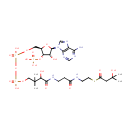
Search Results for compounds
Searching compounds for
returned 4373 results.
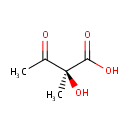
(S)-2-Acetolactate (PAMDB000697)
IUPAC:
(2S)-2-hydroxy-2-methyl-3-oxobutanoic acid
CAS: Not Available
Description: (S)-2-Acetolactate is an intermediate in the biosynthesis of valine, leucine and isoleucine (KEGG ID C06010 ). It is the sixth to last step in the synthesis of protein and is converted from 2-hydroxy-3-methyl-2-oxobutanoate via the enzyme acetolactate synthase [EC:2.2.1.6]. It is then converted to 3-hydroxy-3-methyl-2-oxobutanoate via the enzyme ketol-acid reductoisomerase [EC:1.1.1.86].
3-Hydroxyisovaleryl-CoA (PAMDB000698)
IUPAC:
{[(2R,3S,4R,5R)-5-(6-amino-9H-purin-9-yl)-4-hydroxy-2-({[hydroxy({[hydroxy(3-hydroxy-3-{[2-({2-[(3-hydroxy-3-methylbutanoyl)sulfanyl]ethyl}carbamoyl)ethyl]carbamoyl}-2,2-dimethylpropoxy)phosphoryl]oxy})phosphoryl]oxy}methyl)oxolan-3-yl]oxy}phosphonic acid
CAS: Not Available
Description: 3-Hydroxyisovaleryl-CoA is an end product of leucine degradation. It is converted from 3-methylbut-2-enoyl-CoA by the enzyme enoyl-CoA hydratase.
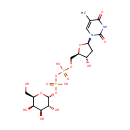
dTDP-D-Galactose (PAMDB000701)
IUPAC:
{[hydroxy({[(2R,3R,4S,5R,6R)-3,4,5-trihydroxy-6-(hydroxymethyl)oxan-2-yl]oxy})phosphoryl]oxy}({[(2R,3S,5R)-3-hydroxy-5-(5-methyl-2,4-dioxo-1,2,3,4-tetrahydropyrimidin-1-yl)oxolan-2-yl]methoxy})phosphinic acid
CAS: 5817-97-0
Description: dTDP-D-galactose is an intermediate involved in nucleotide sugar metabolism. It can be generated by dTDP-D-glucose through the action of the enzyme UDP-glucose 4-epimerase.
Adenosyl cobinamide (PAMDB000706)
IUPAC:
{[(2S,3S,4R,5R)-5-(6-amino-9H-purin-9-yl)-3,4-dihydroxyoxolan-2-yl]methyl}[(1R,2R,3S,4S,8S,9S,14S,18R,19R)-4,9,14-tris(2-carbamoylethyl)-3,8,19-tris(carbamoylmethyl)-18-(2-{[(2R)-2-hydroxypropyl]carbamoyl}ethyl)-2,3,6,8,13,13,16,18-octamethyl-20,21,22,23-tetraazapentacyclo[15.2.1.1?,??1?????1??,???tricosa-5(23),6,10(22),11,15(21),16-hexaen-20-yl]cobaltylium
CAS: Not Available
Description: Adenosyl cobinamide is an intermediate in Porphyrin and chlorophyll metabolism. It is the third to last step in the synthesis of vitamin B12 coenzyme and is converted from adenosyl cobyrinate hexaamide via the enzyme cobalamin biosynthetic protein CobC. It is then converted to adenosyl cobinamide phosphate via the enzyme adenosylcobinamide kinase / adenosylcobinamide-phosphate guanylyltransferase [EC:2.7.1.156 and EC 2.7.7.62].
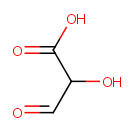
Tartronate semialdehyde (PAMDB000707)
IUPAC:
2-hydroxy-3-oxopropanoic acid
CAS: Not Available
Description: Tartronate semialdehyde is an intermediate in ascorbate and aldarate as well as glyoxylate and dicarboxylate metabolism. It is generated from 2-dehydro-3-deoxy-D-glucarate and 5-dehydro-4-deoxy-D-glucarate via the enzyme 2-dehydro-3-deoxyglucarate aldolase [EC:4.1.2.20].
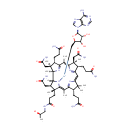
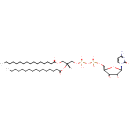
CDP-DG(16:0/16:0) (PAMDB000708)
IUPAC:
{[(2R,3R,5R)-5-(4-amino-2-oxo-1,2-dihydropyrimidin-1-yl)-3,4-dihydroxyoxolan-2-yl]methoxy}({[(2R)-2,3-bis(hexadecanoyloxy)propoxy](hydroxy)phosphoryl}oxy)phosphinic acid
CAS: Not Available
Description: CDP-DG(16:0/16:0) belongs to the family of CDP-diacylglycerols. It is a glycerophospholipid containing a diacylglycerol, with a cytidine diphosphate attached to the oxygen O1 or O2 of the glycerol part. As is the case with diacylglycerols, phosphatidylserines can have many different combinations of fatty acids of varying lengths and saturation attached to the C-1 and C-2 positions. CDP-DG(16:0/16:0), in particular, consists of two hexadecanoyl chain at positions C-1 and C2. In Pseudomonas aeruginosa glycerophospholipid metabolism, The biosynthesis of CDP-diacylglycerol (CDP-DG) involves condensation of phosphatidic acid (PA) and cytidine triphosphate, with elimination of pyrophosphate, catalysed by the enzyme CDP-diacylglycerol synthase. The resulting CDP-diacylglycerol can be utilized immediately for the synthesis of phosphatidylglycerol (PG), and thence cardiolipin (CL), and of phosphatidylinositol (PI). CDP-DG(16:0/16:0) is also a substrate of CDP-diacylglycerol pyrophosphatase. It is involved in CDP-diacylglycerol degradation pathway.
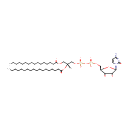
CDP-DG(16:0/18:0) (PAMDB000709)
IUPAC:
{[(2R,3R,5R)-5-(4-amino-2-oxo-1,2-dihydropyrimidin-1-yl)-3,4-dihydroxyoxolan-2-yl]methoxy}({[(2R)-3-(hexadecanoyloxy)-2-(octadecanoyloxy)propoxy](hydroxy)phosphoryl}oxy)phosphinic acid
CAS: Not Available
Description: CDP-DG(16:0/18:0) belongs to the family of CDP-diacylglycerols. It is a glycerophospholipid containing a diacylglycerol, with a cytidine diphosphate attached to the oxygen O1 or O2 of the glycerol part. As is the case with diacylglycerols, phosphatidylserines can have many different combinations of fatty acids of varying lengths and saturation attached to the C-1 and C-2 atoms. CDP-DG(16:0/18:0), in particular, consists of one hexadecanoyl chain to C-1 atom, and one octadecanoyl to the C-2 atom. In Pseudomonas aeruginosa glycerophospholipid metabolism, The biosynthesis of CDP-diacylglycerol (CDP-DG) involves condensation of phosphatidic acid (PA) and cytidine triphosphate, with elimination of pyrophosphate, catalysed by the enzyme CDP-diacylglycerol synthase. The resulting CDP-diacylglycerol can be utilized immediately for the synthesis of phosphatidylglycerol (PG), and thence cardiolipin (CL), and of phosphatidylinositol (PI). CDP-DG(16:0/18:0) is also a substrate of CDP-diacylglycerol pyrophosphatase. It is involved in CDP-diacylglycerol degradation pathway.
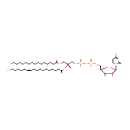
CDP-DG(16:0/18:1(11Z)) (PAMDB000710)
IUPAC:
{[(2R,3R,5R)-5-(4-amino-2-oxo-1,2-dihydropyrimidin-1-yl)-3,4-dihydroxyoxolan-2-yl]methoxy}({[(2R)-3-(hexadecanoyloxy)-2-[(11Z)-octadec-11-enoyloxy]propoxy](hydroxy)phosphoryl}oxy)phosphinic acid
CAS: Not Available
Description: CDP-DG(16:0/18:1(11Z)) belongs to the family of CDP-diacylglycerols. It is a glycerophospholipid containing a diacylglycerol, with a cytidine diphosphate attached to the oxygen O1 or O2 of the glycerol part. As is the case with diacylglycerols, phosphatidylserines can have many different combinations of fatty acids of varying lengths and saturation attached to the C-1 and C-2 atoms. CDP-DG(16:0/18:1(11Z)), in particular, consists of one hexadecanoyl chain to C-1 atom, and one 11Z-octadecenoyl to the C-2 atom. In Pseudomonas aeruginosa glycerophospholipid metabolism, The biosynthesis of CDP-diacylglycerol (CDP-DG) involves condensation of phosphatidic acid (PA) and cytidine triphosphate, with elimination of pyrophosphate, catalysed by the enzyme CDP-diacylglycerol synthase. The resulting CDP-diacylglycerol can be utilized immediately for the synthesis of phosphatidylglycerol (PG), and thence cardiolipin (CL), and of phosphatidylinositol (PI). CDP-DG(16:0/18:1(11Z)) is also a substrate of CDP-diacylglycerol pyrophosphatase. It is involved in CDP-diacylglycerol degradation pathway.
CDP-DG(16:0/18:1(9Z)) (PAMDB000711)
IUPAC:
{[(2R,3R,5R)-5-(4-amino-2-oxo-1,2-dihydropyrimidin-1-yl)-3,4-dihydroxyoxolan-2-yl]methoxy}({[(2R)-3-(hexadecanoyloxy)-2-[(9Z)-octadec-9-enoyloxy]propoxy](hydroxy)phosphoryl}oxy)phosphinic acid
CAS: Not Available
Description: CDP-DG(16:0/18:1(9Z)) belongs to the family of CDP-diacylglycerols. It is a glycerophospholipid containing a diacylglycerol, with a cytidine diphosphate attached to the oxygen O1 or O2 of the glycerol part. As is the case with diacylglycerols, phosphatidylserines can have many different combinations of fatty acids of varying lengths and saturation attached to the C-1 and C-2 atoms. CDP-DG(16:0/18:1(9Z)), in particular, consists of one hexadecanoyl chain to C-1 atom, and one 9Z-octadecenoyl to the C-2 atom. In Pseudomonas aeruginosa glycerophospholipid metabolism, The biosynthesis of CDP-diacylglycerol (CDP-DG) involves condensation of phosphatidic acid (PA) and cytidine triphosphate, with elimination of pyrophosphate, catalysed by the enzyme CDP-diacylglycerol synthase. The resulting CDP-diacylglycerol can be utilized immediately for the synthesis of phosphatidylglycerol (PG), and thence cardiolipin (CL), and of phosphatidylinositol (PI). CDP-DG(16:0/18:1(9Z)) is also a substrate of CDP-diacylglycerol pyrophosphatase. It is involved in CDP-diacylglycerol degradation pathway.
CDP-DG(18:0/16:0) (PAMDB000717)
IUPAC:
{[(2R,3R,5R)-5-(4-amino-2-oxo-1,2-dihydropyrimidin-1-yl)-3,4-dihydroxyoxolan-2-yl]methoxy}({[(2R)-2-(hexadecanoyloxy)-3-(octadecanoyloxy)propoxy](hydroxy)phosphoryl}oxy)phosphinic acid
CAS: Not Available
Description: CDP-DG(18:0/16:0) belongs to the family of CDP-diacylglycerols. It is a glycerophospholipid containing a diacylglycerol, with a cytidine diphosphate attached to the oxygen O1 or O2 of the glycerol part. As is the case with diacylglycerols, phosphatidylserines can have many different combinations of fatty acids of varying lengths and saturation attached to the C-1 and C-2 atoms. CDP-DG(18:0/16:0), in particular, consists of one octadecanoyl chain to C-1 atom, and one hexadecanoyl to the C-2 atom. In Pseudomonas aeruginosa glycerophospholipid metabolism, The biosynthesis of CDP-diacylglycerol (CDP-DG) involves condensation of phosphatidic acid (PA) and cytidine triphosphate, with elimination of pyrophosphate, catalysed by the enzyme CDP-diacylglycerol synthase. The resulting CDP-diacylglycerol can be utilized immediately for the synthesis of phosphatidylglycerol (PG), and thence cardiolipin (CL), and of phosphatidylinositol (PI). CDP-DG(18:0/16:0) is also a substrate of CDP-diacylglycerol pyrophosphatase. It is involved in CDP-diacylglycerol degradation pathway.