|
Record Information |
|---|
| Version |
1.0 |
|---|
| Update Date |
1/22/2018 11:54:54 AM |
|---|
|
Metabolite ID | PAMDB120530 |
|---|
|
Identification |
|---|
| Name: |
estrone-sulfate |
|---|
| Description: | Estrone sulfate is a sulfated estrone derivative. Estrone sulfate acts as a long-lived reservoir that can be converted as needed to the more active estradiol (from estrone via 17 beta-hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase). Estrone Sulfate (E1S) is the most abundant circulating estrogen in non-pregnant women as well as normal men. Estrone is primarily synthesized from estrone sulfate. Estrone is an estrogenic hormone secreted by the ovaries and adipose tissues. Estrone is one of the three estrogens found in humans. The other two are estriol and estradiol. Estrone is the least prevalent of the three. Estradiol plays a critical role on reproductive and sexual functioning in women and it also affects other organs including the bones. Estriol is an estrogen that is prevalent primarily during pregnancy. |
|---|
|
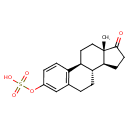
Structure |
|
|---|
| Synonyms: | - Estrone-3-sulfateevexoestrone sulphate
|
|---|
|
Chemical Formula: |
C18H21O5S |
|---|
| Average Molecular Weight: |
349.421 |
|---|
| Monoisotopic Molecular
Weight: |
350.1188 |
|---|
| InChI Key: |
JKKFKPJIXZFSSB-UHFFFAOYSA-M |
|---|
| InChI: | InChI=1S/C18H22O5S/c1-18-9-8-14-13-5-3-12(23-24(20,21)22)10-11(13)2-4-15(14)16(18)6-7-17(18)19/h3,5,10,14-16H,2,4,6-9H2,1H3,(H,20,21,22)/p-1 |
|---|
| CAS
number: |
481-97-0 |
|---|
| IUPAC Name: | [(1S,10R,11S,15S)-15-methyl-14-oxotetracyclo[8.7.0.0?,??0??,???heptadeca-2(7),3,5-trien-5-yl]oxidanesulfonic acid |
|---|
|
Traditional IUPAC Name: |
Ogen |
|---|
| SMILES: | CC23(CCC1(C4(C(CCC1C2CCC(=O)3)=CC(OS([O-])(=O)=O)=CC=4))) |
|---|
|
Chemical Taxonomy |
|---|
|
Taxonomy Description | This compound belongs to the class of organic compounds known as sulfated steroids. These are sterol lipids containing a sulfate group attached to the steroid skeleton. |
|---|
|
Kingdom |
Organic compounds |
|---|
| Super Class | Lipids and lipid-like molecules |
|---|
|
Class |
Steroids and steroid derivatives |
|---|
| Sub Class | Sulfated steroids |
|---|
|
Direct Parent |
Sulfated steroids |
|---|
| Alternative Parents |
|
|---|
| Substituents |
- Sulfated steroid skeleton
- Estrane-skeleton
- 17-oxosteroid
- Oxosteroid
- Phenanthrene
- Arylsulfate
- Tetralin
- Benzenoid
- Sulfuric acid ester
- Sulfuric acid monoester
- Sulfate-ester
- Organic sulfuric acid or derivatives
- Ketone
- Hydrocarbon derivative
- Organic oxide
- Organooxygen compound
- Carbonyl group
- Organic oxygen compound
- Aromatic homopolycyclic compound
|
|---|
| Molecular Framework |
Aromatic homopolycyclic compounds |
|---|
| External Descriptors |
|
|---|
|
Physical Properties |
|---|
| State: |
Solid |
|---|
| Charge: | Not Available |
|---|
|
Melting point: |
254.5 °C |
|---|
| Experimental Properties: |
| Property | Value | Reference |
|---|
| Melting Point | 254.5 °C | Not Available | | Boiling Point | Not Available | Not Available | | Water Solubility | Not Available | Not Available | | LogP | Not Available | Not Available |
|
|---|
| Predicted Properties |
|
|---|
|
Biological Properties |
|---|
| Cellular Locations: |
Not Available |
|---|
| Reactions: | |
|---|
|
Pathways: |
|
|---|
|
Spectra |
|---|
| Spectra: |
|
|---|
|
References |
|---|
| References: |
- Matsushima S, Maeda K, Kondo C, Hirano M, Sasaki M, Suzuki H, Sugiyama Y: Identification of the hepatic efflux transporters of organic anions using double-transfected Madin-Darby canine kidney II cells expressing human organic anion-transporting polypeptide 1B1 (OATP1B1)/multidrug resistance-associated protein 2, OATP1B1/multidrug resistance 1, and OATP1B1/breast cancer resistance protein. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 2005 Sep;314(3):1059-67. Epub 2005 May 18. [15901800 ]
- Satoh H, Yamashita F, Tsujimoto M, Murakami H, Koyabu N, Ohtani H, Sawada Y: Citrus juices inhibit the function of human organic anion-transporting polypeptide OATP-B. Drug Metab Dispos. 2005 Apr;33(4):518-23. Epub 2005 Jan 7. [15640378 ]
- Craddock AL, Love MW, Daniel RW, Kirby LC, Walters HC, Wong MH, Dawson PA: Expression and transport properties of the human ileal and renal sodium-dependent bile acid transporter. Am J Physiol. 1998 Jan;274(1 Pt 1):G157-69. [9458785 ]
- Choi HY, Hobkirk R: Chromatofocusing of mammalian estrone sulfate sulfohydrolase activity. J Steroid Biochem. 1986 Dec;25(6):985-9. [3467142 ]
- Sherstha R, McKinley C, Russ P, Scherzinger A, Bronner T, Showalter R, Everson GT: Postmenopausal estrogen therapy selectively stimulates hepatic enlargement in women with autosomal dominant polycystic kidney disease. Hepatology. 1997 Nov;26(5):1282-6. [9362373 ]
- Gniot-Szulzycka J, Jakubowska A: Oestrone sulphate sulphohydrolase activity in nuclear envelopes from human placenta cell nuclei. Acta Biochim Pol. 1991;38(1):7-16. [1796709 ]
- Fredricsson B, Carlstrom K, Kjessler B, Lindstedt J, Ploen L, Ritzen M, de la Torre B: Incomplete androgen insensitivity: asymmetry in morphology and steroid profile and metabolism of the gonads. An analysis of a case. Acta Endocrinol (Copenh). 1985 Dec;110(4):564-71. [4090916 ]
- Fuchikami H, Satoh H, Tsujimoto M, Ohdo S, Ohtani H, Sawada Y: Effects of herbal extracts on the function of human organic anion-transporting polypeptide OATP-B. Drug Metab Dispos. 2006 Apr;34(4):577-82. Epub 2006 Jan 13. [16415120 ]
- Milewich L, Sontheimer RD, Herndon JH Jr: Steroid sulfatase activity in epidermis of acne-prone and non-acne-prone skin of patients with acne vulgaris. Arch Dermatol. 1990 Oct;126(10):1312-4. [2145810 ]
- Stewart JD, Lou Y, Squires EJ, Coussens PM: Using human microarrays to identify differentially expressed genes associated with increased steroidogenesis in boars. Anim Biotechnol. 2005;16(2):139-51. [16335808 ]
- Ekaratanawong S, Anzai N, Jutabha P, Miyazaki H, Noshiro R, Takeda M, Kanai Y, Sophasan S, Endou H: Human organic anion transporter 4 is a renal apical organic anion/dicarboxylate exchanger in the proximal tubules. J Pharmacol Sci. 2004 Mar;94(3):297-304. [15037815 ]
- Creidi P, Faivre B, Agache P, Richard E, Haudiquet V, Sauvanet JP: Effect of a conjugated oestrogen (Premarin) cream on ageing facial skin. A comparative study with a placebo cream. Maturitas. 1994 Oct;19(3):211-23. [7799828 ]
- Bomba-Opon DA, Niesluchowska-Frydrych B, Szucka-May H, Kaminski P, Marianowski L: [Effects of oral administration of estrogen replacement therapy in surgical menopause] Ginekol Pol. 2001 Dec;72(12A):1377-82. [11883282 ]
- AvRuskin TW, Krishnan N, Juan CS: Congenital adrenal hypoplasia and male pseudohermaphroditism due to DAX1 mutation, SF1 mutation or neither: a patient report. J Pediatr Endocrinol Metab. 2004 Aug;17(8):1125-32. [15379426 ]
- Michaud DS, Manson JE, Spiegelman D, Barbieri RL, Sepkovic DW, Bradlow HL, Hankinson SE: Reproducibility of plasma and urinary sex hormone levels in premenopausal women over a one-year period. Cancer Epidemiol Biomarkers Prev. 1999 Dec;8(12):1059-64. [10613337 ]
|
|---|
| Synthesis Reference: |
Price, Wm. H. Alkali metal estrone sulfates. (1959), US 2917522 19591215 Patent language unavailable. |
|---|
| Material Safety Data Sheet (MSDS) |
Not Available |
|---|
|
Links |
|---|
| External Links: |
|
|---|