|
Record Information |
|---|
| Version |
1.0 |
|---|
| Update Date |
1/22/2018 11:54:54 AM |
|---|
|
Metabolite ID | PAMDB120516 |
|---|
|
Identification |
|---|
| Name: |
biliverdin-IX-α |
|---|
| Description: | Dicarboxylate anion of biliverdin; major species at pH 7.3. |
|---|
|
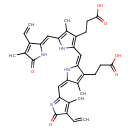
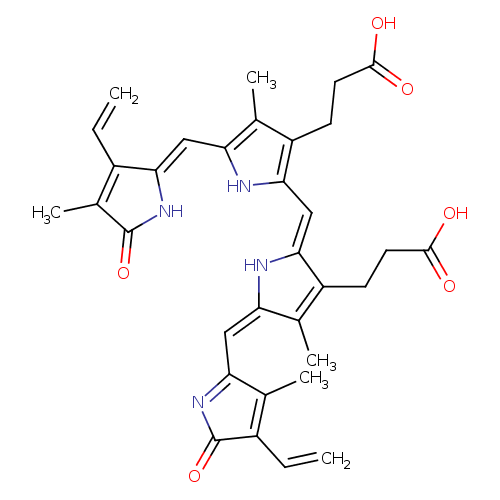
Structure |
|
|---|
| Synonyms: | - biliverdin
- biliverdin dianion
|
|---|
|
Chemical Formula: |
C33H32N4O6 |
|---|
| Average Molecular Weight: |
580.639 |
|---|
| Monoisotopic Molecular
Weight: |
582.24786 |
|---|
| InChI Key: |
QBUVFDKTZJNUPP-BBROENKCSA-L |
|---|
| InChI: | InChI=1S/C33H34N4O6/c1-7-20-19(6)32(42)37-27(20)14-25-18(5)23(10-12-31(40)41)29(35-25)15-28-22(9-11-30(38)39)17(4)24(34-28)13-26-16(3)21(8-2)33(43)36-26/h7-8,13-15,35H,1-2,9-12H2,3-6H3,(H,36,43)(H,37,42)(H,38,39)(H,40,41)/p-2/b26-13-,27-14-,28-15- |
|---|
| CAS
number: |
114-25-0 |
|---|
| IUPAC Name: | 3-(2-{[(2Z,5E)-3-(2-carboxyethyl)-5-[(3-ethenyl-4-methyl-2-oxo-2H-pyrrol-5-yl)methylidene]-4-methyl-2,5-dihydro-1H-pyrrol-2-ylidene]methyl}-5-{[(2Z)-3-ethenyl-4-methyl-5-oxo-2,5-dihydro-1H-pyrrol-2-ylidene]methyl}-4-methyl-1H-pyrrol-3-yl)propanoic acid |
|---|
|
Traditional IUPAC Name: |
3-(2-{[(2Z,5E)-3-(2-carboxyethyl)-5-[(4-ethenyl-3-methyl-5-oxopyrrol-2-yl)methylidene]-4-methyl-1H-pyrrol-2-ylidene]methyl}-5-{[(2Z)-3-ethenyl-4-methyl-5-oxo-1H-pyrrol-2-ylidene]methyl}-4-methyl-1H-pyrrol-3-yl)propanoic acid |
|---|
| SMILES: | C=CC1(=C(C)C(NC1=CC4(=C(C)C(CCC(=O)[O-])=C(C=C2(C(CCC(=O)[O-])=C(C)C(=N2)C=C3(C(C)=C(C=C)C(=O)N3)))N4))=O) |
|---|
|
Chemical Taxonomy |
|---|
|
Taxonomy Description | This compound belongs to the class of chemical entities known as bilirubins. These are organic compounds containing a dicarboxylic acyclic tetrapyrrole derivative. |
|---|
|
Kingdom |
Chemical entities |
|---|
| Super Class | Organic compounds |
|---|
|
Class |
Organoheterocyclic compounds |
|---|
| Sub Class | Tetrapyrroles and derivatives |
|---|
|
Direct Parent |
Bilirubins |
|---|
| Alternative Parents |
|
|---|
| Substituents |
- Bilirubin skeleton
- Dipyrrin
- Dicarboxylic acid or derivatives
- Substituted pyrrole
- Pyrrole
- Pyrroline
- Heteroaromatic compound
- Carboxamide group
- Lactam
- N-acylimine
- Secondary carboxylic acid amide
- Azacycle
- Organic 1,3-dipolar compound
- Carboxylic acid derivative
- Carboxylic acid
- Propargyl-type 1,3-dipolar organic compound
- Hydrocarbon derivative
- Organopnictogen compound
- Organic oxygen compound
- Carbonyl group
- Organonitrogen compound
- Organooxygen compound
- Organic nitrogen compound
- Organic oxide
- Aromatic heteromonocyclic compound
|
|---|
| Molecular Framework |
Aromatic heteromonocyclic compounds |
|---|
| External Descriptors |
Not Available |
|---|
|
Physical Properties |
|---|
| State: |
Solid |
|---|
| Charge: | -2 |
|---|
|
Melting point: |
> 300 °C |
|---|
| Experimental Properties: |
| Property | Value | Reference |
|---|
| Melting Point | > 300 °C | Not Available | | Boiling Point | Not Available | Not Available | | Water Solubility | Not Available | Not Available | | LogP | Not Available | Not Available |
|
|---|
| Predicted Properties |
|
|---|
|
Biological Properties |
|---|
| Cellular Locations: |
Not Available |
|---|
| Reactions: | |
|---|
|
Pathways: |
|
|---|
|
Spectra |
|---|
| Spectra: |
|
|---|
|
References |
|---|
| References: |
- Sreekumar A, Poisson LM, Rajendiran TM, Khan AP, Cao Q, Yu J, Laxman B, Mehra R, Lonigro RJ, Li Y, Nyati MK, Ahsan A, Kalyana-Sundaram S, Han B, Cao X, Byun J, Omenn GS, Ghosh D, Pennathur S, Alexander DC, Berger A, Shuster JR, Wei JT, Varambally S, Beecher C, Chinnaiyan AM: Metabolomic profiles delineate potential role for sarcosine in prostate cancer progression. Nature. 2009 Feb 12;457(7231):910-4. [19212411 ]
- Briz O, Macias RI, Serrano MA, Gonzalez-Gallego J, Bayon JE, Marin JJ: Excretion of foetal bilirubin by the rat placenta-maternal liver tandem. Placenta. 2003 May;24(5):462-72. [12744922 ]
- Trull FR, Ibars O, Lightner DA: Conformation inversion of bilirubin formed by reduction of the biliverdin-human serum albumin complex: evidence from circular dichroism. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1992 Nov 1;298(2):710-4. [1416999 ]
- Kunikata T, Itoh S, Ozaki T, Kondo M, Isobe K, Onishi S: Formation of propentdyopents and biliverdin, oxidized metabolites of bilirubin, in infants receiving oxygen therapy. Pediatr Int. 2000 Aug;42(4):331-6. [10986860 ]
- Odrcich MJ, Graham CH, Kimura KA, McLaughlin BE, Marks GS, Nakatsu K, Brien JF: Heme oxygenase and nitric oxide synthase in the placenta of the guinea-pig during gestation. Placenta. 1998 Sep;19(7):509-16. [9778124 ]
- Poon HF, Calabrese V, Scapagnini G, Butterfield DA: Free radicals: key to brain aging and heme oxygenase as a cellular response to oxidative stress. J Gerontol A Biol Sci Med Sci. 2004 May;59(5):478-93. [15123759 ]
- Beruter J, Colombo JP, Schlunegger UP: Isolation and identification of the urinary pigment uroerythrin. Eur J Biochem. 1975 Aug 1;56(1):239-44. [1175621 ]
- Chrastil J: Spectrophotometric determination of cysteine and cystine in urine. Analyst. 1990 Oct;115(10):1383-4. [2270876 ]
|
|---|
| Synthesis Reference: |
Mora, Maria E.; Bari, Sara E.; Awruch, Josefina; Delfino, Jose M. On how the conformation of biliverdins influences their reduction to bilirubins: A biological and molecular modeling study. Bioorganic & Medicinal Chemistry (2003), 11(21), 4661-467 |
|---|
| Material Safety Data Sheet (MSDS) |
Not Available |
|---|
|
Links |
|---|
| External Links: |
|
|---|