|
Record Information |
|---|
| Version |
1.0 |
|---|
| Update Date |
1/22/2018 11:54:54 AM |
|---|
|
Metabolite ID | PAMDB120185 |
|---|
|
Identification |
|---|
| Name: |
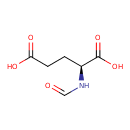
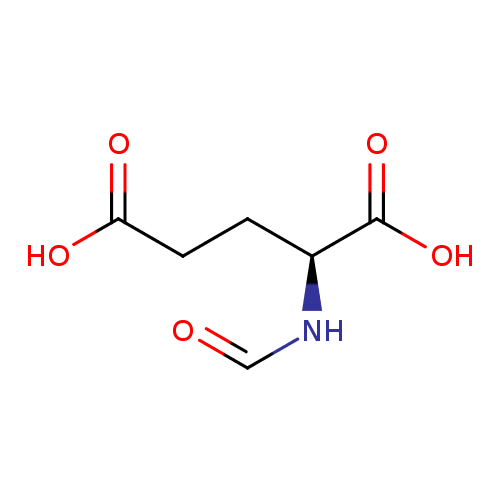
N-formyl-L-glutamate |
|---|
| Description: | A doubly-charged N-acyl-L-α-amino acid anion resulting from deprotonation of both carboxy groups of N-formyl-L-glutamic acid. |
|---|
|
Structure |
|
|---|
| Synonyms: | - (2S)-2-(formylamino)pentanedioate
- N-formyl-L-glutamate
|
|---|
|
Chemical Formula: |
C6H7NO5 |
|---|
| Average Molecular Weight: |
173.125 |
|---|
| Monoisotopic Molecular
Weight: |
175.04807 |
|---|
| InChI Key: |
ADZLWSMFHHHOBV-BYPYZUCNSA-L |
|---|
| InChI: | InChI=1S/C6H9NO5/c8-3-7-4(6(11)12)1-2-5(9)10/h3-4H,1-2H2,(H,7,8)(H,9,10)(H,11,12)/p-2/t4-/m0/s1 |
|---|
| CAS
number: |
1681-96-5 |
|---|
| IUPAC Name: | (2S)-2-formamidopentanedioate |
|---|
|
Traditional IUPAC Name: |
N-formyl-L-glutamic acid |
|---|
| SMILES: | C(=O)NC(CCC(=O)[O-])C(=O)[O-] |
|---|
|
Chemical Taxonomy |
|---|
|
Taxonomy Description | This compound belongs to the class of chemical entities known as glutamic acid and derivatives. These are compounds containing glutamic acid or a derivative thereof resulting from reaction of glutamic acid at the amino group or the carboxy group, or from the replacement of any hydrogen of glycine by a heteroatom. |
|---|
|
Kingdom |
Chemical entities |
|---|
| Super Class | Organic compounds |
|---|
|
Class |
Organic acids and derivatives |
|---|
| Sub Class | Carboxylic acids and derivatives |
|---|
|
Direct Parent |
Glutamic acid and derivatives |
|---|
| Alternative Parents |
|
|---|
| Substituents |
- Glutamic acid or derivatives
- N-acyl-l-alpha-amino acid
- N-formyl-alpha-amino acid
- N-formyl-alpha amino acid or derivatives
- Dicarboxylic acid or derivatives
- Fatty acid
- Secondary carboxylic acid amide
- Carboxamide group
- Carboxylic acid
- Organopnictogen compound
- Carbonyl group
- Organooxygen compound
- Organonitrogen compound
- Organic oxygen compound
- Organic nitrogen compound
- Hydrocarbon derivative
- Organic oxide
- Aliphatic acyclic compound
|
|---|
| Molecular Framework |
Aliphatic acyclic compounds |
|---|
| External Descriptors |
|
|---|
|
Physical Properties |
|---|
| State: |
Solid |
|---|
| Charge: | -2 |
|---|
|
Melting point: |
Not Available |
|---|
| Experimental Properties: |
| Property | Value | Reference |
|---|
| Melting Point | Not Available | Not Available | | Boiling Point | Not Available | Not Available | | Water Solubility | Not Available | Not Available | | LogP | Not Available | Not Available |
|
|---|
| Predicted Properties |
|
|---|
|
Biological Properties |
|---|
| Cellular Locations: |
Not Available |
|---|
| Reactions: | |
|---|
|
Pathways: |
|
|---|
|
Spectra |
|---|
| Spectra: |
Not Available |
|---|
|
References |
|---|
| References: |
- Martí-Arbona R, Xu C, Steele S, Weeks A, Kuty GF, Seibert CM, Raushel FM (2006)Annotating enzymes of unknown function: N-formimino-L-glutamate deiminase is a member of the amidohydrolase superfamily. Biochemistry 45, Pubmed: 16475788
- Coote JG, Hassall H (1973)The degradation of L-histidine, imidazolyl-L-lactate and imidazolylpropionate by Pseudomonas testosteroni. The Biochemical journal 132, Pubmed: 4146796
- Haas D, Leisinger T (1975)N-acetylglutamate 5-phosphotransferase of Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Catalytic and regulatory properties. European journal of biochemistry 52, Pubmed: 240684
- Hu L, Mulfinger LM, Phillips AT (1987)Purification and properties of formylglutamate amidohydrolase from Pseudomonas putida. Journal of bacteriology 169, Pubmed: 3308850
- Miyake M, Innami T, Kakimoto Y (1983)A beta-citryl-L-glutamate-hydrolysing enzyme in rat testes. Biochimica et biophysica acta 760, Pubmed: 6414521
|
|---|
| Synthesis Reference: |
Borek, Blanche Ann; Waelsch, Heinrich. The enzymic degradation of histidine. Journal of Biological Chemistry (1953), 205 459-74. |
|---|
| Material Safety Data Sheet (MSDS) |
Not Available |
|---|
|
Links |
|---|
| External Links: |
|
|---|