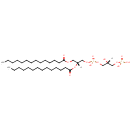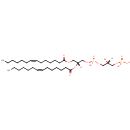
Search Results for compounds
Searching compounds for
returned 4373 results.
Octadecanoyl-phosphate (n-C18:1) (PAMDB001667)
IUPAC:
[(9Z)-octadec-9-enoyloxy]phosphonate
CAS: Not Available
Description: Caprylic acid belongs to the class of Straight Chain Fatty Acids. These are fatty acids with a straight aliphatic chain. (inferred from compound structure)Caprylic acid is invovled in Biosynthesis of alkaloids derived from terpenoid and polyketide, Biosynthesis of plant secondary metabolites, and Fatty acid biosynthesis. (KEGG)Caprylic acid is the common name for the eight-carbon saturated fatty acid known by the systematic name octanoic acid. It is found naturally in the milk of various mammals, and it is a minor constituent of coconut oil and palm kernel oil. It is an oily liquid that is minimally soluble in water with a slightly unpleasant rancid-like smell and taste. Two other acids are named after goats: caproic (C6) and capric (C10). Along with caprylic acid these total 15% in goat milk fat. (WikiPedia)
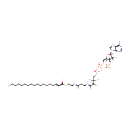
Octadecenoyl-CoA (N-C18:1CoA) (PAMDB001668)
IUPAC:
4-({[({[(2R,3S,4R,5R)-5-(6-amino-9H-purin-9-yl)-4-hydroxy-3-(phosphonatooxy)oxolan-2-yl]methoxy}(hydroxy)phosphoryl)oxy](hydroxy)phosphoryl}oxy)-2-hydroxy-3,3-dimethyl-N-(2-{[2-(octadec-2-enoylsulfanyl)ethyl]carboximidato}ethyl)butanecarboximidate
CAS: Not Available
Description: Octadecenoyl-coa (n-c18:1coa) belongs to the class of Acyl CoAs. These are organic compounds contaning a coenzyme A substructure linked to another moeity through an ester bond. (inferred from compound structure)
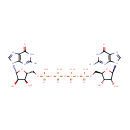
P1,P4-Bis(5'-guanosyl) tetraphosphate (PAMDB001671)
IUPAC:
{[(2R,3S,4R,5R)-5-(2-amino-6-oxo-6,9-dihydro-1H-purin-9-yl)-3,4-dihydroxyoxolan-2-yl]methoxy}({[({[({[(2R,3S,4R,5R)-5-(2-amino-6-oxo-6,9-dihydro-1H-purin-9-yl)-3,4-dihydroxyoxolan-2-yl]methoxy}(hydroxy)phosphoryl)oxy](hydroxy)phosphoryl}oxy)(hydroxy)phosphoryl]oxy})phosphinic acid
CAS: 4130-19-2
Description: Diguanosine tetraphosphate is a diguanosine polyphosphate. It consists of two guanosines joined by a chain of 4 phosphates.
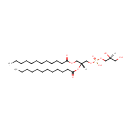
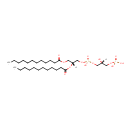
PG(12:0/12:0) (PAMDB001672)
IUPAC:
[(2R)-2,3-bis(dodecanoyloxy)propoxy][(2S)-2,3-dihydroxypropoxy]phosphinic acid
CAS: Not Available
Description: PG(12:0/12:0) is a phosphatidylglycerol. Phosphatidylglycerols consist of a glycerol 3-phosphate backbone esterified to either saturated or unsaturated fatty acids on carbons 1 and 2. As is the case with diacylglycerols, phosphatidylglycerols can have many different combinations of fatty acids of varying lengths and saturation attached to the C-1 and C-2 positions. PG(12:0/12:0), in particular, consists of two dodecanoyl chains at positions C-1 and C-2. In Pseudomonas aeruginosa glycerophospholipid metabolism, phosphatidylglycerol is formed from phosphatidic acid (1,2-diacyl-sn-glycerol 3-phosphate) by a sequence of enzymatic reactions that proceeds via two intermediates, cytidine diphosphate diacylglycerol (CDP-diacylglycerol) and phosphatidylglycerophosphate (PGP, a phosphorylated phosphatidylglycerol). Phosphatidylglycerols, along with CDP-diacylglycerol, also serve as precursor molecules for the synthesis of cardiolipin, a phospholipid found in membranes.
PG(14:1(7Z)/14:1(7Z)) (PAMDB001673)
IUPAC:
[(2R)-2,3-bis[(7Z)-tetradec-7-enoyloxy]propoxy][(2S)-2,3-dihydroxypropoxy]phosphinic acid
CAS: Not Available
Description: PG(14:1(7Z)/14:1(7Z)) is a phosphatidylglycerol. Phosphatidylglycerols consist of a glycerol 3-phosphate backbone esterified to either saturated or unsaturated fatty acids on carbons 1 and 2. As is the case with diacylglycerols, phosphatidylglycerols can have many different combinations of fatty acids of varying lengths and saturation attached to the C-1 and C-2 positions. PG(14:1(7Z)/14:1(7Z)), in particular, consists of two 7Z,tetradecenoyl chains at positions C-1 and C-2. In Pseudomonas aeruginosa glycerophospholipid metabolism, phosphatidylglycerol is formed from phosphatidic acid (1,2-diacyl-sn-glycerol 3-phosphate) by a sequence of enzymatic reactions that proceeds via two intermediates, cytidine diphosphate diacylglycerol (CDP-diacylglycerol) and phosphatidylglycerophosphate (PGP, a phosphorylated phosphatidylglycerol). Phosphatidylglycerols, along with CDP-diacylglycerol, also serve as precursor molecules for the synthesis of cardiolipin, a phospholipid found in membranes.
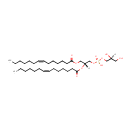
PG(18:0/18:0) (PAMDB001674)
IUPAC:
[(2R)-2,3-bis(octadecanoyloxy)propoxy][(2R)-2,3-dihydroxypropoxy]phosphinic acid
CAS: Not Available
Description: PG(18:0/18:0) is a phosphatidylglycerol. Phosphatidylglycerols consist of a glycerol 3-phosphate backbone esterified to either saturated or unsaturated fatty acids on carbons 1 and 2. As is the case with diacylglycerols, phosphatidylglycerols can have many different combinations of fatty acids of varying lengths and saturation attached to the C-1 and C-2 positions. PG(18:0/18:0), in particular, consists of two octadecanoyl chains at positions C-1 and C-2. In Pseudomonas aeruginosa glycerophospholipid metabolism, phosphatidylglycerol is formed from phosphatidic acid (1,2-diacyl-sn-glycerol 3-phosphate) by a sequence of enzymatic reactions that proceeds via two intermediates, cytidine diphosphate diacylglycerol (CDP-diacylglycerol) and phosphatidylglycerophosphate (PGP, a phosphorylated phosphatidylglycerol). Phosphatidylglycerols, along with CDP-diacylglycerol, also serve as precursor molecules for the synthesis of cardiolipin, a phospholipid found in membranes.
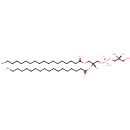
PGP(12:0/12:0) (PAMDB001675)
IUPAC:
[(2R)-3-({[(2R)-2,3-bis(dodecanoyloxy)propoxy](hydroxy)phosphoryl}oxy)-2-hydroxypropoxy]phosphonic acid
CAS: Not Available
Description: PGP(12:0/12:0) belongs to the class of glycerophosphoglycerophosphates, also called phosphatidylglycerophosphates (PGPs). These lipids contain a common glycerophosphate skeleton linked to at least one fatty acyl chain and a glycero-3-phosphate moiety. As is the case with diacylglycerols, phosphatidylglycerophosphates can have many different combinations of fatty acids of varying lengths and saturation attached to the C-1 and C-2 positions. PGP(12:0/12:0), in particular, consists of two dodecanoyl chains at positions C-1 and C-2. In Pseudomonas aeruginosa, PGPs can be found in the cytoplasmic membrane. The are synthesized by the addition of glycerol 3-phosphate to a CDP-diacylglycerol. In turn, PGPs are dephosphorylated to Phosphatidylglycerols (PGs) by the enzyme Phosphatidylglycerophosphatase.
PGP(14:0/14:0) (PAMDB001676)
IUPAC:
[(2R)-3-({[(2R)-2,3-bis(tetradecanoyloxy)propoxy](hydroxy)phosphoryl}oxy)-2-hydroxypropoxy]phosphonic acid
CAS: Not Available
Description: PGP(14:0/14:0) belongs to the class of glycerophosphoglycerophosphates, also called phosphatidylglycerophosphates (PGPs). These lipids contain a common glycerophosphate skeleton linked to at least one fatty acyl chain and a glycero-3-phosphate moiety. As is the case with diacylglycerols, phosphatidylglycerophosphates can have many different combinations of fatty acids of varying lengths and saturation attached to the C-1 and C-2 positions. PGP(14:0/14:0), in particular, consists of two tetradecanoyl chains at positions C-1 and C-2. In Pseudomonas aeruginosa, PGPs can be found in the cytoplasmic membrane. The are synthesized by the addition of glycerol 3-phosphate to a CDP-diacylglycerol. In turn, PGPs are dephosphorylated to Phosphatidylglycerols (PGs) by the enzyme Phosphatidylglycerophosphatase.
PGP(14:1(7Z)/14:1(7Z)) (PAMDB001677)
IUPAC:
[(2R)-3-({[(2R)-2,3-bis[(7Z)-tetradec-7-enoyloxy]propoxy](hydroxy)phosphoryl}oxy)-2-hydroxypropoxy]phosphonic acid
CAS: Not Available
Description: PGP(14:1(7Z)/14:1(7Z)) belongs to the class of glycerophosphoglycerophosphates, also called phosphatidylglycerophosphates (PGPs). These lipids contain a common glycerophosphate skeleton linked to at least one fatty acyl chain and a glycero-3-phosphate moiety. As is the case with diacylglycerols, phosphatidylglycerophosphates can have many different combinations of fatty acids of varying lengths and saturation attached to the C-1 and C-2 positions. PGP(14:1(7Z)/14:1(7Z)), in particular, consists of two 7Z,tetradecenoyl chains at positions C-1 and C-2. In Pseudomonas aeruginosa, PGPs can be found in the cytoplasmic membrane. The are synthesized by the addition of glycerol 3-phosphate to a CDP-diacylglycerol. In turn, PGPs are dephosphorylated to Phosphatidylglycerols (PGs) by the enzyme Phosphatidylglycerophosphatase.
PGP(16:0/16:0) (PAMDB001678)
IUPAC:
[(2R)-3-({[(2R)-2,3-bis(hexadecanoyloxy)propoxy](hydroxy)phosphoryl}oxy)-2-hydroxypropoxy]phosphonic acid
CAS: Not Available
Description: PGP(16:0/16:0) belongs to the class of glycerophosphoglycerophosphates, also called phosphatidylglycerophosphates (PGPs). These lipids contain a common glycerophosphate skeleton linked to at least one fatty acyl chain and a glycero-3-phosphate moiety. As is the case with diacylglycerols, phosphatidylglycerophosphates can have many different combinations of fatty acids of varying lengths and saturation attached to the C-1 and C-2 positions. PGP(16:0/16:0), in particular, consists of two hexadecanoyl chains at positions C-1 and C-2. In Pseudomonas aeruginosa, PGPs can be found in the cytoplasmic membrane. The are synthesized by the addition of glycerol 3-phosphate to a CDP-diacylglycerol. In turn, PGPs are dephosphorylated to Phosphatidylglycerols (PGs) by the enzyme Phosphatidylglycerophosphatase.