|
Record Information |
|---|
| Version |
1.0 |
|---|
| Update Date |
1/22/2018 11:54:54 AM |
|---|
|
Metabolite ID | PAMDB120085 |
|---|
|
Identification |
|---|
| Name: |
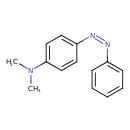
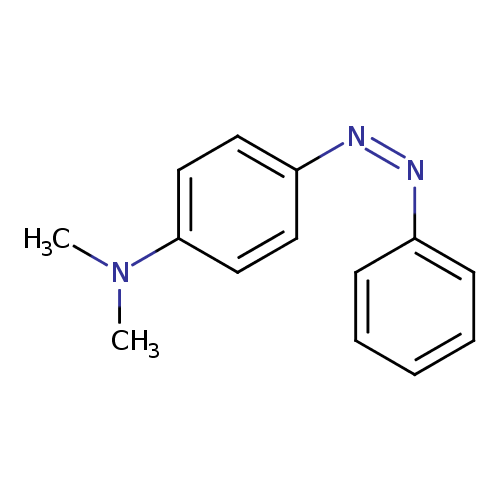
4-dimethylaminophenylazobenzene |
|---|
| Description: | 4-(Dimethylamino)azobenzene is formerly used as a food dye, use discontinued.Methyl yellow, or C.I. 11020, is a chemical compound which may be used as a pH indicator. In aqueous solution at low pH, methyl yellow appears red. Between pH 2.9 and 4.0, methyl yellow undergoes a transition, to become yellow above pH 4.0. As "butter yellow" the agent had been used as a food additive before its toxicity was recognized (Opie EL). (Wikipedia)
4-(dimethylamino)azobenzene belongs to the family of Aromatic Homomonocyclic Compounds. These are aromatic compounds containig only one ring, which is homocyclic. |
|---|
|
Structure |
|
|---|
| Synonyms: | - 4-(Dimethylamino)azobenzene
- 4-(dimethylamino)azobenzene
- 4-(Dimethylamino)phenylazobenzene
- 4-(N,N-Dimethylamino)azobenzene
- 4-(Phenylazo)-N,N-dimethylaniline
- Dimethyl yellow
- Methyl yellow
- N,N-dimethyl-4-(phenylazo)aniline
- N,N-Dimethyl-4-(phenylazo)benzenamine
- N,N-dimethyl-4-(phenylazo)benzenamine
|
|---|
|
Chemical Formula: |
C14H15N3 |
|---|
| Average Molecular Weight: |
225.293 |
|---|
| Monoisotopic Molecular
Weight: |
225.1266 |
|---|
| InChI Key: |
JCYPECIVGRXBMO-FOCLMDBBSA-N |
|---|
| InChI: | InChI=1S/C14H15N3/c1-17(2)14-10-8-13(9-11-14)16-15-12-6-4-3-5-7-12/h3-11H,1-2H3/b16-15+ |
|---|
| CAS
number: |
60-11-7 |
|---|
| IUPAC Name: | N,N-dimethyl-4-(phenyldiazenyl)aniline |
|---|
|
Traditional IUPAC Name: |
N,N-dimethyl-4-[(Z)-2-phenyldiazen-1-yl]aniline |
|---|
| SMILES: | CN(C)C1(C=CC(=CC=1)N=NC2(C=CC=CC=2)) |
|---|
|
Chemical Taxonomy |
|---|
|
Taxonomy Description | This compound belongs to the class of organic compounds known as azobenzenes. These are organonitrogen aromatic compounds that contain a central azo group, where each nitrogen atom is conjugated to a bezene ring. |
|---|
|
Kingdom |
Organic compounds |
|---|
| Super Class | Organoheterocyclic compounds |
|---|
|
Class |
Azobenzenes |
|---|
| Sub Class | Not Available |
|---|
|
Direct Parent |
Azobenzenes |
|---|
| Alternative Parents |
|
|---|
| Substituents |
- Azobenzene
- Substituted aniline
- Dialkylarylamine
- Aniline
- Benzenoid
- Monocyclic benzene moiety
- Tertiary amine
- Azo compound
- Organic 1,3-dipolar compound
- Propargyl-type 1,3-dipolar organic compound
- Hydrocarbon derivative
- Organonitrogen compound
- Amine
- Aromatic homomonocyclic compound
|
|---|
| Molecular Framework |
Aromatic homomonocyclic compounds |
|---|
| External Descriptors |
Not Available |
|---|
|
Physical Properties |
|---|
| State: |
Not Available |
|---|
| Charge: | 0 |
|---|
|
Melting point: |
117 °C |
|---|
| Experimental Properties: |
| Property | Value | Reference |
|---|
| Melting Point | 117 °C | Not Available | | Boiling Point | Not Available | Not Available | | Water Solubility | 0.00023 mg/mL at 25 °C | Not Available | | LogP | 4.58 | Not Available |
|
|---|
| Predicted Properties |
|
|---|
|
Biological Properties |
|---|
| Cellular Locations: |
Not Available |
|---|
| Reactions: | |
|---|
|
Pathways: |
|
|---|
|
Spectra |
|---|
| Spectra: |
Not Available |
|---|
|
References |
|---|
| References: |
- Yannai, Shmuel. (2004) Dictionary of food compounds with CD-ROM: Additives, flavors, and ingredients. Boca Raton: Chapman & Hall/CRC.
|
|---|
| Synthesis Reference: |
Not Available |
|---|
| Material Safety Data Sheet (MSDS) |
Not Available |
|---|
|
Links |
|---|
| External Links: |
|
|---|