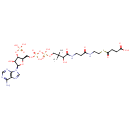|
Record Information |
|---|
| Version |
1.0 |
|---|
| Update Date |
1/22/2018 11:54:54 AM |
|---|
|
Metabolite ID | PAMDB110378 |
|---|
|
Identification |
|---|
| Name: |
succinyl-CoA |
|---|
| Description: | An acyl-CoA oxoanion that is the pentaanion of succinyl-CoA, arising from deprotonation of the phosphate, diphosphate and carboxylic acid OH groups. |
|---|
|
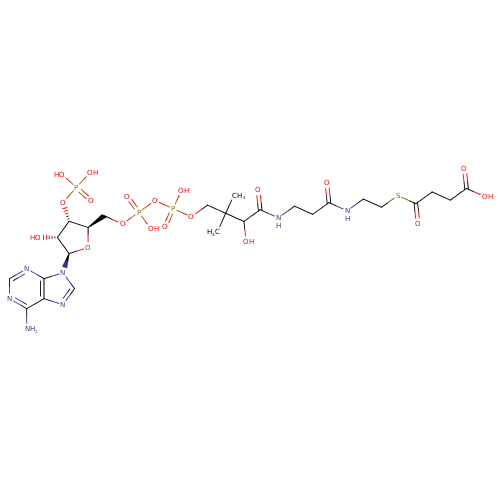
Structure |
|
|---|
| Synonyms: | -
suc-coa
-
succ-coenzyme-A
-
succ-S-coenzyme-A
-
succinyl-S-coenzyme-A
-
succ-S-CoA
-
succinylcoenzyme-A
-
succ-CoA
-
suc-co-A
-
succinyl-S-CoA
-
succinyl-coenzyme A
|
|---|
|
Chemical Formula: |
C25H35N7O19P3S
|
|---|
| Average Molecular Weight: |
862.57 |
|---|
| Monoisotopic Molecular
Weight: |
867.1312523603 |
|---|
| InChI Key: |
VNOYUJKHFWYWIR-ITIYDSSPSA-I |
|---|
| InChI: |
InChI=1S/C25H40N7O19P3S/c1-25(2,20(38)23(39)28-6-5-14(33)27-7-8-55-16(36)4-3-15(34)35)10-48-54(45,46)51-53(43,44)47-9-13-19(50-52(40,41)42)18(37)24(49-13)32-12-31-17-21(26)29-11-30-22(17)32/h11-13,18-20,24,37-38H,3-10H2,1-2H3,(H,27,33)(H,28,39)(H,34,35)(H,43,44)(H,45,46)(H2,26,29,30)(H2,40,41,42)/p-5/t13-,18-,19-,20+,24-/m1/s1 |
|---|
| CAS
number: |
604-98-8 |
|---|
| IUPAC Name: | 3'- phosphonatoadenosine 5'- phosphonatoadenosine 5'- {3- {3- [(3R)- [(3R)- 4- 4- {[3- {[3- ({2- ({2- [(3- [(3- carboxylatopropanoyl)sulfanyl]ethyl}amino)- carboxylatopropanoyl)sulfanyl]ethyl}amino)- 3- 3- oxopropyl]amino}- oxopropyl]amino}- 3- 3- hydroxy- hydroxy- 2,2- 2,2- dimethyl- dimethyl- 4- 4- oxobutyl]diphosphate} oxobutyl]diphosphate} |
|---|
|
Traditional IUPAC Name: |
4-({2-[3-(3-{[({[(2R,3S,4R,5R)-5-(6-aminopurin-9-yl)-4-hydroxy-3-(phosphonooxy)oxolan-2-yl]methoxy(hydroxy)phosphoryl}oxy(hydroxy)phosphoryl)oxy]methyl}-2-hydroxy-3-methylbutanamido)propanamido]ethyl}sulfanyl)-4-oxobutanoic acid |
|---|
| SMILES: | CC(C)(C(O)C(=O)NCCC(=O)NCCSC(=O)CCC(=O)[O-])COP(=O)(OP(=O)(OCC1(C(OP([O-])(=O)[O-])C(O)C(O1)N3(C2(=C(C(N)=NC=N2)N=C3))))[O-])[O-] |
|---|
|
Chemical Taxonomy |
|---|
|
Taxonomy Description | This compound belongs to the class of chemical entities known as acyl coas. These are organic compounds containing a coenzyme A substructure linked to an acyl chain. |
|---|
|
Kingdom |
Chemical entities |
|---|
| Super Class | Organic compounds |
|---|
|
Class |
Lipids and lipid-like molecules |
|---|
| Sub Class | Fatty Acyls |
|---|
|
Direct Parent |
Acyl CoAs |
|---|
| Alternative Parents |
|
|---|
| Substituents |
- Coenzyme a or derivatives
- Purine ribonucleoside 3',5'-bisphosphate
- Purine ribonucleoside bisphosphate
- Purine ribonucleoside diphosphate
- Pentose phosphate
- Pentose-5-phosphate
- Ribonucleoside 3'-phosphate
- Beta amino acid or derivatives
- Glycosyl compound
- N-glycosyl compound
- 6-aminopurine
- Monosaccharide phosphate
- Organic pyrophosphate
- Pentose monosaccharide
- Imidazopyrimidine
- Purine
- Aminopyrimidine
- Hydroxy fatty acid
- Monoalkyl phosphate
- Thia fatty acid
- Imidolactam
- Fatty amide
- Alkyl phosphate
- Monosaccharide
- N-acyl-amine
- N-substituted imidazole
- Organic phosphoric acid derivative
- Phosphoric acid ester
- Primary aromatic amine
- Pyrimidine
- Heteroaromatic compound
- Imidazole
- Azole
- Oxolane
- Amino acid
- Secondary alcohol
- Thiocarboxylic acid ester
- Secondary carboxylic acid amide
- Amino acid or derivatives
- Carboxamide group
- Carbothioic s-ester
- Thiocarboxylic acid or derivatives
- Organoheterocyclic compound
- Sulfenyl compound
- Monocarboxylic acid or derivatives
- Azacycle
- Carboxylic acid derivative
- Carboxylic acid
- Oxacycle
- Organopnictogen compound
- Organic nitrogen compound
- Alcohol
- Amine
- Organonitrogen compound
- Primary amine
- Carbonyl group
- Organic oxide
- Organooxygen compound
- Organosulfur compound
- Hydrocarbon derivative
- Organic oxygen compound
- Aromatic heteropolycyclic compound
|
|---|
| Molecular Framework |
Aromatic heteropolycyclic compounds |
|---|
| External Descriptors |
Not Available |
|---|
|
Physical Properties |
|---|
| State: |
Solid |
|---|
| Charge: | -5 |
|---|
|
Melting point: |
Not Available |
|---|
| Experimental Properties: |
| Property | Value | Reference |
|---|
| Melting Point | Not Available | Not Available | | Boiling Point | Not Available | Not Available | | Water Solubility | Not Available | Not Available | | LogP | Not Available | Not Available |
|
|---|
| Predicted Properties |
|
|---|
|
Biological Properties |
|---|
| Cellular Locations: |
Not Available |
|---|
| Reactions: | |
|---|
|
Pathways: |
|
|---|
|
Spectra |
|---|
| Spectra: |
|
|---|
|
References |
|---|
| References: |
- Tanaka H, Kohroki J, Iguchi N, Onishi M, Nishimune Y: Cloning and characterization of a human orthologue of testis-specific succinyl CoA: 3-oxo acid CoA transferase (Scot-t) cDNA. Mol Hum Reprod. 2002 Jan;8(1):16-23. [11756565 ]
- Elpeleg O, Miller C, Hershkovitz E, Bitner-Glindzicz M, Bondi-Rubinstein G, Rahman S, Pagnamenta A, Eshhar S, Saada A: Deficiency of the ADP-forming succinyl-CoA synthase activity is associated with encephalomyopathy and mitochondrial DNA depletion. Am J Hum Genet. 2005 Jun;76(6):1081-6. Epub 2005 Apr 22. [15877282 ]
- Westin MA, Hunt MC, Alexson SE: The identification of a succinyl-CoA thioesterase suggests a novel pathway for succinate production in peroxisomes. J Biol Chem. 2005 Nov 18;280(46):38125-32. Epub 2005 Aug 31. [16141203 ]
|
|---|
| Synthesis Reference: |
Wollemann, M. Mechanism of the succinyl-coenzyme A synthesis in brain extracts. Acta Physiologica Academiae Scientiarum Hungaricae (1959), 16 153-4. |
|---|
| Material Safety Data Sheet (MSDS) |
Not Available |
|---|
|
Links |
|---|
| External Links: |
|
|---|