|
Record Information |
|---|
| Version |
1.0 |
|---|
| Update Date |
1/22/2018 11:54:54 AM |
|---|
|
Metabolite ID | PAMDB120223 |
|---|
|
Identification |
|---|
| Name: |
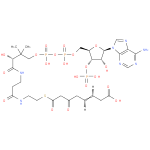
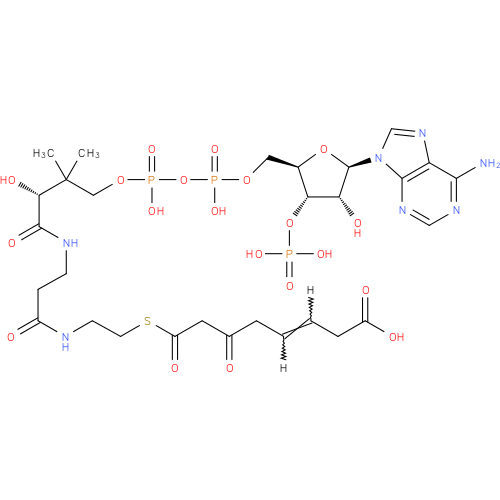
3-oxo-5,6-didehydrosuberyl-CoA |
|---|
| Description: | An acyl-CoA that results from the formal condensation of the thiol group of coenzyme A with the carboxy group of 3-oxo-5,6-dehydrosuberic acid. |
|---|
|
Structure |
|
|---|
| Synonyms: | - (5Z)-7-carboxy-3-oxohept-5-enoyl-CoA
|
|---|
|
Chemical Formula: |
C29H39N7O20P3S |
|---|
| Average Molecular Weight: |
930.643 |
|---|
| Monoisotopic Molecular
Weight: |
935.1575 |
|---|
| InChI Key: |
IFFFDKYRRUVOFP-KIOIQADTSA-I |
|---|
| InChI: | InChI=1S/C29H44N7O20P3S/c1-29(2,24(43)27(44)32-8-7-18(38)31-9-10-60-20(41)11-16(37)5-3-4-6-19(39)40)13-53-59(50,51)56-58(48,49)52-12-17-23(55-57(45,46)47)22(42)28(54-17)36-15-35-21-25(30)33-14-34-26(21)36/h3-4,14-15,17,22-24,28,42-43H,5-13H2,1-2H3,(H,31,38)(H,32,44)(H,39,40)(H,48,49)(H,50,51)(H2,30,33,34)(H2,45,46,47)/p-5/b4-3-/t17-,22-,23-,24+,28-/m1/s1 |
|---|
| CAS
number: |
Not Available |
|---|
| IUPAC Name: | Not Available |
|---|
|
Traditional IUPAC Name: |
Not Available |
|---|
| SMILES: | CC(C)(C(O)C(=O)NCCC(=O)NCCSC(=O)CC(CC=CCC(=O)[O-])=O)COP(=O)(OP(=O)(OCC1(C(OP([O-])(=O)[O-])C(O)C(O1)N3(C2(=C(C(N)=NC=N2)N=C3))))[O-])[O-] |
|---|
|
Chemical Taxonomy |
|---|
|
Taxonomy Description | This compound belongs to the class of organic compounds known as 3-oxo-acyl coas. These are organic compounds containing a 3-oxo acylated coenzyme A derivative. |
|---|
|
Kingdom |
Organic compounds |
|---|
| Super Class | Lipids and lipid-like molecules |
|---|
|
Class |
Fatty Acyls |
|---|
| Sub Class | Fatty acyl thioesters |
|---|
|
Direct Parent |
3-oxo-acyl CoAs |
|---|
| Alternative Parents |
|
|---|
| Substituents |
- Coenzyme a or derivatives
- Purine ribonucleoside 3',5'-bisphosphate
- Purine ribonucleoside bisphosphate
- Purine ribonucleoside diphosphate
- Pentose phosphate
- Pentose-5-phosphate
- Ribonucleoside 3'-phosphate
- Beta amino acid or derivatives
- Glycosyl compound
- N-glycosyl compound
- 6-aminopurine
- Monosaccharide phosphate
- Organic pyrophosphate
- Imidazopyrimidine
- Purine
- Medium-chain fatty acid
- Aminopyrimidine
- Hydroxy fatty acid
- Fatty acid
- Fatty amide
- Imidolactam
- Monosaccharide
- N-acyl-amine
- N-substituted imidazole
- Organic phosphoric acid derivative
- Alkyl phosphate
- Phosphoric acid ester
- 1,3-dicarbonyl compound
- Pyrimidine
- Unsaturated fatty acid
- Imidazole
- Heteroaromatic compound
- Azole
- Oxolane
- Amino acid
- Carbothioic s-ester
- Ketone
- Carboxamide group
- Amino acid or derivatives
- Carboxylic acid salt
- Thiocarboxylic acid ester
- Secondary alcohol
- Secondary carboxylic acid amide
- Sulfenyl compound
- Carboxylic acid
- Carboxylic acid derivative
- Oxacycle
- Organoheterocyclic compound
- Monocarboxylic acid or derivatives
- Azacycle
- Thiocarboxylic acid or derivatives
- Carbonyl group
- Organopnictogen compound
- Organic nitrogen compound
- Alcohol
- Primary amine
- Organic oxide
- Amine
- Hydrocarbon derivative
- Organonitrogen compound
- Organooxygen compound
- Organosulfur compound
- Organic oxygen compound
- Organic anion
- Aromatic heteropolycyclic compound
|
|---|
| Molecular Framework |
Aromatic heteropolycyclic compounds |
|---|
| External Descriptors |
- a small molecule (CPD0-2364)
|
|---|
|
Physical Properties |
|---|
| State: |
Not Available |
|---|
| Charge: | 0 |
|---|
|
Melting point: |
Not Available |
|---|
| Experimental Properties: |
Not Available |
|---|
| Predicted Properties |
|
|---|
|
Biological Properties |
|---|
| Cellular Locations: |
Not Available |
|---|
| Reactions: | |
|---|
|
Pathways: |
- phenylacetate degradation I (aerobic)PWY0-321
|
|---|
|
Spectra |
|---|
| Spectra: |
Not Available |
|---|
|
References |
|---|
| References: |
- Teufel R, Mascaraque V, Ismail W, Voss M, Perera J, Eisenreich W, Haehnel W, Fuchs G (2010)Bacterial phenylalanine and phenylacetate catabolic pathway revealed. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America 107, Pubmed: 20660314
- Teufel R, Gantert C, Voss M, Eisenreich W, Haehnel W, Fuchs G (2011)Studies on the mechanism of ring hydrolysis in phenylacetate degradation: a metabolic branching point. The Journal of biological chemistry 286, Pubmed: 21296885
|
|---|
| Synthesis Reference: |
Not Available |
|---|
| Material Safety Data Sheet (MSDS) |
Not Available |
|---|
|
Links |
|---|
| External Links: |
|
|---|