Search Results for compounds
Searching compounds for
returned 4373 results.
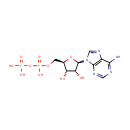
ADP (PAMDB000345)
IUPAC:
[({[(2R,3S,4R,5R)-5-(6-amino-9H-purin-9-yl)-3,4-dihydroxyoxolan-2-yl]methoxy}(hydroxy)phosphoryl)oxy]phosphonic acid
CAS: 58-64-0
Description: Adenosine diphosphate, abbreviated ADP, is a nucleotide. It is an ester of pyrophosphoric acid with the nucleotide adenine. ADP consists of the pyrophosphate group, the pentose sugar ribose, and the nucleobase adenine.
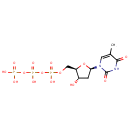
Thymidine 5'-triphosphate (PAMDB000346)
IUPAC:
{[hydroxy({[hydroxy({[(2R,3S,5R)-3-hydroxy-5-(5-methyl-2,4-dioxo-1,2,3,4-tetrahydropyrimidin-1-yl)oxolan-2-yl]methoxy})phosphoryl]oxy})phosphoryl]oxy}phosphonic acid
CAS: 365-08-2
Description: Thymidine triphosphate or TTP is one of the four nucleoside triphosphates that make up DNA. It can be used by DNA ligase to create overlapping "sticky ends" so that protruding ends of opened microbial plasmids maybe closed up.
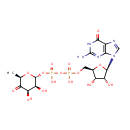
GDP-4-Dehydro-6-deoxy-D-mannose (PAMDB000347)
IUPAC:
[({[(2R,3S,4R,5R)-5-(2-amino-6-oxo-6,9-dihydro-1H-purin-9-yl)-3,4-dihydroxyoxolan-2-yl]methoxy}(hydroxy)phosphoryl)oxy]({[(2R,3S,4R,6R)-3,4-dihydroxy-6-methyl-5-oxooxan-2-yl]oxy})phosphinic acid
CAS: 18186-48-6
Description: GDP-4-Dehydro-6-deoxy-D-mannose is an intermediate in fructose and mannose metabolism. GDP-4-Dehydro-6-deoxy-D-mannose is generated by GDP-D-mannose-4,6-dehydratase (GMD). This compound is then converted by the FX protein (GDP-4-keto-6-D-deoxymannose epimerase/GDP-4-keto-6-L-galactose reductase) to GDP-L-fucose. . It is also involved in amino sugar and nucleotide sugar metabolism. (KEGG)
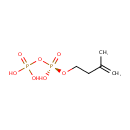
Isopentenyl pyrophosphate (PAMDB000348)
IUPAC:
({hydroxy[(3-methylbut-3-en-1-yl)oxy]phosphoryl}oxy)phosphonic acid
CAS: 358-71-4
Description: Isopentenyl pyrophosphate, IPP or isopentenyl diphosphate, is an intermediate in the HMG-CoA reductase pathway used by organisms in the biosynthesis of terpenes and terpenoids. IPP is formed from Mevalonate-5-pyrophosphate, in a reaction catalyzed by the enzyme mevalonate-5-pyrophosphate decarboxylase. (wikipedia)
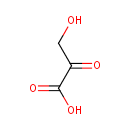
Hydroxypyruvic acid (PAMDB000351)
IUPAC:
3-hydroxy-2-oxopropanoic acid
CAS: 1113-60-6
Description: Hydroxypyruvic acid is an intermediate in the metabolism of Glycine, serine and threonine. It is a substrate for Serine--pyruvate aminotransferase and Glyoxylate reductase/hydroxypyruvate reductase.
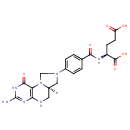
5,10-Methylene-THF (PAMDB000353)
IUPAC:
(2S)-2-({4-[(6aR)-3-amino-1-oxo-1H,2H,5H,6H,6aH,7H,8H,9H-imidazolidino[1,5-f]pteridin-8-yl]phenyl}formamido)pentanedioic acid
CAS: 31690-11-6
Description: 5,10-Methylene-THF is an intermediate in the metabolism of methane and the metabolism of nitrogen. 5,10-Methylenetetrahydrofolate (5,10-CH2-THF) is the substrate used by the enzyme methylenetetrahydrofolate reductase (MTHFR) to generate 5-methyltetrahydrofolate (5-MTHF, or levomefolic acid). 5,10-CH2-THF can also be used as a coenzyme in the biosynthesis of thymidine. More specifically it is the C1-donor in the reactions catalyzed by thymidylate synthase and thymidylate synthase (FAD). It also acts as a coenzyme in the synthesis of serine from glycine via the enzyme serine hydroxymethyl transferase. Methylenetetrahydrofolate reductase catalyzes the conversion of 5,10-methylenetetrahydrofolate to 5-methyltetrahydrofolate, a cosubstrate for homocysteine remethylation to methionine.
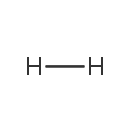
Hydrogen (gas) (PAMDB000355)
IUPAC:
Not Available
CAS: 1333-74-0
Description: Hydrogen is a colorless, odorless, nonmetallic, tasteless, highly flammable diatomic gas with the molecular formula H2. With an atomic weight of 1.00794, hydrogen is the lightest element. Besides the common H1 isotope, hydrogen exists as the stable isotope Deuterium and the unstable, radioactive isotope Tritium. Hydrogen is the most abundant of the chemical elements, constituting roughly 75% of the universe's elemental mass. Hydrogen can form compounds with most elements and is present in water and most organic compounds. It plays a particularly important role in acid-base chemistry, in which many reactions involve the exchange of protons between soluble molecules. Oxidation of hydrogen, in the sense of removing its electron, formally gives H+, containing no electrons and a nucleus which is usually composed of one proton. That is why H+ is often called a proton. This species is central to discussion of acids. Under the Bronsted-Lowry theory, acids are proton donors, while bases are proton acceptors. The transport of protons or hydrogen ions across the membrane(ie the creation of a proton gradient) is critical to the generation of energy (ATP) for all living cells.
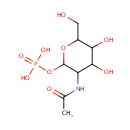
N-Acetyl-glucosamine 1-phosphate (PAMDB000357)
IUPAC:
{[3-acetamido-4,5-dihydroxy-6-(hydroxymethyl)oxan-2-yl]oxy}phosphonic acid
CAS: Not Available
Description: N-acetyl-glucosamine 1-phosphate is a member of the chemical class known as N-acetyl-alpha-hexosamine-1-phosphates. These are carbohydrates derivative which is structurally characterized by the presence of an hexosamine bearing a phosphate group attached to the C1 carbon atom, and another moeity N-linked through the amine group.
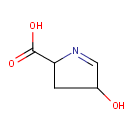
Pyrroline hydroxycarboxylic acid (PAMDB000359)
IUPAC:
4-hydroxy-3,4-dihydro-2H-pyrrole-2-carboxylic acid
CAS: 22573-88-2
Description: Pyrroline hydroxycarboxylic acid is an intermediate in arginine and proline metabolism. It is converted to trans-4-hydroxy-L-proline via pyrroline-5-carboxylate reductase, and to L-erythro-4-Hydroxyglutamate via delta-1-pyrroline-5-carboxylate dehydrogenase. (KEGG)
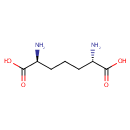
Diaminopimelic acid (PAMDB000360)
IUPAC:
(2S,6S)-2,6-diaminoheptanedioic acid
CAS: 583-93-7
Description: Diaminopimelic acid (DAP) is an amino acid, representing an epsilon-carboxy derivative of lysine. DAP found in the cell walls of Pseudomonas aeruginosa and is a component of peptidoglycan of Gram-negative bacteria.