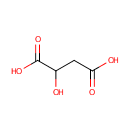
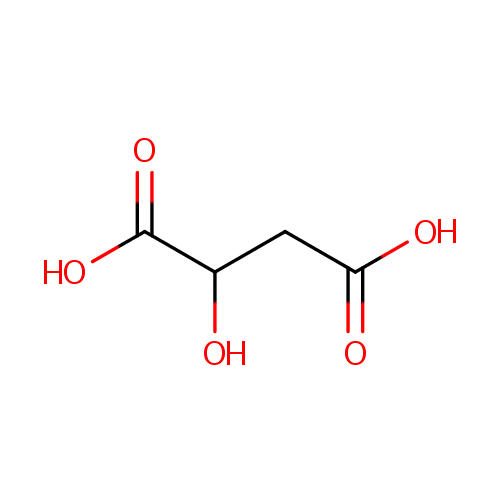
L-Malic acid (PAMDB000058)
| Record Information | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Version | 1.0 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Update Date | 1/22/2018 11:54:54 AM | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Metabolite ID | PAMDB000058 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Identification | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Name: | L-Malic acid | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Description: | Malic acid is a tart-tasting organic dicarboxylic acid that plays a role in many sour or tart foods. In its ionized form it is malate, an intermediate of the TCA cycle along with fumarate. It can also be formed from pyruvate as one of the anaplerotic reactions. Apples contain malic acid, which contributes to the sourness of a green apple. Malic acid can make a wine taste tart, although the amount decreases with increasing fruit ripeness. (wikipedia) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Structure | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Synonyms: |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Chemical Formula: | C4H6O5 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Average Molecular Weight: | 134.0874 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Monoisotopic Molecular Weight: | 134.021523302 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| InChI Key: | BJEPYKJPYRNKOW-UHFFFAOYSA-N | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| InChI: | InChI=1S/C4H6O5/c5-2(4(8)9)1-3(6)7/h2,5H,1H2,(H,6,7)(H,8,9) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| CAS number: | 97-67-6 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| IUPAC Name: | 2-hydroxybutanedioic acid | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Traditional IUPAC Name: | malic acid | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| SMILES: | OC(CC(O)=O)C(O)=O | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Chemical Taxonomy | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Taxonomy Description | This compound belongs to the class of organic compounds known as hydroxy fatty acids. These are fatty acids in which the chain bears a hydroxyl group. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Kingdom | Organic compounds | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Super Class | Lipids and lipid-like molecules | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Class | Fatty Acyls | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Sub Class | Fatty acids and conjugates | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Direct Parent | Hydroxy fatty acids | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Alternative Parents | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Substituents |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Molecular Framework | Aliphatic acyclic compounds | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| External Descriptors | Not Available | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Physical Properties | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| State: | Solid | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Charge: | -2 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Melting point: | 107 °C | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Experimental Properties: |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Predicted Properties |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Biological Properties | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Cellular Locations: | Cytoplasm | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Reactions: | Fumaric acid + Water <> L-Malic acid Acetyl-CoA + Glyoxylic acid + Water <> Coenzyme A + Hydrogen ion + L-Malic acid L-Malic acid + NAD > Carbon dioxide + NADH + Pyruvic acid L-Malic acid + Ubiquinone-8 > Oxalacetic acid + Ubiquinol-8 L-Malic acid + Menaquinone 8 > Menaquinol 8 + Oxalacetic acid L-Malic acid + NADP > Carbon dioxide + NADPH + Pyruvic acid L-Malic acid + NAD <> Hydrogen ion + NADH + Oxalacetic acid L-Malic acid + NAD <> Pyruvic acid + Carbon dioxide + NADH + Hydrogen ion L-Malic acid + NADP <> Pyruvic acid + Carbon dioxide + NADPH + Hydrogen ion L-Malic acid + Coenzyme A <> Acetyl-CoA + Water + Glyoxylic acid L-Malic acid + FAD <> FADH2 + Oxalacetic acid L-Malic acid + a quinone > Oxalacetic acid + a quinol L-Malic acid + Oxygen <> Oxalacetic acid + Hydrogen peroxide L-Malic acid + NAD > Oxalacetic acid + NADH More...L-Malic acid + a quinone > Oxalacetic acid + reduced quinone L-Malic acid + NAD + Oxalacetic acid <> Pyruvic acid + Carbon dioxide + NADH L-Malic acid + Quinone <> Oxalacetic acid + Hydroquinone L-Malic acid + NADP + Oxalacetic acid <> Pyruvic acid + Carbon dioxide + NADPH L-Malic acid + L-Malic acid <> Fumaric acid + Water L-Malic acid + NAD + L-Malic acid <> Oxalacetic acid + NADH + Hydrogen ion L-Malic acid + Quinone + L-Malic acid > Oxalacetic acid + Hydroquinone L-Malic acid + NADP + L-Malic acid > Carbon dioxide + NADPH + Pyruvic acid + NADPH L-Malic acid + NAD + L-Malic acid > Carbon dioxide + NADH + Pyruvic acid Glyoxylic acid + Water + Acetyl-CoA > Coenzyme A + Hydrogen ion + L-Malic acid + L-Malic acid | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Pathways: |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Spectra | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Spectra: |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| References | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| References: |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Synthesis Reference: | McKenzie, Alex.; Plenderleith, H. J.; Walker, Nellie. Optical activation of racemic acid by d-malic acid. Journal of the Chemical Society, Transactions (1923), 123 2875-80. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Material Safety Data Sheet (MSDS) | Download (PDF) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Links | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| External Links: |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Enzymes
- General function:
- Involved in fumarate hydratase activity
- Specific function:
- (S)-malate = fumarate + H(2)O
- Gene Name:
- fumC
- Locus Tag:
- PA0854
- Molecular weight:
- 49.1 kDa
Reactions
| (S)-malate = fumarate + H(2)O. |
- General function:
- Involved in oxidoreductase activity
- Specific function:
- (S)-malate + NAD(+) = pyruvate + CO(2) + NADH
- Gene Name:
- sfcA
- Locus Tag:
- PA3471
- Molecular weight:
- 62.4 kDa
Reactions
| (S)-malate + NAD(+) = pyruvate + CO(2) + NADH. |
- General function:
- Involved in malate dehydrogenase (quinone) activity
- Specific function:
- (S)-malate + a quinone = oxaloacetate + reduced quinone
- Gene Name:
- mqo
- Locus Tag:
- PA3452
- Molecular weight:
- 57.2 kDa
Reactions
| (S)-malate + a quinone = oxaloacetate + reduced quinone. |
- General function:
- Involved in catalytic activity
- Specific function:
- Accounts for almost the entire malate-synthesizing activity in cells metabolizing glyoxylate
- Gene Name:
- glcB
- Locus Tag:
- PA0482
- Molecular weight:
- 78.7 kDa
Reactions
| Acetyl-CoA + H(2)O + glyoxylate = (S)-malate + CoA. |
- General function:
- Involved in oxidoreductase activity
- Specific function:
- (S)-malate + NADP(+) = pyruvate + CO(2) + NADPH
- Gene Name:
- maeB
- Locus Tag:
- PA5046
- Molecular weight:
- 45.4 kDa
Reactions
| (S)-malate + NADP(+) = pyruvate + CO(2) + NADPH. |
Transporters
- General function:
- Involved in symporter activity
- Specific function:
- Responsible for the aerobic transport of the dicarboxylates fumarate, L- and D-malate and to a lesser extent succinate, from the periplasm across the inner membrane
- Gene Name:
- dctA
- Locus Tag:
- PA1183
- Molecular weight:
- 46 kDa