienedicarboxylate + Water + 2-Hydroxy-6-ketononatrienedioate <> Succinic acid + Fumaric acid Adenylsuccinic acid + SAICAR <> Fumaric acid + Adenosine monophosphate + AICAR L-Malic acid + L-Malic acid <> Fumaric acid + Water Succinic acid + Ubiquinone-10 + FAD <> Fumaric acid + QH2 + FADH2 Succinic acid + Ubiquinone-1 > Ubiquinol-1 + Fumaric acid Succinic acid + Ubiquinone-2 > Fumaric acid + Ubiquinol-2 Succinic acid + Ubiquinone-3 > Fumaric acid + Ubiquinol-3 Succinic acid + Ubiquinone-4 > Fumaric acid + Ubiquinol-4 Succinic acid + Ubiquinone-5 > Fumaric acid + Ubiquinol-5 Succinic acid + Ubiquinone-6 > Fumaric acid + Ubiquinol-6 Succinic acid + Ubiquinone-7 > Fumaric acid + Ubiquinol-7 Succinic acid + Ubiquinone-8 > Fumaric acid + Ubiquinol 8 + Ubiquinol-8 Succinic acid + Coenzyme Q9 > Fumaric acid + Ubiquinol-9 Succinic acid + Ubiquinone-10 > Fumaric acid + Ubiquinol-10 + Ubiquinol-10 L-Aspartic acid + L-Aspartic acid > Fumaric acid + Ammonia L-Aspartic acid + L-Aspartic acid > Fumaric acid + Ammonium N(6)-(1,2-dicarboxyethyl)AMP > Fumaric acid + Adenosine monophosphate SAICAR + SAICAR > AICAR + Fumaric acid N(6)-(1,2-dicarboxyethyl)AMP + Adenylsuccinic acid > Fumaric acid + Adenosine monophosphate 2-Hydroxy-6-ketononatrienedioate + Water > Hydrogen ion + Fumaric acid + 2-Hydroxy-2,4-pentadienoate + 2-Hydroxy-2,4-pentadienoate | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Pathways: |
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Spectra | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Spectra: | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| References | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| References: |
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Synthesis Reference: | Dong, Changsheng; Ma, Xinming. Method for preparation of fumaric acid from the tail gas acid spray solution from oxidation of phthalic anhydride. Faming Zhuanli Shenqing Gongkai Shuomingshu (2007), 5pp. | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Material Safety Data Sheet (MSDS) | Download (PDF) | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Links | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| External Links: |
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Enzymes
- General function:
- Involved in fumarate hydratase activity
- Specific function:
- (S)-malate = fumarate + H(2)O
- Gene Name:
- fumC
- Locus Tag:
- PA0854
- Molecular weight:
- 49.1 kDa
Reactions
| (S)-malate = fumarate + H(2)O. |
- General function:
- Involved in electron carrier activity
- Specific function:
- Two distinct, membrane-bound, FAD-containing enzymes are responsible for the catalysis of fumarate and succinate interconversion; the fumarate reductase is used in anaerobic growth, and the succinate dehydrogenase is used in aerobic growth
- Gene Name:
- sdhB
- Locus Tag:
- PA1584
- Molecular weight:
- 26.2 kDa
Reactions
| Succinate + acceptor = fumarate + reduced acceptor. |
- General function:
- Involved in catalytic activity
- Specific function:
- (S)-dihydroorotate + a quinone = orotate + a quinol
- Gene Name:
- pyrD
- Locus Tag:
- PA3050
- Molecular weight:
- 36.1 kDa
Reactions
| (S)-dihydroorotate + a quinone = orotate + a quinol. |
- General function:
- Involved in N6-(1,2-dicarboxyethyl)AMP AMP-lyase (fumarate-forming) activity
- Specific function:
- N(6)-(1,2-dicarboxyethyl)AMP = fumarate + AMP
- Gene Name:
- purB
- Locus Tag:
- PA2629
- Molecular weight:
- 50.5 kDa
Reactions
| N(6)-(1,2-dicarboxyethyl)AMP = fumarate + AMP. |
| (S)-2-(5-amino-1-(5-phospho-D-ribosyl)imidazole-4-carboxamido)succinate = fumarate + 5-amino-1-(5-phospho-D-ribosyl)imidazole-4-carboxamide. |
- General function:
- Involved in aspartate ammonia-lyase activity
- Specific function:
- L-aspartate = fumarate + NH(3)
- Gene Name:
- aspA
- Locus Tag:
- PA5429
- Molecular weight:
- 51.1 kDa
Reactions
| L-aspartate = fumarate + NH(3). |
- General function:
- Involved in electron carrier activity
- Specific function:
- Two distinct, membrane-bound, FAD-containing enzymes are responsible for the catalysis of fumarate and succinate interconversion; the fumarate reductase is used in anaerobic growth, and the succinate dehydrogenase is used in aerobic growth
- Gene Name:
- sdhA
- Locus Tag:
- PA1583
- Molecular weight:
- 63.5 kDa
Reactions
| Succinate + acceptor = fumarate + reduced acceptor. |
- General function:
- Involved in succinate dehydrogenase activity
- Specific function:
- Membrane-anchoring subunit of succinate dehydrogenase (SDH)
- Gene Name:
- sdhD
- Locus Tag:
- PA1582
- Molecular weight:
- 13.7 kDa
- General function:
- Involved in electron carrier activity
- Specific function:
- Catalyzes the oxidation of L-aspartate to iminoaspartate
- Gene Name:
- nadB
- Locus Tag:
- PA0761
- Molecular weight:
- 60 kDa
Reactions
| L-aspartate + O(2) = iminosuccinate + H(2)O(2). |
- General function:
- Involved in argininosuccinate lyase activity
- Specific function:
- 2-(N(omega)-L-arginino)succinate = fumarate + L-arginine
- Gene Name:
- argH
- Locus Tag:
- PA5263
- Molecular weight:
- 51.6 kDa
Reactions
| 2-(N(omega)-L-arginino)succinate = fumarate + L-arginine. |
- General function:
- Involved in succinate dehydrogenase activity
- Specific function:
- Membrane-anchoring subunit of succinate dehydrogenase (SDH)
- Gene Name:
- sdhC
- Locus Tag:
- PA1581
- Molecular weight:
- 13.7 kDa
Transporters
- General function:
- Involved in symporter activity
- Specific function:
- Responsible for the aerobic transport of the dicarboxylates fumarate, L- and D-malate and to a lesser extent succinate, from the periplasm across the inner membrane
- Gene Name:
- dctA
- Locus Tag:
- PA1183
- Molecular weight:
- 46 kDa