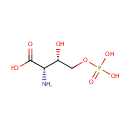
Search Results for compounds
Searching compounds for
returned 4373 results.
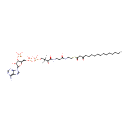
3-Oxohexadecanoyl-CoA (PAMDB000669)
IUPAC:
{[(2R,3S,4R,5R)-5-(6-amino-9H-purin-9-yl)-4-hydroxy-2-({[hydroxy({[hydroxy(3-hydroxy-2,2-dimethyl-3-{[2-({2-[(3-oxohexadecanoyl)sulfanyl]ethyl}carbamoyl)ethyl]carbamoyl}propoxy)phosphoryl]oxy})phosphoryl]oxy}methyl)oxolan-3-yl]oxy}phosphonic acid
CAS: 34619-89-1
Description: 3-Oxohexadecanoyl-CoA has a role in the synthesis and oxidation of fatty acid. It is also involved in fatty acid elongation. Acetyl-CoA is acted upon by the enzyme, acetyl-CoA C-acyltransferase to produce 3-Oxohexadecanoyl-CoA. Since coenzyme A is chemically a thiol, it can react with carboxylic acids to form thioesters, thus functioning as an acyl group carrier. A molecule of coenzyme A carrying an acetyl group is also referred to as acetyl-CoA. When it is not attached to an acyl group it is usually referred to as 'CoASH' or 'HSCoA'.
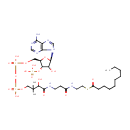
Decanoyl-CoA (N-C10:0CoA) (PAMDB000670)
IUPAC:
{[(2R,3S,4R,5R)-5-(6-amino-9H-purin-9-yl)-2-[({[({3-[(2-{[2-(decanoylsulfanyl)ethyl]carbamoyl}ethyl)carbamoyl]-3-hydroxy-2,2-dimethylpropoxy}(hydroxy)phosphoryl)oxy](hydroxy)phosphoryl}oxy)methyl]-4-hydroxyoxolan-3-yl]oxy}phosphonic acid
CAS: 1264-57-9
Description: Decanoyl-CoA is an intermediate in fatty acid elongationand its formation is from acetyl-CoA. It is also involved in fatty acid metabolism. (KEGG)
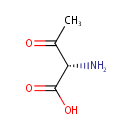
L-2-Amino-3-oxobutanoic acid (PAMDB000671)
IUPAC:
(2S)-2-amino-3-oxobutanoic acid
CAS: Not Available
Description: L-2-Amino-3-oxobutanoic acid or L-2-amino acetic acid is involved in glycine/serine metabolism and is a breakdown product from glycine. It spontaneously decomposes to aminoacetone. Delta-aminolevuliinate synthase is the enzyme that catalyzes the interconversion between glycine and L-2-amino-3-oxobutanoic acid. Glycine C-acetyltransferase is also capable of catalyzing this reaction.
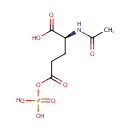
N-Acetyl-L-glutamyl 5-phosphate (PAMDB000672)
IUPAC:
(2S)-2-acetamido-5-oxo-5-(phosphonooxy)pentanoic acid
CAS: 15383-57-0
Description: N-Acetyl-L-glutamyl 5-phosphate is an intermediate in urea cycle and metabolism of amino groups. The enzyme N-acetyl-gamma-glutamyl-phosphate reductase [EC:1.2.1.38] catalyzes the conversion of this metabolite into N-acetyl-L-glutamate 5-semialdehyde. This reaction is irreversible and occurs in the cytoplasm (BiGG database)
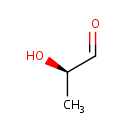
D-Lactaldehyde (PAMDB000673)
IUPAC:
(2R)-2-hydroxypropanal
CAS: 3946-09-6
Description: D- and L-lactaldehyde are also good substrates for aldose reductase. The aldose reductase-catalyzed reduction of methylglyoxal produces 95% acetol, 5% D-lactaldehyde.
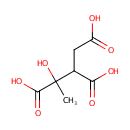
Methylisocitric acid (PAMDB000674)
IUPAC:
1-hydroxy-1-methylpropane-1,2,3-tricarboxylic acid
CAS: Not Available
Description: Methylisocitric acid is a product of bacterial metabolism in the gut. It can be produced by 2-methylisocitrate lyase and by 2-methylisocitrate dehydratase.
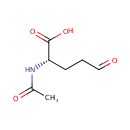
N-Acetyl-L-glutamate 5-semialdehyde (PAMDB000675)
IUPAC:
(2S)-2-acetamido-5-oxopentanoic acid
CAS: 13074-21-0
Description: N-Acetyl-L-glutamate 5-semialdehyde is an intermediate in Urea cycle and metabolism of amino groups. N-Acetyl-L-glutamate 5-semialdehyde is the
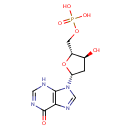
DIMP (PAMDB000681)
IUPAC:
{[(2R,3S,5R)-3-hydroxy-5-(6-oxo-6,9-dihydro-3H-purin-9-yl)oxolan-2-yl]methoxy}phosphonic acid
CAS: 3393-18-8
Description: dIMP is a deoxyribonucleoside and is considered a derivative of the nucleoside inosine, differing from the latter by the replacement of a hydroxyl group (-OH) by hydrogen (-H) at the 2' position of its ribose sugar moiety. The hydrolytic deamination of dAMP residues in DNA yields dIMP residues. The deamination of adenine residues in DNA generates hypoxanthine, which is mutagenic since it can pair not only with thymine but also with cytosine and therefore would result in A-T to G-C transitions after DNA replication. Hypoxanthine DNA glycosylase (EC 3.2.2.15) excises hypoxanthine from DNA containing dIMP residues in cells. (PMID: 10684927, 8016081)
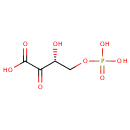
2-Oxo-3-hydroxy-4-phosphobutanoic acid (PAMDB000690)
IUPAC:
(3R)-3-hydroxy-2-oxo-4-(phosphonooxy)butanoic acid
CAS: Not Available
Description: 2-Oxo-3-hydroxy-4-phosphobutanoic acid is involved in the interconversion of O-phospho-4-hydroxy-L-threonine. This reaction is catalyzed by phosphoserine aminotransferase 1. These amino acid derivatives are sometimes considered to be part of the vitamin B6 pathway.
O-Phospho-4-hydroxy-L-threonine (PAMDB000691)
IUPAC:
(2S,3S)-2-amino-3-hydroxy-4-(phosphonooxy)butanoic acid
CAS: Not Available
Description: O-Phospho-4-hydroxy-L-threonine is involved in the vitamin B6 metabolism system. O-Phospho-4-hydroxy-L-threonine is a precursor for pyridoxine. O-Phospho-4-hydroxy-L-threonine can be converted to 4-hydroxy-L-threonine and 2-Amino-3-oxo-4-phosphonooxybutyrate by threonine synthase [EC:4.2.3.1] and 4-hydroxythreonine-4-phosphate dehydrogenase [EC:1.1.1.262], respectively.