|
Record Information |
|---|
| Version |
1.0 |
|---|
| Update Date |
1/22/2018 11:54:54 AM |
|---|
|
Metabolite ID | PAMDB006813 |
|---|
|
Identification |
|---|
| Name: |
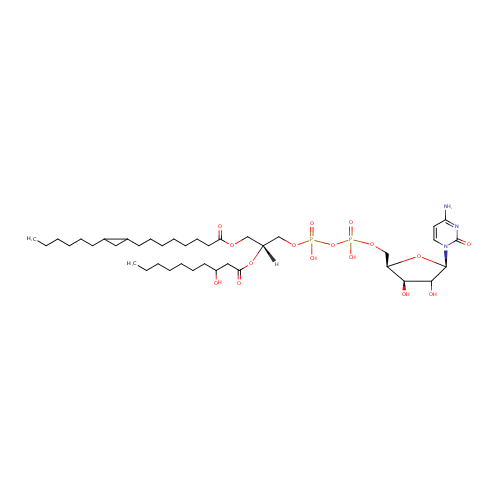
CDP-DG(17:0cycw7c/10:0(3-OH)) |
|---|
| Description: | CDP-DG(17:0cycw7c/10:0(3-OH)) belongs to the family of CDP-diacylglycerols. It is a glycerophospholipid containing a diacylglycerol, with a cytidine diphosphate attached to the oxygen O1 or O2 of the glycerol part. As is the case with diacylglycerols, phosphatidylserines can have many different combinations of fatty acids of varying lengths and saturation attached to the C-1 and C-2 atoms. CDP-DG(17:0cycw7c/10:0(3-OH)), in particular, consists of one heptadec-9-10-cyclo-anoyl chain to C-1 atom, and one 3-hydroxydecanoyl to the C-2 atom. In Pseudomonas aeruginosa glycerophospholipid metabolism, The biosynthesis of CDP-diacylglycerol (CDP-DG) involves condensation of phosphatidic acid (PA) and cytidine triphosphate, with elimination of pyrophosphate, catalysed by the enzyme CDP-diacylglycerol synthase. The resulting CDP-diacylglycerol can be utilized immediately for the synthesis of phosphatidylglycerol (PG), and thence cardiolipin (CL), and of phosphatidylinositol (PI). CDP-DG(17:0cycw7c/10:0(3-OH)) is also a substrate of CDP-diacylglycerol pyrophosphatase. It is involved in CDP-diacylglycerol degradation pathway. |
|---|
|
Structure |
|
|---|
| Synonyms: | Not Available |
|---|
|
Chemical Formula: |
C39H69N3O16P2 |
|---|
| Average Molecular Weight: |
897.934 |
|---|
| Monoisotopic Molecular
Weight: |
897.41530715 |
|---|
| InChI Key: |
JAJPAICKPQOUMM-KMRAWJHVSA-N |
|---|
| InChI: | InChI=1S/C39H69N3O16P2/c1-3-5-7-10-15-19-30(43)24-35(45)56-31(25-53-34(44)20-16-12-9-11-14-18-29-23-28(29)17-13-8-6-4-2)26-54-59(49,50)58-60(51,52)55-27-32-36(46)37(47)38(57-32)42-22-21-33(40)41-39(42)48/h21-22,28-32,36-38,43,46-47H,3-20,23-27H2,1-2H3,(H,49,50)(H,51,52)(H2,40,41,48)/t28?,29?,30?,31-,32-,36+,37?,38-/m1/s1 |
|---|
| CAS
number: |
Not Available |
|---|
| IUPAC Name: | {[(2R,3R,5R)-5-(4-amino-2-oxo-1,2-dihydropyrimidin-1-yl)-3,4-dihydroxyoxolan-2-yl]methoxy}({[(2R)-3-{[8-(2-hexylcyclopropyl)octanoyl]oxy}-2-[(3-hydroxydecanoyl)oxy]propoxy](hydroxy)phosphoryl}oxy)phosphinic acid |
|---|
|
Traditional IUPAC Name: |
[(2R,3R,5R)-5-(4-amino-2-oxopyrimidin-1-yl)-3,4-dihydroxyoxolan-2-yl]methoxy([(2R)-3-{[8-(2-hexylcyclopropyl)octanoyl]oxy}-2-[(3-hydroxydecanoyl)oxy]propoxy(hydroxy)phosphoryl]oxy)phosphinic acid |
|---|
| SMILES: | [H][C@@](COC(=O)CCCCCCCC1CC1CCCCCC)(COP(O)(=O)OP(O)(=O)OC[C@H]1O[C@H](C(O)[C@H]1O)N1C=CC(N)=NC1=O)OC(=O)CC(O)CCCCCCC |
|---|
|
Chemical Taxonomy |
|---|
|
Taxonomy Description | This compound belongs to the class of organic compounds known as cdp-diacylglycerols. These are glycerolipids containing a diacylglycerol, with a cytidine diphosphate attached to the oxygen O1 or O2 of the glycerol part. |
|---|
|
Kingdom |
Organic compounds |
|---|
| Super Class | Lipids and lipid-like molecules |
|---|
|
Class |
Glycerophospholipids |
|---|
| Sub Class | CDP-glycerols |
|---|
|
Direct Parent |
CDP-diacylglycerols |
|---|
| Alternative Parents |
|
|---|
| Substituents |
- Cdp-diacylglycerol
- Diacyl-glycerol-3-pyrophosphate
- Pentose phosphate
- Pentose-5-phosphate
- Glycosyl compound
- N-glycosyl compound
- Monosaccharide phosphate
- Organic pyrophosphate
- Beta-hydroxy acid
- Fatty acid ester
- Hydroxypyrimidine
- Monoalkyl phosphate
- Fatty acyl
- Alkyl phosphate
- Pyrimidine
- Phosphoric acid ester
- Dicarboxylic acid or derivatives
- Hydropyrimidine
- Hydroxy acid
- Monosaccharide
- Organic phosphoric acid derivative
- Heteroaromatic compound
- Oxolane
- Secondary alcohol
- 1,2-diol
- Carboxylic acid ester
- Oxacycle
- Organoheterocyclic compound
- Carboxylic acid derivative
- Azacycle
- Organooxygen compound
- Organic oxide
- Organic oxygen compound
- Alcohol
- Organic nitrogen compound
- Carbonyl group
- Organonitrogen compound
- Hydrocarbon derivative
- Aromatic heteromonocyclic compound
|
|---|
| Molecular Framework |
Aromatic heteromonocyclic compounds |
|---|
| External Descriptors |
Not Available |
|---|
|
Physical Properties |
|---|
| State: |
Not Available |
|---|
| Charge: | -2 |
|---|
|
Melting point: |
Not Available |
|---|
| Experimental Properties: |
|
|---|
| Predicted Properties |
|
|---|
|
Biological Properties |
|---|
| Cellular Locations: |
Membrane |
|---|
| Reactions: | |
|---|
|
Pathways: |
Not Available |
|---|
|
Spectra |
|---|
| Spectra: |
|
|---|
|
References |
|---|
| References: |
- Kanehisa, M., Goto, S., Sato, Y., Furumichi, M., Tanabe, M. (2012). "KEGG for integration and interpretation of large-scale molecular data sets." Nucleic Acids Res 40:D109-D114. Pubmed: 22080510
- Keseler, I. M., Collado-Vides, J., Santos-Zavaleta, A., Peralta-Gil, M., Gama-Castro, S., Muniz-Rascado, L., Bonavides-Martinez, C., Paley, S., Krummenacker, M., Altman, T., Kaipa, P., Spaulding, A., Pacheco, J., Latendresse, M., Fulcher, C., Sarker, M., Shearer, A. G., Mackie, A., Paulsen, I., Gunsalus, R. P., Karp, P. D. (2011). "EcoCyc: a comprehensive database of Escherichia coli biology." Nucleic Acids Res 39:D583-D590. Pubmed: 21097882
- Uniprot Consortium (2012). "Reorganizing the protein space at the Universal Protein Resource (UniProt)." Nucleic Acids Res 40:D71-D75. Pubmed: 22102590
- Yurtsever D. (2007). Fatty acid methyl ester profiling of Enterococcus and Esherichia coli for microbial source tracking. M.sc. Thesis. Villanova University: U.S.A
|
|---|
| Synthesis Reference: |
Not Available |
|---|
| Material Safety Data Sheet (MSDS) |
Not Available |
|---|
|
Links |
|---|
| External Links: |
| Resource | Link |
|---|
| CHEBI ID | Not Available | | HMDB ID | Not Available | | Pubchem Compound ID | Not Available | | Kegg ID | Not Available | | ChemSpider ID | Not Available | | Wikipedia ID | Not Available | | BioCyc ID | Not Available |
|
|---|