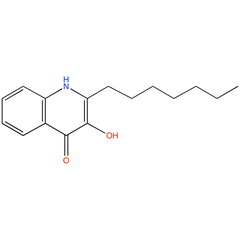
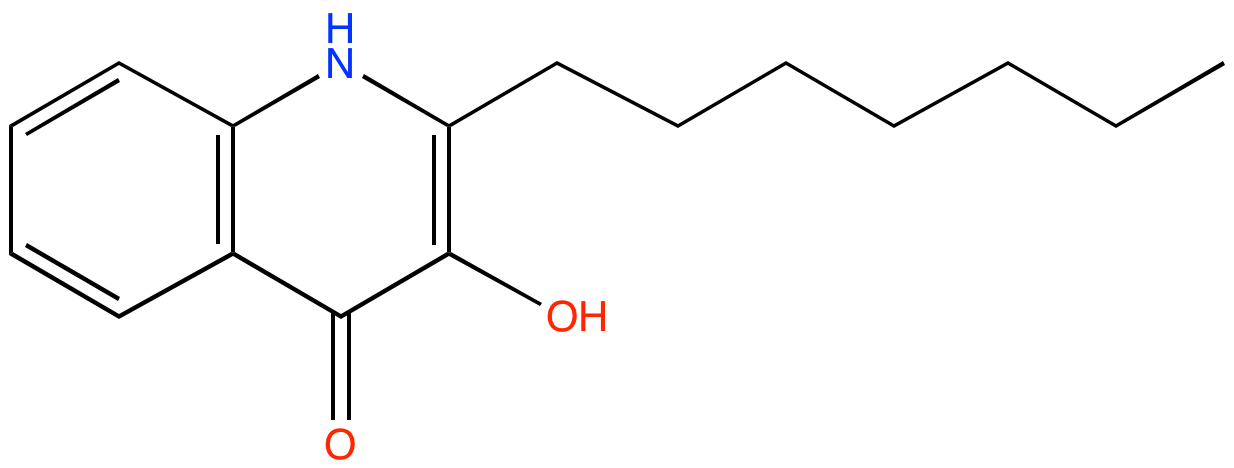
2-heptyl-3-hydroxy-4-quinolone (PAMDB100069)
| Record Information | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Version | 1.0 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Update Date | 1/22/2018 11:54:54 AM | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Metabolite ID | PAMDB100069 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Identification | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Name: | 2-heptyl-3-hydroxy-4-quinolone | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Description: | The Pseudomonas quinolone signal (PQS) is a quorum sensing molecule unique to Pseudomonas aeruginosa. This molecule is active when the density of bacterial cells reaches a quorum. PQS is an important signaling molecule that enhances the production of virulence factors by P. aeruginosa including the production of phenazines and elastases. PQS has also been reported to chelate ferric iron and induce vesicle formation at the membrane. PQS is produced from the hydroxylation of HHQ by mono-oxygenase PqsH. | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Structure | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Synonyms: | • 2-Heptyl-3-hydroxy-4(1H)-chinolinon [German] [ACD/IUPAC Name] • 2-Heptyl-3-hydroxy-4(1H)-quinoléinone [French] [ACD/IUPAC Name] • 2-Heptyl-3-hydroxy-4(1H)-quinolinone [ACD/IUPAC Name] • 2-heptyl-3-hydroxy-4-quinolone • 2-heptyl-3-hydroxyl-4(1H)-quinolone • 2-Heptyl-3-hydroxyquinolin-4(1H)-one • 3,4-dihydroxy-2-heptylquinoline • 4(1H)-Quinolinone, 2-heptyl-3-hydroxy- [ACD/Index Name] • 10.1021/jm400830r • 108985-27-9 [RN] • 2-heptyl-3,4-dihydroxyquinoline • 2-Heptyl-3-hydroxy-1H-quinolin-4-one • 2-heptyl-3-hydroxy-4(1H)-quinolone • 2-Heptyl-3-hydroxyl-4-chinolon • 2-Heptyl-3-hydroxyl-4-quinolone • 2-Heptyl-3-hydroxy-quinolone • 521313-35-9 [RN] • MFCD07437949 [MDL number] • PQS • Pseudomonas quinolone signal | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Chemical Formula: |
C16H21NO2 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Average Molecular Weight: | 259.3434 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Monoisotopic Molecular Weight: | 259.157227 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| InChI Key: | CEIUIHOQDSVZJQ-UHFFFAOYSA-N | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| InChI: | InChI=1S/C16H21NO2/c1-2-3-4-5-6-11-14-16(19)15(18)12-9-7-8-10-13(12)17-14/h7-10,19H,2-6,11H2,1H3,(H,17,18) | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| CAS number: | Not Available | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| IUPAC Name: | 2-heptyl-3-hydroxy-1H-quinolin-4-one | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Traditional IUPAC Name: | Pseudomonas quinolone signal | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| SMILES: | CCCCCCCc1c(c(=O)c2ccccc2[nH]1)O | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Chemical Taxonomy | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Taxonomy Description | This compound belongs to the class of organic compounds known as hydroxyquinolones. These are compounds containing a quinoline moiety bearing a hydroxyl group and a ketone. Quinoline or benzo[b]pyridine is a bicyclic compound that consists of benzene fused to a pyridine. | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Kingdom | Organic compounds | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Super Class | Organoheterocyclic compounds | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Class | Quinolines and derivatives | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Sub Class | Quinolones and derivatives | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Direct Parent | Hydroxyquinolones | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Alternative Parents | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Substituents |
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Molecular Framework | Aromatic heteropolycyclic compounds | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| External Descriptors |
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Physical Properties | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| State: |
Solid, off white powder | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Charge: | 0 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Melting point: |
Soluble in methanol | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Experimental Properties: | Not Available | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Predicted Properties |
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Biological Properties | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Cellular Locations: | Not Available | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Reactions: | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Pathways: |
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Spectra | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Spectra: | Not Available | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| References | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| References: |
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Synthesis Reference: | Not Available | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Material Safety Data Sheet (MSDS) | Not Available | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Links | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| External Links: |
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||