Search Results for compounds
Searching compounds for
returned 4373 results.
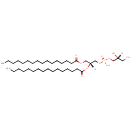
PG(16:0/16:0) (PAMDB000791)
IUPAC:
[(2R)-2,3-bis(hexadecanoyloxy)propoxy][(2R)-2,3-dihydroxypropoxy]phosphinic acid
CAS: Not Available
Description: PG(16:0/16:0) is a phosphatidylglycerol. Phosphatidylglycerols consist of a glycerol 3-phosphate backbone esterified to either saturated or unsaturated fatty acids on carbons 1 and 2. As is the case with diacylglycerols, phosphatidylglycerols can have many different combinations of fatty acids of varying lengths and saturation attached to the C-1 and C-2 positions. PG(16:0/16:0), in particular, consists of two hexadecanoyl chains at positions C-1 and C-2. In Pseudomonas aeruginosa glycerophospholipid metabolism, phosphatidylglycerol is formed from phosphatidic acid (1,2-diacyl-sn-glycerol 3-phosphate) by a sequence of enzymatic reactions that proceeds via two intermediates, cytidine diphosphate diacylglycerol (CDP-diacylglycerol) and phosphatidylglycerophosphate (PGP, a phosphorylated phosphatidylglycerol). Phosphatidylglycerols, along with CDP-diacylglycerol, also serve as precursor molecules for the synthesis of cardiolipin, a phospholipid found in membranes.
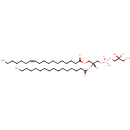
PG(16:0/16:1(9Z)) (PAMDB000792)
IUPAC:
[(2S)-2,3-dihydroxypropoxy][(2R)-3-[(9Z)-hexadec-9-enoyloxy]-2-(hexadecanoyloxy)propoxy]phosphinic acid
CAS: Not Available
Description: PG(16:0/16:1(9Z)) is a phosphatidylglycerol. Phosphatidylglycerols consist of a glycerol 3-phosphate backbone esterified to either saturated or unsaturated fatty acids on carbons 1 and 2. As is the case with diacylglycerols, phosphatidylglycerols can have many different combinations of fatty acids of varying lengths and saturation attached to the C-1 and C-2 positions. PG(16:0/16:1(9Z)), in particular, consists of one hexadecanoyl chain to the C-1 atom, and one 9Z-hexadecenoyl to the C-2 atom. In Pseudomonas aeruginosa glycerophospholipid metabolism, phosphatidylglycerol is formed from phosphatidic acid (1,2-diacyl-sn-glycerol 3-phosphate) by a sequence of enzymatic reactions that proceeds via two intermediates, cytidine diphosphate diacylglycerol (CDP-diacylglycerol) and phosphatidylglycerophosphate (PGP, a phosphorylated phosphatidylglycerol). Phosphatidylglycerols, along with CDP-diacylglycerol, also serve as precursor molecules for the synthesis of cardiolipin, a phospholipid found in membranes.
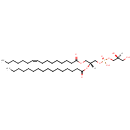
PG(16:0/18:1(11Z)) (PAMDB000793)
IUPAC:
[(2S)-2,3-dihydroxypropoxy][(2R)-2-(hexadecanoyloxy)-3-[(11Z)-octadec-11-enoyloxy]propoxy]phosphinic acid
CAS: Not Available
Description: PG(16:0/18:1(11Z)) is a phosphatidylglycerol. Phosphatidylglycerols consist of a glycerol 3-phosphate backbone esterified to either saturated or unsaturated fatty acids on carbons 1 and 2. As is the case with diacylglycerols, phosphatidylglycerols can have many different combinations of fatty acids of varying lengths and saturation attached to the C-1 and C-2 positions. PG(16:0/18:1(11Z)), in particular, consists of one hexadecanoyl chain to the C-1 atom, and one 11Z-octadecenoyl to the C-2 atom. In Pseudomonas aeruginosa glycerophospholipid metabolism, phosphatidylglycerol is formed from phosphatidic acid (1,2-diacyl-sn-glycerol 3-phosphate) by a sequence of enzymatic reactions that proceeds via two intermediates, cytidine diphosphate diacylglycerol (CDP-diacylglycerol) and phosphatidylglycerophosphate (PGP, a phosphorylated phosphatidylglycerol). Phosphatidylglycerols, along with CDP-diacylglycerol, also serve as precursor molecules for the synthesis of cardiolipin, a phospholipid found in membranes.
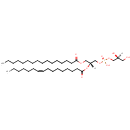
PG(16:1(9Z)/16:0) (PAMDB000794)
IUPAC:
[(2S)-2,3-dihydroxypropoxy][(2R)-2-[(9Z)-hexadec-9-enoyloxy]-3-(hexadecanoyloxy)propoxy]phosphinic acid
CAS: Not Available
Description: PG(16:1(9Z)/16:0) is a phosphatidylglycerol. Phosphatidylglycerols consist of a glycerol 3-phosphate backbone esterified to either saturated or unsaturated fatty acids on carbons 1 and 2. As is the case with diacylglycerols, phosphatidylglycerols can have many different combinations of fatty acids of varying lengths and saturation attached to the C-1 and C-2 positions. PG(16:1(9Z)/16:0), in particular, consists of one 9Z-hexadecenoyl chain to the C-1 atom, and one hexadecanoyl to the C-2 atom. In Pseudomonas aeruginosa glycerophospholipid metabolism, phosphatidylglycerol is formed from phosphatidic acid (1,2-diacyl-sn-glycerol 3-phosphate) by a sequence of enzymatic reactions that proceeds via two intermediates, cytidine diphosphate diacylglycerol (CDP-diacylglycerol) and phosphatidylglycerophosphate (PGP, a phosphorylated phosphatidylglycerol). Phosphatidylglycerols, along with CDP-diacylglycerol, also serve as precursor molecules for the synthesis of cardiolipin, a phospholipid found in membranes.
PG(16:1(9Z)/16:1(9Z)) (PAMDB000795)
IUPAC:
[(2R)-2,3-bis[(9Z)-hexadec-9-enoyloxy]propoxy][(2R)-2,3-dihydroxypropoxy]phosphinic acid
CAS: Not Available
Description: PG(16:1(9Z)/16:1(9Z)) is a phosphatidylglycerol. Phosphatidylglycerols consist of a glycerol 3-phosphate backbone esterified to either saturated or unsaturated fatty acids on carbons 1 and 2. As is the case with diacylglycerols, phosphatidylglycerols can have many different combinations of fatty acids of varying lengths and saturation attached to the C-1 and C-2 positions. PG(16:1(9Z)/16:1(9Z)), in particular, consists of two 9Z-hexadecenoyl chains at positions C-1 and C-2. In Pseudomonas aeruginosa glycerophospholipid metabolism, phosphatidylglycerol is formed from phosphatidic acid (1,2-diacyl-sn-glycerol 3-phosphate) by a sequence of enzymatic reactions that proceeds via two intermediates, cytidine diphosphate diacylglycerol (CDP-diacylglycerol) and phosphatidylglycerophosphate (PGP, a phosphorylated phosphatidylglycerol). Phosphatidylglycerols, along with CDP-diacylglycerol, also serve as precursor molecules for the synthesis of cardiolipin, a phospholipid found in membranes.
PG(16:1(9Z)/18:1(11Z)) (PAMDB000796)
IUPAC:
[(2S)-2,3-dihydroxypropoxy][(2R)-2-[(9Z)-hexadec-9-enoyloxy]-3-[(11Z)-octadec-11-enoyloxy]propoxy]phosphinic acid
CAS: Not Available
Description: PG(16:1(9Z)/18:1(11Z)) is a phosphatidylglycerol. Phosphatidylglycerols consist of a glycerol 3-phosphate backbone esterified to either saturated or unsaturated fatty acids on carbons 1 and 2. As is the case with diacylglycerols, phosphatidylglycerols can have many different combinations of fatty acids of varying lengths and saturation attached to the C-1 and C-2 positions. PG(16:1(9Z)/18:1(11Z)), in particular, consists of one 9Z-hexadecenoyl chain to the C-1 atom, and one 11Z-octadecenoyl to the C-2 atom. In Pseudomonas aeruginosa glycerophospholipid metabolism, phosphatidylglycerol is formed from phosphatidic acid (1,2-diacyl-sn-glycerol 3-phosphate) by a sequence of enzymatic reactions that proceeds via two intermediates, cytidine diphosphate diacylglycerol (CDP-diacylglycerol) and phosphatidylglycerophosphate (PGP, a phosphorylated phosphatidylglycerol). Phosphatidylglycerols, along with CDP-diacylglycerol, also serve as precursor molecules for the synthesis of cardiolipin, a phospholipid found in membranes.
PG(18:1(11Z)/16:0) (PAMDB000797)
IUPAC:
[(2S)-2,3-dihydroxypropoxy][(2R)-3-(hexadecanoyloxy)-2-[(11Z)-octadec-11-enoyloxy]propoxy]phosphinic acid
CAS: Not Available
Description: PG(18:1(11Z)/16:0) is a phosphatidylglycerol. Phosphatidylglycerols consist of a glycerol 3-phosphate backbone esterified to either saturated or unsaturated fatty acids on carbons 1 and 2. As is the case with diacylglycerols, phosphatidylglycerols can have many different combinations of fatty acids of varying lengths and saturation attached to the C-1 and C-2 positions. PG(18:1(11Z)/16:0), in particular, consists of one 11Z-octadecenoyl chain to the C-1 atom, and one hexadecanoyl to the C-2 atom. In Pseudomonas aeruginosa glycerophospholipid metabolism, phosphatidylglycerol is formed from phosphatidic acid (1,2-diacyl-sn-glycerol 3-phosphate) by a sequence of enzymatic reactions that proceeds via two intermediates, cytidine diphosphate diacylglycerol (CDP-diacylglycerol) and phosphatidylglycerophosphate (PGP, a phosphorylated phosphatidylglycerol). Phosphatidylglycerols, along with CDP-diacylglycerol, also serve as precursor molecules for the synthesis of cardiolipin, a phospholipid found in membranes.
PG(18:1(11Z)/16:1(9Z)) (PAMDB000798)
IUPAC:
[(2S)-2,3-dihydroxypropoxy][(2R)-3-[(9Z)-hexadec-9-enoyloxy]-2-[(11Z)-octadec-11-enoyloxy]propoxy]phosphinic acid
CAS: Not Available
Description: PG(18:1(11Z)/16:1(9Z)) is a phosphatidylglycerol. Phosphatidylglycerols consist of a glycerol 3-phosphate backbone esterified to either saturated or unsaturated fatty acids on carbons 1 and 2. As is the case with diacylglycerols, phosphatidylglycerols can have many different combinations of fatty acids of varying lengths and saturation attached to the C-1 and C-2 positions. PG(18:1(11Z)/16:1(9Z)), in particular, consists of one 11Z-octadecenoyl chain to the C-1 atom, and one 9Z-hexadecenoyl to the C-2 atom. In Pseudomonas aeruginosa glycerophospholipid metabolism, phosphatidylglycerol is formed from phosphatidic acid (1,2-diacyl-sn-glycerol 3-phosphate) by a sequence of enzymatic reactions that proceeds via two intermediates, cytidine diphosphate diacylglycerol (CDP-diacylglycerol) and phosphatidylglycerophosphate (PGP, a phosphorylated phosphatidylglycerol). Phosphatidylglycerols, along with CDP-diacylglycerol, also serve as precursor molecules for the synthesis of cardiolipin, a phospholipid found in membranes.
PG(18:1(11Z)/18:1(11Z)) (PAMDB000799)
IUPAC:
[(2R)-2,3-bis[(11Z)-octadec-11-enoyloxy]propoxy][(2R)-2,3-dihydroxypropoxy]phosphinic acid
CAS: Not Available
Description: PG(18:1(11Z)/18:1(11Z)) is a phosphatidylglycerol. Phosphatidylglycerols consist of a glycerol 3-phosphate backbone esterified to either saturated or unsaturated fatty acids on carbons 1 and 2. As is the case with diacylglycerols, phosphatidylglycerols can have many different combinations of fatty acids of varying lengths and saturation attached to the C-1 and C-2 positions. PG(18:1(11Z)/18:1(11Z)), in particular, consists of two 11Z-octadecenoyl chains at positions C-1 and C-2. In Pseudomonas aeruginosa glycerophospholipid metabolism, phosphatidylglycerol is formed from phosphatidic acid (1,2-diacyl-sn-glycerol 3-phosphate) by a sequence of enzymatic reactions that proceeds via two intermediates, cytidine diphosphate diacylglycerol (CDP-diacylglycerol) and phosphatidylglycerophosphate (PGP, a phosphorylated phosphatidylglycerol). Phosphatidylglycerols, along with CDP-diacylglycerol, also serve as precursor molecules for the synthesis of cardiolipin, a phospholipid found in membranes.
CL(18:1(9Z)/18:1(9Z)/18:1(9Z)/18:1(9Z)) (PAMDB000801)
IUPAC:
[(2R)-2,3-bis[(9Z)-octadec-9-enoyloxy]propoxy][3-({[(2R)-2,3-bis[(9Z)-octadec-9-enoyloxy]propoxy](hydroxy)phosphoryl}oxy)-2-hydroxypropoxy]phosphinic acid
CAS: Not Available
Description: CL(18:1(9Z)/18:1(9Z)/18:1(9Z)/18:1(9Z)) is a cardiolipin (CL). Cardiolipins are sometimes called a 'double' phospholipid because they have four fatty acid tails, instead of the usual two. CL(18:1(9Z)/18:1(9Z)/18:1(9Z)/18:1(9Z)) contains four chains of (9Z-octadecenoyl) at the C1, C2, C3 and C4 positions. While the theoretical charge of cardiolipins is -2, under normal physiological conditions (pH near 7), the molecule may carry only one negative charge. In prokaryotes such as Pseudomonas aeruginosa, the enzyme known as diphosphatidylglycerol synthase catalyses the transfer of the phosphatidyl moiety of one phosphatidylglycerol to the free 3'-hydroxyl group of another, with the elimination of one molecule of glycerol. In Pseudomonas aeruginosa, which acylates its glycerophospholipids with acyl chains ranging in length from 12 to 19 carbons and possibly containing an unsaturation, or a cyclopropane group more than 100 possible CL molecular species are theoretically possible. Pseudomonas aeruginosa membranes consist of ~5% cardiolipin (CL), 20-25% phosphatidylglycerol (PG), and 70-80% phosphatidylethanolamine (PE) as well as smaller amounts of phosphatidylserine (PS). CL is distributed between the two leaflets of the bilayers and is located preferentially at the poles and septa in Pseudomonas aeruginosa and other rod-shaped bacteria. It is known that the polar positioning of the proline transporter ProP and the mechanosensitive ion channel MscS in Pseudomonas aeruginosa is dependent on CL. It is believed that cell shape may influence the localization of CL and the localization of certain membrane proteins.