Search Results for compounds
Searching compounds for
returned 4373 results.
Displaying compounds 1831 - 1840 of
4373 in total
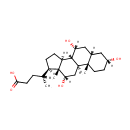
3-Alpha,7-alpha,12-alpha-trihydroxy-5-beta-cholanate (PAMDB003557)
IUPAC:
(4R)-4-[(1S,2S,5R,7S,9R,10R,11S,14R,15R,16S)-5,9,16-trihydroxy-2,15-dimethyltetracyclo[8.7.0.0?,??0??,???heptadecan-14-yl]pentanoic acid
CAS: Not Available
Description: 3-Alpha,7-alpha,12-alpha-trihydroxy-5-beta-cholanate is a steroid derivative or bile acid. It is a substrate for the enzyme 7-alpha-hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase, which catalyzes the following reaction: 3-alpha,7-alpha,12-alpha-trihydroxy-5-beta-cholanate + NAD+ = 3-alpha,12-alpha-dihydroxy-7-oxo-5-beta-cholanate + NADH.
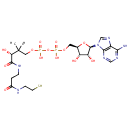
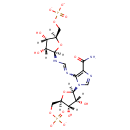
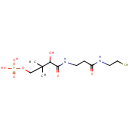
3'-dephospho-CoA (PAMDB003559)
IUPAC:
[({[(2R,3S,4R,5R)-5-(6-amino-9H-purin-9-yl)-3,4-dihydroxyoxolan-2-yl]methoxy}(hydroxy)phosphoryl)oxy][(3R)-3-hydroxy-2,2-dimethyl-3-({2-[(2-sulfanylethyl)carbamoyl]ethyl}carbamoyl)propoxy]phosphinic acid
CAS: 3633-59-8
Description: 3'-dephospho-CoA is a substrate for the enzyme 2-(5''-triphosphoribosyl)-3'-dephosphocoenzyme-A synthase (CitG), which catalyzes the formation of 2-(5''-triphosphoribosyl)-3'-dephosphocoenzyme-A, the precursor of the prosthetic group of the holo-acyl carrier protein (gamma chain) of citrate lyase, from ATP and dephospho-CoA. The reaction is: ATP + 3-dephospho-CoA = 2'-(5-triphosphoribosyl)-3'-dephospho-CoA + adenine. The gamma-subunit of citrate lyase (EC 4.1.3.6) contains the prosthetic group 2'-(5"-phosphoribosyl)-3'-dephospho-CoA and serves as an acyl carrier protein (ACP) in Pseudomonas aeruginosa. It has been shown that in Pseudomonas aeruginosa the proteins CitG and CitX are essential for holo-ACP synthesis and that CitG catalyzes the conversion of ATP and dephospho-CoA to adenine and 2'-(5"-triphosphoribosyl)-3'-dephospho-CoA [PMID:11042274]
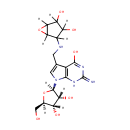
epoxyqueuosine (PAMDB003576)
IUPAC:
4-[({7-[(2R,3R,4S,5R)-3,4-dihydroxy-5-(hydroxymethyl)oxolan-2-yl]-4-hydroxy-2-imino-1H,2H,7H-pyrrolo[2,3-d]pyrimidin-5-yl}methyl)amino]-6-oxabicyclo[3.1.0]hexane-2,3-diol
CAS: Not Available
Description: Epoxyqueuosine is an intermediate in queosine biosynthesis. Queuosine is an important 7-deazapurine-modified nucleoside that is present in certain tRNAs in bacteria and most eukaryotes. Eposyqueosiine is a subsstrate for Epoxyqueuosine reductase catalyzes the final step in the de novo synthesis of queuosine, the anticodon loop modification found in tRNA(Asp), tRNA(Asn), tRNA(His), and tRNA(Tyr)
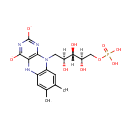
FMNH(2) (PAMDB003577)
IUPAC:
7,8-dimethyl-10-[(2S,3S,4R)-2,3,4-trihydroxy-5-(phosphonooxy)pentyl]-5H,10H-benzo[g]pteridine-2,4-bis(olate)
CAS: 5666-16-0
Description: FMNH2 is the reduced form of flavin mononucleotide. It is a substrate of the enzyme FMN reductase (EC 1.5.1.29), an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction FMNH2 + NAD(P)+ <=> FMN + NAD(P)H + H+. Flavin mononucleotide (FMN), or riboflavin-5??phosphate, is a biomolecule produced from riboflavin (vitamin B2) by the enzyme riboflavin kinase and functions as prosthetic group of various oxidoreductases including NADH dehydrogenase. During a catalytic cycle, the reversible interconversion of oxidized (FMN), semiquinone (FMNH?? and reduced (FMNH2) forms occurs in the various oxidoreductases. FMN is a stronger oxidizing agent than NAD and is particularly useful because it can take part in both one- and two-electron transfers.
1-(5-phosphoribosyl)-5-((5-phosphoribosylamino)methylideneamino)imidazole-4-carboxamide (PAMDB003585)
IUPAC:
[(2R,3S,4R,5R)-5-(N'-{4-carbamoyl-1-[(2R,3R,4S,5R)-3,4-dihydroxy-5-[(phosphonatooxy)methyl]oxolan-2-yl]-1H-imidazol-5-yl}imidamido)-3,4-dihydroxyoxolan-2-yl]methyl phosphate
CAS: Not Available
Description: 1-(5-phosphoribosyl)-5-((5-phosphoribosylamino)methylideneamino)imidazole-4-carboxamide is an intermediate in the histidine biosynthesis pathway. It is a substrate for the enzyme 1-(5-phosphoribosyl)-5-[(5-phosphoribosylamino)methylideneamino] imidazole-4-carboxamide isomerase which catalyzes the reaction 1-(5-phosphoribosyl)-5-((5-phosphoribosylamino)methylideneamino)imidazole-4-carboxamide = 5-((5-phospho-1-deoxyribulos-1-ylamino)methylideneamino)-1-(5-phosphoribosyl)imidazole-4-carboxamide
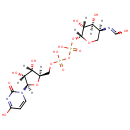
UDP-4-Deoxy-4-formamido-beta-L-arabinose (PAMDB003589)
IUPAC:
N-[(3S,4S,5R,6R)-6-({[({[(2R,3S,4R,5R)-3,4-dihydroxy-5-(4-hydroxy-2-oxo-1,2-dihydropyrimidin-1-yl)oxolan-2-yl]methoxy}(hydroxy)phosphoryl)oxy](hydroxy)phosphoryl}oxy)-4,5-dihydroxyoxan-3-yl]carboximidic acid
CAS: Not Available
Description: UDP-4-Deoxy-4-formamido-beta-L-arabinose is an intermediate in the polymixin resistance pathway. It is a substrate for the enzyme Bifunctional polymyxin resistance protein ArnA that catalyzes the oxidative decarboxylation of UDP-glucuronic acid (UDP-GlcUA) to UDP-4-keto-arabinose (UDP-Ara4O) and the addition of a formyl group to UDP-4-amino-4-deoxy-L-arabinose (UDP-L-Ara4N) to form UDP-L-4-formamido-arabinose (UDP-L-Ara4FN). The modified arabinose is attached to lipid A and is required for resistance to polymyxin and cationic antimicrobial peptides. Some Gram-negative bacteria, specifically Salmonella typhimurium and Pseudomonas aeruginosa, can become resistant to polymyxin by the modification of their lipid A structure via the attachment of 4-amino-4-deoxy-L-arabinopyranose (L-Ara4N) groups to one or more phosphate groups. This addition causes an absolute increase in lipid A charge, thus lowering the affinity of positively charged polymyxins.
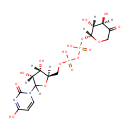
UDP-beta-L-Threo-pentapyranos-4-ulose (PAMDB003592)
IUPAC:
{[(2R,3S,4R)-3,4-dihydroxy-5-(4-hydroxy-2-oxo-1,2-dihydropyrimidin-1-yl)oxolan-2-yl]methoxy}[({[(2R,3R,4R)-3,4-dihydroxy-5-oxooxan-2-yl]oxy}(hydroxy)phosphoryl)oxy]phosphinic acid
CAS: Not Available
Description: UDP-beta-L-Threo-pentapyranos-4-ulose is an intermediate in the polymixin resistance pathway. It is a substrate for the enzyme UDP-4-amino-4-deoxy-L-arabinose aminotransferase which catalyzes the reaction UDP-4-amino-4-deoxy-beta-L-arabinopyranose + 2-oxoglutarate = UDP-beta-L-threo-pentapyranos-4-ulose + L-glutamate. Some Gram-negative bacteria, specifically Salmonella typhimurium and Pseudomonas aeruginosa, can become resistant to polymyxin by the modification of their lipid A structure via the attachment of 4-amino-4-deoxy-L-arabinopyranose (L-Ara4N) groups to one or more phosphate groups. This addition causes an absolute increase in lipid A charge, thus lowering the affinity of positively charged polymyxins.
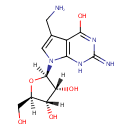
7-Aminomethyl-7-deazaguanosine (PAMDB003600)
IUPAC:
(2R,3R,4S,5R)-2-[5-(aminomethyl)-4-hydroxy-2-imino-1H,2H,7H-pyrrolo[2,3-d]pyrimidin-7-yl]-5-(hydroxymethyl)oxolane-3,4-diol
CAS: Not Available
Description: 7-Aminomethyl-7-deazaguanosine is an intermediate in tRNA charging and tRNA queosine synthesis. It is a substrate for S-adenosylmethionine:tRNA ribosyltransferase-isomerase which catalyzes the reaction: S-adenosylmethionine + 7-aminomethyl-7-deazaguanosine = methionine + adenine + epoxyqueuosine
pantotheine 4'-phosphate (PAMDB003606)
IUPAC:
[3-hydroxy-2,2-dimethyl-3-({2-[(2-sulfanylethyl)carbamoyl]ethyl}carbamoyl)propoxy]phosphonic acid
CAS: 2226-71-3
Description: A phosphopantetheine that has formula C11H23N2O7PS
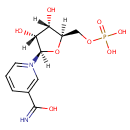
NMN (PAMDB003612)
IUPAC:
1-[(2R,3R,4S,5R)-3,4-dihydroxy-5-[(phosphonooxy)methyl]oxolan-2-yl]-3-(C-hydroxycarbonimidoyl)-1???pyridin-1-ylium
CAS: 1094-61-7
Description: 3-Carbamoyl-1-beta-D-ribofuranosyl pyridinium hydroxide-5'phosphate, inner salt. A nucleotide in which the nitrogenous base, nicotinamide, is in beta-N-glycosidic linkage with the C-1 position of D-ribose