|
Record Information |
|---|
| Version |
1.0 |
|---|
| Update Date |
1/22/2018 11:54:54 AM |
|---|
|
Metabolite ID | PAMDB110821 |
|---|
|
Identification |
|---|
| Name: |
dihydrolipoamide |
|---|
| Description: | Dihydrolipoamide is an intermediate in glycolysis/gluconeogenesis, citrate cycle (TCA cycle), alanine, aspartate and pyruvate metabolism, and valine, leucine and isoleucine degradation (KEGG ID C00579). It is converted to lipoamide via the enzyme dihydrolipoamide dehydrogenase [EC:1.8.1.4]. Dihydrolipoamide is also a substrate of enzyme Acyltransferases [EC 2.3.1.-]. (KEGG). |
|---|
|
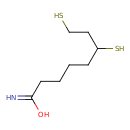
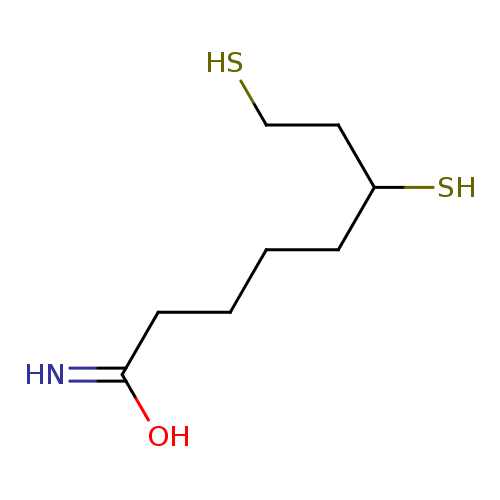
Structure |
|
|---|
| Synonyms: | - 6,8-Dimercaptooctanamide
- Dihydrothioctamide
- 6,8-Bis-sulfanyloctanamide
- 6,8-dimercapto-Octanamide
- 6,8-Disulfanyloctanamide
- Dihydrolipoamide, (+-)-isomer
|
|---|
|
Chemical Formula: |
C8H17NOS2
|
|---|
| Average Molecular Weight: |
207.35 |
|---|
| Monoisotopic Molecular
Weight: |
207.075155553 |
|---|
| InChI Key: |
VLYUGYAKYZETRF-SSDOTTSWSA-N |
|---|
| InChI: |
InChI=1S/C8H17NOS2/c9-8(10)4-2-1-3-7(12)5-6-11/h7,11-12H,1-6H2,(H2,9,10)/t7-/m1/s1 |
|---|
| CAS
number: |
3884-47-7 |
|---|
| IUPAC Name: | (6R)-6,8-disulfanyloctanamide |
|---|
|
Traditional IUPAC Name: |
dihydrothioctamide |
|---|
| SMILES: | C(CCC(N)=O)CC(S)CCS |
|---|
|
Chemical Taxonomy |
|---|
|
Taxonomy Description | This compound belongs to the class of chemical entities known as fatty amides. These are carboxylic acid amide derivatives of fatty acids, that are formed from a fatty acid and an amine. |
|---|
|
Kingdom |
Chemical entities |
|---|
| Super Class | Organic compounds |
|---|
|
Class |
Lipids and lipid-like molecules |
|---|
| Sub Class | Fatty Acyls |
|---|
|
Direct Parent |
Fatty amides |
|---|
| Alternative Parents |
|
|---|
| Substituents |
- Fatty amide
- Primary carboxylic acid amide
- Carboxamide group
- Carboxylic acid derivative
- Alkylthiol
- Organic nitrogen compound
- Organic oxygen compound
- Organopnictogen compound
- Organic oxide
- Hydrocarbon derivative
- Organosulfur compound
- Organooxygen compound
- Organonitrogen compound
- Carbonyl group
- Aliphatic acyclic compound
|
|---|
| Molecular Framework |
Aliphatic acyclic compounds |
|---|
| External Descriptors |
|
|---|
|
Physical Properties |
|---|
| State: |
Solid |
|---|
| Charge: | 0 |
|---|
|
Melting point: |
Not Available |
|---|
| Experimental Properties: |
| Property | Value | Reference |
|---|
| Melting Point | Not Available | Not Available | | Boiling Point | Not Available | Not Available | | Water Solubility | Not Available | Not Available | | LogP | Not Available | Not Available |
|
|---|
| Predicted Properties |
|
|---|
|
Biological Properties |
|---|
| Cellular Locations: |
Not Available |
|---|
| Reactions: | |
|---|
|
Pathways: |
- Pyruvate Metabolism pae00620
- Valine, Leucine and Isoleucine Degradation pae00280
|
|---|
|
Spectra |
|---|
| Spectra: |
|
|---|
|
References |
|---|
| References: |
- Brautigam CA, Chuang JL, Tomchick DR, Machius M, Chuang DT: Crystal structure of human dihydrolipoamide dehydrogenase: NAD+/NADH binding and the structural basis of disease-causing mutations. J Mol Biol. 2005 Jul 15;350(3):543-52. [15946682 ]
- Kim H: Asparagine-473 residue is important to the efficient function of human dihydrolipoamide dehydrogenase. J Biochem Mol Biol. 2005 Mar 31;38(2):248-52. [15826505 ]
- McMillan PJ, Stimmler LM, Foth BJ, McFadden GI, Muller S: The human malaria parasite Plasmodium falciparum possesses two distinct dihydrolipoamide dehydrogenases. Mol Microbiol. 2005 Jan;55(1):27-38. [15612914 ]
- Li XJ, Grunwald D, Mathieu J, Morel F, Stasia MJ: Crucial role of two potential cytosolic regions of Nox2, 191TSSTKTIRRS200 and 484DESQANHFAVHHDEEKD500, on NADPH oxidase activation. J Biol Chem. 2005 Apr 15;280(15):14962-73. Epub 2005 Jan 31. [15684431 ]
- Deres P, Halmosi R, Toth A, Kovacs K, Palfi A, Habon T, Czopf L, Kalai T, Hideg K, Sumegi B, Toth K: Prevention of doxorubicin-induced acute cardiotoxicity by an experimental antioxidant compound. J Cardiovasc Pharmacol. 2005 Jan;45(1):36-43. [15613977 ]
|
|---|
| Synthesis Reference: |
Weitzman, P. D. J.; Hewson, Janet K.; Parker, M. G. Preparation of dihydrolipoamide by electrolytic reduction. FEBS Letters (1974), 43(1), 101-3. |
|---|
| Material Safety Data Sheet (MSDS) |
Not Available |
|---|
|
Links |
|---|
| External Links: |
|
|---|