|
Record Information |
|---|
| Version |
1.0 |
|---|
| Update Date |
1/22/2018 11:54:54 AM |
|---|
|
Metabolite ID | PAMDB110819 |
|---|
|
Identification |
|---|
| Name: |
α-ribazole |
|---|
| Description: | N1-(alpha-D-ribosyl)-5,6-dimethyl-benzimidazole is an intermediate in riboflavin metabolism. It is converted from N1-(5-Phospho-alpha-D-ribosyl)-5,6-dimethylbenzimidazole via dephosphorylation by the enzyme phosphohistidine phosphatase 1 (EC 3.1.3.-). Humans do not have all the enzymes needed to synthesize or metabolize riboflavin. However, gut microflora do have the necessary enzymatic machinery to produce and metabolize this vitamin. Riboflavin (or vitamin B2) is an easily absorbed micronutrient with a key role in maintaining health in humans and animals. It is the central component of the cofactors FAD and FMN, and is therefore required by all flavoproteins. Riboflavin is yellow or yellow-orange in color and in addition to being used as a food coloring it is also used to fortify some foods including baby foods, breakfast cereals, pastas, sauces, processed cheese, fruit drinks, vitamin-enriched milk products, some energy drinks, and vitamin supplements. |
|---|
|
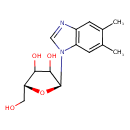
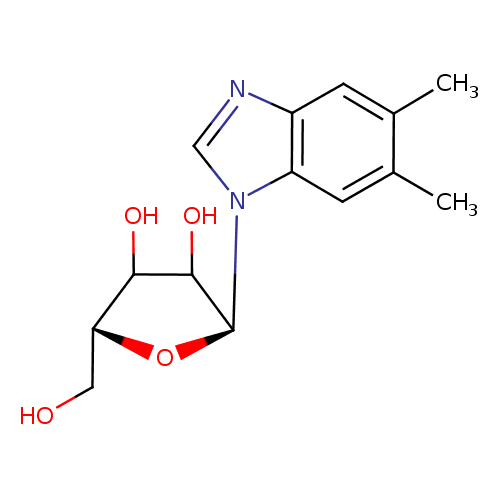
Structure |
|
|---|
| Synonyms: | -
N1-(α-D-ribosyl)-5,6-dimethylbenzimidazole
|
|---|
|
Chemical Formula: |
C14H18N2O4
|
|---|
| Average Molecular Weight: |
278.31 |
|---|
| Monoisotopic Molecular
Weight: |
278.1266570766 |
|---|
| InChI Key: |
HLRUKOJSWOKCPP-SYQHCUMBSA-N |
|---|
| InChI: |
InChI=1S/C14H18N2O4/c1-7-3-9-10(4-8(7)2)16(6-15-9)14-13(19)12(18)11(5-17)20-14/h3-4,6,11-14,17-19H,5H2,1-2H3/t11-,12-,13-,14+/m1/s1 |
|---|
| CAS
number: |
Not Available |
|---|
| IUPAC Name: | 5,6-dimethyl-1-α-D-ribofuranosyl-1H-benzimidazole |
|---|
|
Traditional IUPAC Name: |
(2S,5R)-2-(5,6-dimethyl-1,3-benzodiazol-1-yl)-5-(hydroxymethyl)oxolane-3,4-diol |
|---|
| SMILES: | CC2(C(C)=CC1(N(C=NC=1C=2)C3(C(O)C(O)C(CO)O3))) |
|---|
|
Chemical Taxonomy |
|---|
|
Taxonomy Description | This compound belongs to the class of chemical entities known as benzimidazole ribonucleosides and ribonucleotides. These are nucleosides with a structure that consists of an imidazole moiety of benzimidazole is N-linked to a ribose (or deoxyribose). Nucleotides have a phosphate group linked to the C5 carbon of the ribose (or deoxyribose) moiety. |
|---|
|
Kingdom |
Chemical entities |
|---|
| Super Class | Organic compounds |
|---|
|
Class |
Nucleosides, nucleotides, and analogues |
|---|
| Sub Class | Benzimidazole ribonucleosides and ribonucleotides |
|---|
|
Direct Parent |
Benzimidazole ribonucleosides and ribonucleotides |
|---|
| Alternative Parents |
|
|---|
| Substituents |
- 1-ribofuranosylbenzimidazole
- Glycosyl compound
- N-glycosyl compound
- Pentose monosaccharide
- Benzimidazole
- Monosaccharide
- N-substituted imidazole
- Benzenoid
- Azole
- Heteroaromatic compound
- Imidazole
- Tetrahydrofuran
- Secondary alcohol
- Oxacycle
- Azacycle
- Organoheterocyclic compound
- Organic nitrogen compound
- Alcohol
- Hydrocarbon derivative
- Organopnictogen compound
- Organic oxygen compound
- Organonitrogen compound
- Organooxygen compound
- Primary alcohol
- Aromatic heteropolycyclic compound
|
|---|
| Molecular Framework |
Aromatic heteropolycyclic compounds |
|---|
| External Descriptors |
Not Available |
|---|
|
Physical Properties |
|---|
| State: |
Solid |
|---|
| Charge: | 0 |
|---|
|
Melting point: |
Not Available |
|---|
| Experimental Properties: |
| Property | Value | Reference |
|---|
| Melting Point | Not Available | Not Available | | Boiling Point | Not Available | Not Available | | Water Solubility | Not Available | Not Available | | LogP | Not Available | Not Available |
|
|---|
| Predicted Properties |
|
|---|
|
Biological Properties |
|---|
| Cellular Locations: |
Not Available |
|---|
| Reactions: | |
|---|
|
Pathways: |
- adenosylcobalamin biosynthesis from cobyrinate a,c-diamide IIPWY-5508
|
|---|
|
Spectra |
|---|
| Spectra: |
|
|---|
|
References |
|---|
| References: |
Not Available |
|---|
| Synthesis Reference: |
Not Available |
|---|
| Material Safety Data Sheet (MSDS) |
Not Available |
|---|
|
Links |
|---|
| External Links: |
|
|---|