|
Record Information |
|---|
| Version |
1.0 |
|---|
| Update Date |
1/22/2018 11:54:54 AM |
|---|
|
Metabolite ID | PAMDB120154 |
|---|
|
Identification |
|---|
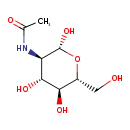
| Name: |
N-acetyl-β-D-glucosamine |
|---|
| Description: | An N-acetyl-D-glucosamine having β-configuration at the anomeric centre. |
|---|
|
Structure |
|
|---|
| Synonyms: | - 2-Acetamido-2-deoxy-D-glucose
- 2-Acetylamino-2-deoxy-D-glucose
- Acetylglucosamine
- βGlcNAc
- GlcNAc-β
- N-Acetyl-beta-D-glucosamine
- N-acetyl-β-D-glucosamine
- N-Acetyl-D-glucosamine
- N-acetylglucosamine
|
|---|
|
Chemical Formula: |
C8H15NO6 |
|---|
| Average Molecular Weight: |
221.21 |
|---|
| Monoisotopic Molecular
Weight: |
221.08994 |
|---|
| InChI Key: |
OVRNDRQMDRJTHS-FMDGEEDCSA-N |
|---|
| InChI: | InChI=1S/C8H15NO6/c1-3(11)9-5-7(13)6(12)4(2-10)15-8(5)14/h4-8,10,12-14H,2H2,1H3,(H,9,11)/t4-,5-,6-,7-,8-/m1/s1 |
|---|
| CAS
number: |
14131-68-1 |
|---|
| IUPAC Name: | 2-acetamido-2-deoxy-β-D-glucopyranose |
|---|
|
Traditional IUPAC Name: |
N-acetyl-D-glucosamine |
|---|
| SMILES: | CC(=O)NC1(C(O)OC(CO)C(O)C(O)1) |
|---|
|
Chemical Taxonomy |
|---|
|
Taxonomy Description | This compound belongs to the class of chemical entities known as acylaminosugars. These are organic compounds containing a sugar linked to a chain through N-acyl group. |
|---|
|
Kingdom |
Chemical entities |
|---|
| Super Class | Organic compounds |
|---|
|
Class |
Organic oxygen compounds |
|---|
| Sub Class | Organooxygen compounds |
|---|
|
Direct Parent |
Acylaminosugars |
|---|
| Alternative Parents |
|
|---|
| Substituents |
- Acylaminosugar
- N-acyl-alpha-hexosamine
- Hexose monosaccharide
- Monosaccharide
- Oxane
- Acetamide
- Carboxamide group
- Hemiacetal
- Secondary carboxylic acid amide
- Secondary alcohol
- Carboxylic acid derivative
- Oxacycle
- Organoheterocyclic compound
- Polyol
- Alcohol
- Hydrocarbon derivative
- Organic oxide
- Organic nitrogen compound
- Organopnictogen compound
- Organonitrogen compound
- Primary alcohol
- Carbonyl group
- Aliphatic heteromonocyclic compound
|
|---|
| Molecular Framework |
Aliphatic heteromonocyclic compounds |
|---|
| External Descriptors |
|
|---|
|
Physical Properties |
|---|
| State: |
Solid |
|---|
| Charge: | 0 |
|---|
|
Melting point: |
Not Available |
|---|
| Experimental Properties: |
| Property | Value | Reference |
|---|
| Melting Point | Not Available | Not Available | | Boiling Point | Not Available | Not Available | | Water Solubility | Not Available | Not Available | | LogP | Not Available | Not Available |
|
|---|
| Predicted Properties |
|
|---|
|
Biological Properties |
|---|
| Cellular Locations: |
Not Available |
|---|
| Reactions: | |
|---|
|
Pathways: |
|
|---|
|
Spectra |
|---|
| Spectra: |
|
|---|
|
References |
|---|
| References: |
- Zajonc DM, Savage PB, Bendelac A, Wilson IA, Teyton L (2008)Crystal structures of mouse CD1d-iGb3 complex and its cognate Valpha14 T cell receptor suggest a model for dual recognition of foreign and self glycolipids. Journal of molecular biology 377, Pubmed: 18295796
- Obukhova P, Rieben R, Bovin N (2007)Normal human serum contains high levels of anti-Gal alpha 1-4GlcNAc antibodies. Xenotransplantation 14, Pubmed: 17991151
- von Gunten S, Smith DF, Cummings RD, Riedel S, Miescher S, Schaub A, Hamilton RG, Bochner BS (2009)Intravenous immunoglobulin contains a broad repertoire of anticarbohydrate antibodies that is not restricted to the IgG2 subclass. The Journal of allergy and clinical immunology 123, Pubmed: 19443021
- Kuk JH, Jung WJ, Jo GH, Kim YC, Kim KY, Park RD (2005)Production of N-acetyl-beta-D-glucosamine from chitin by Aeromonas sp. GJ-18 crude enzyme. Applied microbiology and biotechnology 68, Pubmed: 15692805
- Wu D, Zajonc DM, Fujio M, Sullivan BA, Kinjo Y, Kronenberg M, Wilson IA, Wong CH (2006)Design of natural killer T cell activators: structure and function of a microbial glycosphingolipid bound to mouse CD1d. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America 103, Pubmed: 16537470
- Schneider C, Smith DF, Cummings RD, Boligan KF, Hamilton RG, Bochner BS, Miescher S, Simon HU, Pashov A, Vassilev T, von Gunten S (2015)The human IgG anti-carbohydrate repertoire exhibits a universal architecture and contains specificity for microbial attachment sites. Science translational medicine 7, Pubmed: 25568069
- Cooper DK, Good AH, Koren E, Oriol R, Malcolm AJ, Ippolito RM, Neethling FA, Ye Y, Romano E, Zuhdi N (1993)Identification of alpha-galactosyl and other carbohydrate epitopes that are bound by human anti-pig antibodies: relevance to discordant xenografting in man. Transplant immunology 1, Pubmed: 7521740
|
|---|
| Synthesis Reference: |
Kuk, J. H.; Jung, W. J.; Jo, G. H.; Kim, Y. C.; Kim, K. Y.; Park, R. D. Production of N-acetyl-b-D-glucosamine from chitin by Aeromonas sp. GJ-18 crude enzyme. Applied Microbiology and Biotechnology (2005), 68(3), 384-389. |
|---|
| Material Safety Data Sheet (MSDS) |
Download (PDF) |
|---|
|
Links |
|---|
| External Links: |
|
|---|