Search Results for compounds
Searching compounds for
returned 4373 results.
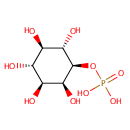
Myo-inositol 1-phosphate (PAMDB000086)
IUPAC:
{[(1R,2S,3R,4R,5S,6S)-2,3,4,5,6-pentahydroxycyclohexyl]oxy}phosphonic acid
CAS: 573-35-3
Description: Myo-inositol 1-phosphate is an inositol having myo- configuration substituted at position 1 by a phosphate group. (ChEBI) There are 2 stereoisomers of myo-inositol 1-phosphate: 1D-myo-inositol 1-phosphate and 1L-myo-inositol 1-phosphate. The D-isomer is the isomer that is more commonly referred to when discussing myo-inositol 1-phosphate (in KEGG, for example), and is a constituent of phospholipids and inositol polyphosphates. The L-isomer is also known as 1D-myo-inositol 3-phosphate. (EcoCyc) The enzyme myo-inositol-1(or 4)-monophosphatase (an inositol monophosphatase) (EC:3.1.3.25) catalyzes the removal of the phosphate group from both isomers of myo-inositol 1-phosphate. (KEGG)
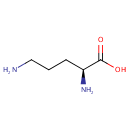
Ornithine (PAMDB000087)
IUPAC:
(2S)-2,5-diaminopentanoic acid
CAS: 70-26-8
Description: Ornithine is an amino acid produced in the urea cycle by the splitting off of urea from arginine. It is a central part of the urea cycle, which allows for the disposal of excess nitrogen. L-Ornithine is also a precursor of citrulline and arginine.
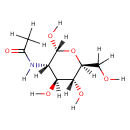
N-Acetyl-D-glucosamine (PAMDB000088)
IUPAC:
N-[(2R,3S,4S,5R,6S)-2,4,5-trihydroxy-6-(hydroxymethyl)oxan-3-yl]acetamide
CAS: 7512-17-6
Description: N-Acetyl-D-Glucosamine (N-acetlyglucosamine) is a monosaccharide derivative of glucose. Chemically it is an amide between glucosamine and acetic acid. A single N-acetlyglucosamine moiety linked to serine or threonine residues on nuclear and cytoplasmic proteins -O-GlcNAc, is an ubiquitous post-translational protein modification. O-GlcNAc modified proteins are involved in sensing the nutrient status of the surrounding cellular environment and adjusting the activity of cellular proteins accordingly. O-GlcNAc initiates a protective response to stress, modulates a cell's capacity to grow and divide, and regulates gene transcription. (PMID 16237703)
NADP (PAMDB000089)
IUPAC:
1-[(2R,3R,4S,5R)-5-[({[({[(2R,3R,4R,5R)-5-(6-amino-9H-purin-9-yl)-3-hydroxy-4-(phosphonooxy)oxolan-2-yl]methoxy}(hydroxy)phosphoryl)oxy](hydroxy)phosphoryl}oxy)methyl]-3,4-dihydroxyoxolan-2-yl]-3-carbamoyl-1???pyridin-1-ylium
CAS: 53-59-8
Description: Nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide phosphate. A coenzyme composed of ribosylnicotinamide 5-phosphate (NMN) coupled by pyrophosphate linkage to the 5-phosphate adenosine 2,5-bisphosphate. It serves as an electron carrier in a number of reactions, being alternately oxidized (NADP+) and reduced (NADPH). (Dorland, 27th ed.) Hydrogen carrier in biochemical redox systems. In the hexose monophosphoric acid system it is reduced to Dihydrocoenzyme and reoxidation in the presence of flavoproteins (Dictionary of Organic Compounds)
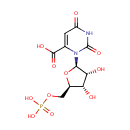
Orotidylic acid (PAMDB000090)
IUPAC:
3-[(2R,3R,4S,5R)-3,4-dihydroxy-5-[(phosphonooxy)methyl]oxolan-2-yl]-2,6-dioxo-1,2,3,6-tetrahydropyrimidine-4-carboxylic acid
CAS: 2149-82-8
Description: Orotidylic acid (OMP), is a pyrimidine nucleotide which is the last intermediate in the biosynthesis of uridine monophosphate. Decarboxylation by Orotidylate decarboxylase affords Uridine 5'-phosphate which is the route to Uridine and its derivatives de novo and consequently one of the most important processes in nucleic acid synthesis (Dictionary of Organic Compounds). In Pseudomonas aeruginosa, the enzyme UMP synthase converts OMP into uridine 5'- monophosphate. If UMP synthase is defective, orotic aciduria can result. (Wikipedia)
Palmitic acid (PAMDB000091)
IUPAC:
hexadecanoic acid
CAS: 57-10-3
Description: Palmitic acid, or hexadecanoic acid is a saturated fatty acids. Palmitic acid is the first fatty acid produced during lipogenesis (fatty acid synthesis) and from which longer fatty acids can be produced. Palmitate negatively feeds back on acetyl-CoA carboxylase (ACC) which is responsible for converting acetyl-CoA to malonyl-CoA which is used to add to the growing acyl chain, thus preventing further palmitate generation. (Wikipedia)
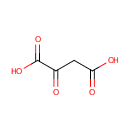
Oxalacetic acid (PAMDB000092)
IUPAC:
2-oxobutanedioic acid
CAS: 328-42-7
Description: Oxaloacetic acid, also known as oxosuccinic acid or oxalacetic acid, is a four-carbon dicarboxylic acid appearing as an intermediate of the citric acid cycle. In vivo, oxaloacetate (the ionized form of oxaloacetic acid) is formed by the oxidation of L-malate, catalyzed by malate dehydrogenase, and reacts with Acetyl-CoA to form citrate, catalyzed by citrate synthase.(wikipedia) A class of ketodicarboxylic acids derived from oxalic acid. Oxaloacetic acid is an intermediate in the citric acid cycle and is converted to aspartic acidD by a transamination reaction.
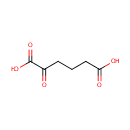
Oxoadipic acid (PAMDB000093)
IUPAC:
2-oxohexanedioic acid
CAS: 3184-35-8
Description: 2-Oxoadipic acid is produced from lysine in the cytosol of cells via the saccharopine and the pipecolic acid pathways. Catabolites of hydroxylysine and tryptophan enter these pathways as 2-aminoadipic- -semialdehyde and 2-oxoadipate, respectively. In the cytoplasm, 2-oxoadipate is decarboxylated to glutaryl-CoA by the 2-oxoadipate dehydrogenase complex and then converted to acetyl-CoA.
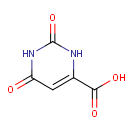
Orotic acid (PAMDB000094)
IUPAC:
2,6-dioxo-1,2,3,6-tetrahydropyrimidine-4-carboxylic acid
CAS: 65-86-1
Description: Orotic acid is a heterocyclic compound and an acid; it is also known as pyrimidinecarboxylic acid. It was once believed to be part of the vitamin B complex and was called vitamin B13, but it is now known that it is not a vitamin but is instead manufactured in the body by intestinal flora. Orotic acid is converted to UMP by UMP synthase, a multifunctional protein with both orotate phosphoribosyltransferase and orotidylate decarboxylase activity. (Wikipedia)
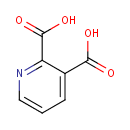
Quinolinic acid (PAMDB000096)
IUPAC:
pyridine-2,3-dicarboxylic acid
CAS: 89-00-9
Description: Quinolinic acid is a dicarboxylic acid. It may be prepared by the oxidation of quinoline, either electrochemically, or with acidic hydrogen peroxide. (Wikipedia)