|
Record Information |
|---|
| Version |
1.0 |
|---|
| Update Date |
1/22/2018 11:54:54 AM |
|---|
|
Metabolite ID | PAMDB003998 |
|---|
|
Identification |
|---|
| Name: |
PS(17:0cycw7c/19:iso) |
|---|
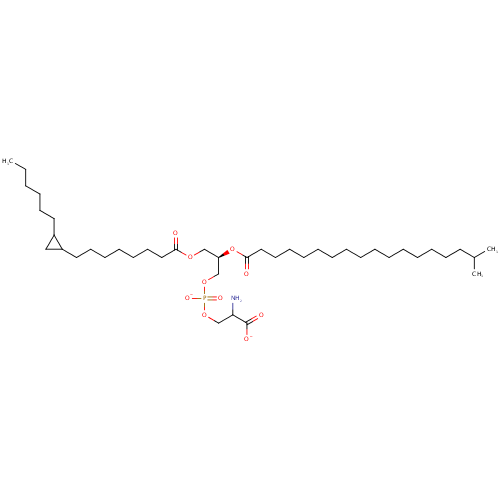
| Description: | PS(17:0cycw7c/19:iso) is a phosphatidylserine. It is a glycerophospholipid in which a phosphorylserine moiety occupies a glycerol substitution site. As is the case with diacylglycerols, phosphatidylserines can have many different combinations of fatty acids of varying lengths and saturation attached to the C-1 and C-2 atoms.. PS(17:0cycw7c/19:iso), in particular, consists of one heptadec-9-10-cyclo-anoyl chain to the C-1 atom, and one 17-methylocatdecanoyl to the C-2 atom. Phosphatidylserine or 1,2-diacyl-sn-glycero-3-phospho-L-serine is distributed widely among animals, plants and microorganisms. Phosphatidylserine is an acidic (anionic) phospholipid with three ionizable groups, i.e. the phosphate moiety, the amino group and the carboxyl function. As with other acidic lipids, it exists in nature in salt form, but it has a high propensity to chelate to calcium via the charged oxygen atoms of both the carboxyl and phosphate moieties, modifying the conformation of the polar head group. This interaction may be of considerable relevance to the biological function of phosphatidylserine. While most phospholipids have a saturated fatty acid on C-1 and an unsaturated fatty acid on C-2 of the glycerol backbone, the fatty acid distribution at the C-1 and C-2 positions of glycerol within phospholipids is continually in flux, owing to phospholipid degradation and the continuous phospholipid remodeling that occurs while these molecules are in membranes. Phosphatidylserines typically carry a net charge of -1 at physiological pH. They mostly have palmitic or stearic acid on carbon 1 and a long chain unsaturated fatty acid (e.g. 18:2, 20:4 and 22:6) on carbon 2. PS biosynthesis involves an exchange reaction of serine for ethanolamine in PE. |
|---|
|
Structure |
|
|---|
| Synonyms: | - 1-heptadec-9-10-cyclo-anoyl-2-17-methylocatdecanoyl-sn-glycero-3-phosphoserine
- 1-heptadec-9-10-cyclo-anoyl-2-17-methylocatdecanoyl-sn-glycero-3-phosphoserine
- Phosphatidylserine(17:0/19:0)
- Phosphatidylserine(36:0)
- PS(17:0/19:0)
- PS(36:0)
- PSer(17:0/19:0)
- PSer(36:0)
|
|---|
|
Chemical Formula: |
C42H78NO10P |
|---|
| Average Molecular Weight: |
788.0432 |
|---|
| Monoisotopic Molecular
Weight: |
787.536334233 |
|---|
| InChI Key: |
PHEXCIGGYVKNCH-ZXMRSIAPSA-L |
|---|
| InChI: | InChI=1S/C42H80NO10P/c1-4-5-6-22-27-36-31-37(36)28-23-18-16-20-24-29-40(44)50-32-38(33-51-54(48,49)52-34-39(43)42(46)47)53-41(45)30-25-19-15-13-11-9-7-8-10-12-14-17-21-26-35(2)3/h35-39H,4-34,43H2,1-3H3,(H,46,47)(H,48,49)/p-2/t36?,37?,38-,39?/m1/s1 |
|---|
| CAS
number: |
Not Available |
|---|
| IUPAC Name: | 2-amino-3-{[(2R)-3-{[8-(2-hexylcyclopropyl)octanoyl]oxy}-2-[(17-methyloctadecanoyl)oxy]propyl phosphonato]oxy}propanoate |
|---|
|
Traditional IUPAC Name: |
2-amino-3-{[(2R)-3-{[8-(2-hexylcyclopropyl)octanoyl]oxy}-2-[(17-methyloctadecanoyl)oxy]propyl phosphonato]oxy}propanoate |
|---|
| SMILES: | CCCCCCC1CC1CCCCCCCC(=O)OC[C@H](COP([O-])(=O)OCC(N)C([O-])=O)OC(=O)CCCCCCCCCCCCCCCC(C)C |
|---|
|
Chemical Taxonomy |
|---|
|
Taxonomy Description | This compound belongs to the class of organic compounds known as phosphatidylserines. These are glycerophosphoserines in which two fatty acids are bonded to the glycerol moiety through ester linkages. |
|---|
|
Kingdom |
Organic compounds |
|---|
| Super Class | Lipids and lipid-like molecules |
|---|
|
Class |
Glycerophospholipids |
|---|
| Sub Class | Glycerophosphoserines |
|---|
|
Direct Parent |
Phosphatidylserines |
|---|
| Alternative Parents |
|
|---|
| Substituents |
- Diacyl-glycerol-3-phosphoserine
- Alpha-amino acid or derivatives
- Alpha-amino acid
- Tricarboxylic acid or derivatives
- Phosphoethanolamine
- Dialkyl phosphate
- Fatty acid ester
- Fatty acyl
- Alkyl phosphate
- Phosphoric acid ester
- Organic phosphoric acid derivative
- Organic phosphate
- Carboxylic acid salt
- Carboxylic acid ester
- Carboxylic acid
- Carboxylic acid derivative
- Hydrocarbon derivative
- Primary amine
- Organooxygen compound
- Organonitrogen compound
- Primary aliphatic amine
- Carbonyl group
- Amine
- Organic anion
- Aliphatic homomonocyclic compound
|
|---|
| Molecular Framework |
Aliphatic homomonocyclic compounds |
|---|
| External Descriptors |
Not Available |
|---|
|
Physical Properties |
|---|
| State: |
Solid |
|---|
| Charge: | -1 |
|---|
|
Melting point: |
Not Available |
|---|
| Experimental Properties: |
|
|---|
| Predicted Properties |
|
|---|
|
Biological Properties |
|---|
| Cellular Locations: |
Membrane |
|---|
| Reactions: | |
|---|
|
Pathways: |
|
|---|
|
Spectra |
|---|
| Spectra: |
|
|---|
|
References |
|---|
| References: |
- Casadei MA, Ma?as P, Niven G, Needs E, Mackey BM. (2002) "Role of membrane fluidity in pressure resistance of Escherichia coli NCTC 8164." Appl Environ Microbiol. 68(12):5965-72. Pubmed: 12450817
- Kanehisa, M., Goto, S., Sato, Y., Furumichi, M., Tanabe, M. (2012). "KEGG for integration and interpretation of large-scale molecular data sets." Nucleic Acids Res 40:D109-D114. Pubmed: 22080510
- Yurtsever D. (2007). Fatty acid methyl ester profiling of Enterococcus and Esherichia coli for microbial source tracking. M.sc. Thesis. Villanova University: U.S.A
|
|---|
| Synthesis Reference: |
Not Available |
|---|
| Material Safety Data Sheet (MSDS) |
Not Available |
|---|
|
Links |
|---|
| External Links: |
| Resource | Link |
|---|
| CHEBI ID | Not Available | | HMDB ID | Not Available | | Pubchem Compound ID | Not Available | | Kegg ID | Not Available | | ChemSpider ID | Not Available | | Wikipedia ID | Not Available | | BioCyc ID | Not Available |
|
|---|