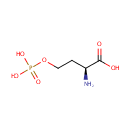
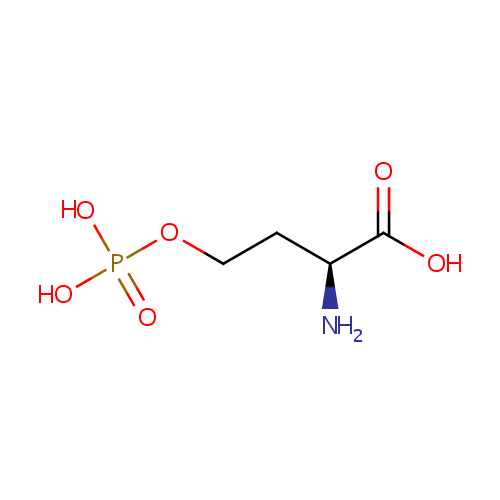
| References: |
- Connick JH, Heywood GC, Smith DA, Stone TW: O-phosphohomoserine, a naturally occurring analogue of phosphonate amino acid antagonists, is an N-methyl-D-aspartate (NMDA) antagonist in rat hippocampus. Neurosci Lett. 1986 Jul 24;68(2):249-51. Pubmed: 3528930
- Donini S, Percudani R, Credali A, Montanini B, Sartori A, Peracchi A: A threonine synthase homolog from a mammalian genome. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2006 Dec 1;350(4):922-8. Epub 2006 Sep 29. Pubmed: 17034760
- Kanehisa, M., Goto, S., Sato, Y., Furumichi, M., Tanabe, M. (2012). "KEGG for integration and interpretation of large-scale molecular data sets." Nucleic Acids Res 40:D109-D114. Pubmed: 22080510
- Keseler, I. M., Collado-Vides, J., Santos-Zavaleta, A., Peralta-Gil, M., Gama-Castro, S., Muniz-Rascado, L., Bonavides-Martinez, C., Paley, S., Krummenacker, M., Altman, T., Kaipa, P., Spaulding, A., Pacheco, J., Latendresse, M., Fulcher, C., Sarker, M., Shearer, A. G., Mackie, A., Paulsen, I., Gunsalus, R. P., Karp, P. D. (2011). "EcoCyc: a comprehensive database of Escherichia coli biology." Nucleic Acids Res 39:D583-D590. Pubmed: 21097882
- Sun G, Yang K, Zhao Z, Guan S, Han X, Gross RW: Shotgun metabolomics approach for the analysis of negatively charged water-soluble cellular metabolites from mouse heart tissue. Anal Chem. 2007 Sep 1;79(17):6629-40. Epub 2007 Aug 1. Pubmed: 17665876
- van der Werf, M. J., Overkamp, K. M., Muilwijk, B., Coulier, L., Hankemeier, T. (2007). "Microbial metabolomics: toward a platform with full metabolome coverage." Anal Biochem 370:17-25. Pubmed: 17765195
- Winder, C. L., Dunn, W. B., Schuler, S., Broadhurst, D., Jarvis, R., Stephens, G. M., Goodacre, R. (2008). "Global metabolic profiling of Escherichia coli cultures: an evaluation of methods for quenching and extraction of intracellular metabolites." Anal Chem 80:2939-2948. Pubmed: 18331064
|
|---|