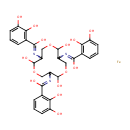
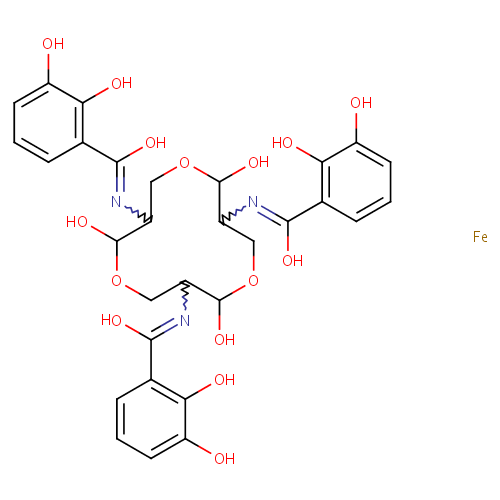
Ferric enterobactin (PAMDB001768)
| Record Information | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Version | 1.0 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Update Date | 1/22/2018 11:54:54 AM | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Metabolite ID | PAMDB001768 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Identification | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Name: | Ferric enterobactin | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Description: | Ferric enterobactin is a member of the chemical class known as Catechols. These are compounds containing a 1,2-benzenediol moeity. Ferric enterobactin is a catecholate siderophore that binds with high affinity (Kd approximately 10-10 M) to the Pseudomonas aeruginosa outer membrane protein FepA. (PMID 10998164) The Pseudomonas aeruginosa FepA protein is an energy- and TonB-dependent, ligand-binding porin that functions as a receptor for the siderophore ferric enterobactin and colicins B and D. (PMID 9268330) The periplasmic protein FepB of Pseudomonas aeruginosa is a component of the ferric enterobactin transport system. (PMID 10986237) The ferric enterobactin receptor, FepA, is a TonB-dependent gated porin that transports the siderophore ferric enterobactin across the outer membrane of gram-negative bacteria. (PMID 7947735) In Pseudomonas aeruginosa, the outer membrane protein FepA is a receptor for the siderophore complex ferric enterobactin and for colicins B and D. (PMID 2201687) FepA is an Pseudomonas aeruginosa outer membrane receptor protein for the siderophore ferric enterobactin. (PMID 7504275) FepA is the Pseudomonas aeruginosa outer membrane receptor for ferric enterobactin, colicin D and colicin B. (PMID 11532122) | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Structure | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Synonyms: |
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Chemical Formula: | C30H33FeN3O15 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Average Molecular Weight: | 731.439 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Monoisotopic Molecular Weight: | 731.126109534 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| InChI Key: | WPYKFMKTUGWUGY-UHFFFAOYSA-N | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| InChI: | InChI=1S/C30H33N3O15.Fe/c34-19-7-1-4-13(22(19)37)25(40)31-16-10-46-29(44)18(33-27(42)15-6-3-9-21(36)24(15)39)12-48-30(45)17(11-47-28(16)43)32-26(41)14-5-2-8-20(35)23(14)38;/h1-9,16-18,28-30,34-39,43-45H,10-12H2,(H,31,40)(H,32,41)(H,33,42); | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| CAS number: | Not Available | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| IUPAC Name: | N-[7,11-bis({[(2,3-dihydroxyphenyl)(hydroxy)methylidene]amino})-2,6,10-trihydroxy-1,5,9-trioxacyclododecan-3-yl]-2,3-dihydroxybenzene-1-carboximidic acid iron | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Traditional IUPAC Name: | N-[7,11-bis({[(2,3-dihydroxyphenyl)(hydroxy)methylidene]amino})-2,6,10-trihydroxy-1,5,9-trioxacyclododecan-3-yl]-2,3-dihydroxybenzenecarboximidic acid iron | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| SMILES: | [Fe].OC1OCC(N=C(O)C2=C(O)C(O)=CC=C2)C(O)OCC(N=C(O)C2=C(O)C(O)=CC=C2)C(O)OCC1N=C(O)C1=C(O)C(O)=CC=C1 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Chemical Taxonomy | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Taxonomy Description | This compound belongs to the class of organic compounds known as catechols. These are compounds containing a 1,2-benzenediol moiety. | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Kingdom | Organic compounds | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Super Class | Benzenoids | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Class | Benzene and substituted derivatives | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Sub Class | Phenols and derivatives | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Direct Parent | Catechols | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Alternative Parents | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Substituents |
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Molecular Framework | Aromatic heteromonocyclic compounds | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| External Descriptors | Not Available | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Physical Properties | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| State: | Not Available | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Charge: | 0 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Melting point: | Not Available | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Experimental Properties: |
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Predicted Properties |
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Biological Properties | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Cellular Locations: | Membrane | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Reactions: | Adenosine triphosphate + Water + Ferric enterobactin > ADP + Ferric enterobactin + Hydrogen ion + Phosphate Adenosine triphosphate + Water + Ferric enterobactin > ADP + Ferric enterobactin + Hydrogen ion + Phosphate Ferric enterobactin + 3 Water >3 2,3-Dihydroxybenzoylserine + Fe3+ +3 Hydrogen ion Enterochelin + Fe3+ > Ferric enterobactin Ferric enterobactin + Water > ferric 2,3-dihydroxybenzoylserine -->-->Ferric enterobactin + Adenosine triphosphate + Water Ferric enterobactin + Adenosine diphosphate + Hydrogen ion + ADP Ferric enterobactin + Adenosine triphosphate + Water Ferric enterobactin + Adenosine diphosphate + Hydrogen ion + ADP | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Pathways: |
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Spectra | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Spectra: |
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| References | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| References: |
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Synthesis Reference: | Not Available | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Material Safety Data Sheet (MSDS) | Not Available | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Links | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| External Links: |
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Enzymes
- General function:
- Involved in nucleotide binding
- Specific function:
- Part of the binding-protein-dependent transport system for ferric enterobactin. Probably responsible for energy coupling to the transport system
- Gene Name:
- fepC
- Locus Tag:
- PA4158
- Molecular weight:
- 28.6 kDa
- General function:
- Involved in transporter activity
- Specific function:
- Part of the binding-protein-dependent transport system for ferric enterobactin. Probably responsible for the translocation of the substrate across the membrane
- Gene Name:
- fepD
- Locus Tag:
- PA4160
- Molecular weight:
- 34.6 kDa
- General function:
- Involved in transporter activity
- Specific function:
- Part of the binding-protein-dependent transport system for ferric enterobactin. Probably responsible for the translocation of the substrate across the membrane
- Gene Name:
- fepG
- Locus Tag:
- PA4161
- Molecular weight:
- 34.8 kDa
- General function:
- Involved in binding
- Specific function:
- Binds ferrienterobactin; part of the binding-protein- dependent transport system for uptake of ferrienterobactin
- Gene Name:
- fepB
- Locus Tag:
- PA4159
- Molecular weight:
- 32.1 kDa
Transporters
- General function:
- Involved in nucleotide binding
- Specific function:
- Part of the binding-protein-dependent transport system for ferric enterobactin. Probably responsible for energy coupling to the transport system
- Gene Name:
- fepC
- Locus Tag:
- PA4158
- Molecular weight:
- 28.6 kDa
- General function:
- Involved in transporter activity
- Specific function:
- Part of the binding-protein-dependent transport system for ferric enterobactin. Probably responsible for the translocation of the substrate across the membrane
- Gene Name:
- fepD
- Locus Tag:
- PA4160
- Molecular weight:
- 34.6 kDa
- General function:
- Involved in transporter activity
- Specific function:
- Part of the binding-protein-dependent transport system for ferric enterobactin. Probably responsible for the translocation of the substrate across the membrane
- Gene Name:
- fepG
- Locus Tag:
- PA4161
- Molecular weight:
- 34.8 kDa
- General function:
- Involved in binding
- Specific function:
- Binds ferrienterobactin; part of the binding-protein- dependent transport system for uptake of ferrienterobactin
- Gene Name:
- fepB
- Locus Tag:
- PA4159
- Molecular weight:
- 32.1 kDa
- General function:
- Involved in receptor activity
- Specific function:
- This protein is involved in the initial step of iron uptake by binding ferrienterobactin (Fe-ENT), an iron chelatin siderophore that allows Pseudomonas aeruginosa to extract iron from the environment. FepA also acts as a receptor for colicins B and D
- Gene Name:
- fepA
- Locus Tag:
- PA2688
- Molecular weight:
- 81 kDa