Search Results for compounds
Searching compounds for
returned 4373 results.
Displaying compounds 951 - 960 of
4373 in total
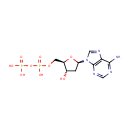
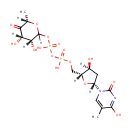
Bis-molybdopterin guanine dinucleotide (PAMDB001713)
IUPAC:
molybdenum(2+) ion 9-[(2R,3R,4S,5R)-3,4-dihydroxy-5-[({[({2-imino-4-oxido-6,7-disulfanyl-1H,2H,5H,5aH,8H,9aH,10H-pyrano[3,2-g]pteridin-8-yl}methyl phosphonato)oxy]phosphinato}oxy)methyl]oxolan-2-yl]-2-imino-3,4,5,9-tetrahydro-2H-purin-6-olate dihydrate
CAS: Not Available
Description: Bis-molybdopterin guanine dinucleotide is a member of the chemical class known as Purine Ribonucleoside Diphosphates. These are purine ribobucleotides with diphosphate group linked to the ribose moiety.
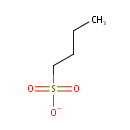
Butanesulfonate (PAMDB001715)
IUPAC:
butane-1-sulfonate
CAS: Not Available
Description: Butanesulfonate is a member of the chemical class known as Sulfonic Acids. These are compounds containing the sulfonic acid group, which has the general structure RS(=O)2OH (R = H).
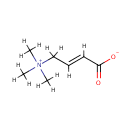
Crotonobetaine (PAMDB001723)
IUPAC:
(2E)-4-(trimethylazaniumyl)but-2-enoate
CAS: 927-89-9
Description: Crotonobetaine is a member of the chemical class known as Quaternary Ammonium Salts. These are compounds containing positively charged polyatomic ion of the structure NR4+, R being an alkyl group or an aryl groupCrotonobetaine is invovled in Carnitine metabolism, and ABC transporters. Crotonobetaine is involved in carnitine metabolism. Carnitine dehydratase from Pseudomonas aeruginosa O44 K74 is an inducible enzyme detectable in cells grown anaerobically in the presence of L-(-)-carnitine or crotonobetaine. (PMID 8188598).
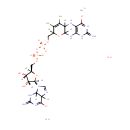
dADP (PAMDB001728)
IUPAC:
[({[(2R,3S,5R)-5-(6-amino-9H-purin-9-yl)-3-hydroxyoxolan-2-yl]methoxy}(hydroxy)phosphoryl)oxy]phosphonic acid
CAS: Not Available
Description: Deoxyadenosine diphosphate is a nucleoside diphosphate. It is related to the common nucleic acid ATP, or adenosine triphosphate, with the -OH (hydroxyl) group on the 2' carbon on the nucleotide's pentose removed (hence the deoxy- part of the name), and with one fewer phosphoryl group than ATP.
dTDP-4-Dehydro-6-deoxy-L-mannose (PAMDB001729)
IUPAC:
[({[(3R,4S,6S)-3,4-dihydroxy-6-methyl-5-oxooxan-2-yl]oxy}(hydroxy)phosphoryl)oxy]({[(2R,3S,5R)-3-hydroxy-5-(4-hydroxy-5-methyl-2-oxo-1,2-dihydropyrimidin-1-yl)oxolan-2-yl]methoxy})phosphinic acid
CAS: Not Available
Description: 4,6-Dideoxy-4-oxo-dTDP-D-glucose is a product of the enzyme TDP-glucose 4,6-dehydratase [EC:4.2.1.46] in the Nucleotide sugars metabolism (KEGG)
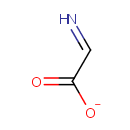
Dehydroglycine (PAMDB001730)
IUPAC:
2-iminoacetate
CAS: Not Available
Description: Dehydroglycine is a member of the chemical class known as Alpha Amino Acids and Derivatives. These are amino acids in which the amino group is attached to the carbon atom immediately adjacent to the carboxylate group (alpha carbon).Dehydroglycine is catalyzed by ThiH. ThiH is a tyrosine lyase that cleaves the C alpha-C beta bond of tyrosine, generating p-cresol as a by-product, to form dehydroglycine. (PMID 19923213)
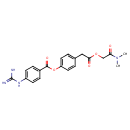
Ethanesulfonate (PAMDB001731)
IUPAC:
4-{2-[(dimethylcarbamoyl)methoxy]-2-oxoethyl}phenyl 4-carbamimidamidobenzoate
CAS: 59721-29-8
Description: Ethanesulfonate is a member of the chemical class known as Depsipeptides. These are natural or synthetic compounds having sequences of amino and hydroxy carboxylic acid residues (usually -amino and -hydroxy acids), commonly but not necessarily regularly alternating. It is also called Coenzyme M. Coenzyme M is a coenzyme required for methyl-transfer reactions in the metabolism of methanogens. The coenzyme is an anion with the formula HSCH2CH2SO_3. It is named 2-mercaptoethanesulfonate and abbreviated HS
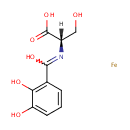
ferric 2,3-dihydroxybenzoylserine (PAMDB001732)
IUPAC:
(2S)-2-{[(2,3-dihydroxyphenyl)(hydroxy)methylidene]amino}-3-hydroxypropanoic acid iron
CAS: Not Available
Description: Ferric 2,3-dihydroxybenzoylserine belongs to the class of Hippuric Acid Derivatives. These are compounds containing an hippuric acid or a derivative, with a structure characterized the presence of a benzoyl group linked to the N-terminal of a glycine. (inferred from compound structure)
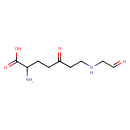
gamma-Glutamyl-gamma-butyraldehyde (PAMDB001737)
IUPAC:
2-amino-5-oxo-7-[(2-oxoethyl)amino]heptanoic acid
CAS: Not Available
Description: Gamma-glutamyl-gamma-butyraldehyde is a member of the chemical class known as Alpha Amino Acids and Derivatives. These are amino acids in which the amino group is attached to the carbon atom immediately adjacent to the carboxylate group (alpha carbon).Gamma-glutamyl-gamma-butyraldehyde is invovled in Arginine and proline metabolism. (KEGG)
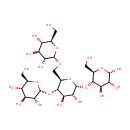
Glycogen (PAMDB001740)
IUPAC:
(2S,3R,4S,5S,6R)-2-{[(2R,3S,4R,5R,6R)-4,5-dihydroxy-6-{[(2R,3S,4R,5R,6S)-4,5,6-trihydroxy-2-(hydroxymethyl)oxan-3-yl]oxy}-3-{[(2R,3R,4S,5S,6R)-3,4,5-trihydroxy-6-(hydroxymethyl)oxan-2-yl]oxy}oxan-2-yl]methoxy}-6-(hydroxymethyl)oxane-3,4,5-triol
CAS: 9005-79-2
Description: Glycogen is a highly branched glucose polymer. It is formed of small chains of 8 to 12 glucose molecules linked together with (1->4) bonds. These small chains are in turn linked together with (1->6) bonds. A single molecule of glycogen can be made of up to 120,000 molecules of glucose. It is stored in the form of granules in the cytosol. (EcoCyc) Glycogen only has one reducing end and a large number of non-reducing ends with a free hydroxyl group at carbon 4. The glycogen granules contain both glycogen and the enzymes of glycogen synthesis (glycogenesis) and degradation (glycogenolysis). The enzymes are nested between the outer branches of the glycogen molecules and act on the non-reducing ends. Therefore, the many non-reducing end-branches of glycogen facilitate its rapid synthesis and breakdown. (HMDB)