|
Record Information |
|---|
| Version |
1.0 |
|---|
| Update Date |
1/22/2018 11:54:54 AM |
|---|
|
Metabolite ID | PAMDB001969 |
|---|
|
Identification |
|---|
| Name: |
Ubiquinol-2 |
|---|
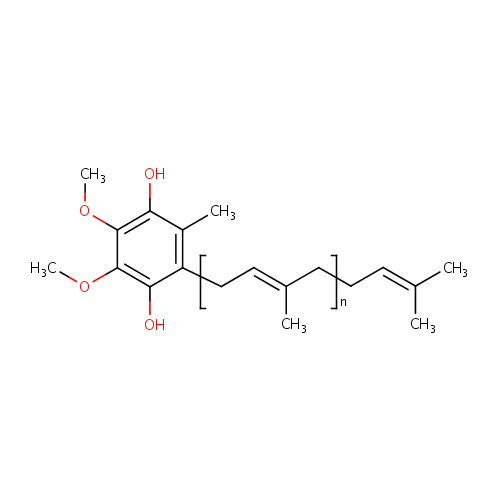
| Description: | Ubiquinol-2 is a member of the chemical class known as Polyprenylbenzoquinols. They are reduced forms of polyprenylbenzoquinines (ubiquinones). These are compounds containing a polyisoprene chain attached to a quinol at the second ring position. Ubiquiol-2 has just 2 isoprene units. Normally in Pseudomonas aeruginosa the active form of Ubiquinol has 8 isoprene units (Ubiquinol-8) and in humans it normally has 10. Ubiquinol-2 is a ??ailed??or incomplete version of Ubiquinol 8 that arises from conjugation by a shortened prenyl tail via 4-hydroxybenzoate polyprenyltransferase. Coenzyme Q(n) exists in three redox states, fully oxidized (ubiquinone), partially reduced (semiquinones or ubisemiquinones), and fully reduced (ubiquinols). The redox functions of ubiquinol in cellular energy production and antioxidant protection are based on the ability to exchange two electrons in a redox cycle between ubiquinol (reduced) and the ubiquinone (oxidized) form. Ubiquionols are important in cellular respiration. They are fat-soluble and therefore mobile in cellular membranes; they play a unique role in the electron transport chain (ETC). In the inner bacterial membrane, electrons from NADH and succinate pass through the ETC to the oxygen, which is then reduced to water. The transfer of electrons through ETC results in the pumping of H+ across the membrane creating a proton gradient across the membrane, which is used by ATP synthase (located on the membrane) to generate ATP. |
|---|
|
Structure |
|
|---|
| Synonyms: | |
|---|
|
Chemical Formula: |
(C5H8)nC14H20O4 |
|---|
| Average Molecular Weight: |
Not Available |
|---|
| Monoisotopic Molecular
Weight: |
Not Available |
|---|
| InChI Key: |
RNUCUWWMTTWKAH-JLHYYAGUSA-N |
|---|
| InChI: | InChI=1S/C19H28O4/c1-12(2)8-7-9-13(3)10-11-15-14(4)16(20)18(22-5)19(23-6)17(15)21/h8,10,20-21H,7,9,11H2,1-6H3/b13-10+ |
|---|
| CAS
number: |
Not Available |
|---|
| IUPAC Name: | Not Available |
|---|
|
Traditional IUPAC Name: |
Not Available |
|---|
| SMILES: | Not Available |
|---|
|
Chemical Taxonomy |
|---|
|
Taxonomy Description | This compound belongs to the class of organic compounds known as prenylated hydroquinones. These are quinones with a structure characterized by the hydroquinone ring substituted by an prenyl side-chain. |
|---|
|
Kingdom |
Organic compounds |
|---|
| Super Class | Lipids and lipid-like molecules |
|---|
|
Class |
Prenol lipids |
|---|
| Sub Class | Quinone and hydroquinone lipids |
|---|
|
Direct Parent |
Prenylated hydroquinones |
|---|
| Alternative Parents |
|
|---|
| Substituents |
- Prenylbenzoquinol
- Ubiquinol skeleton
- O-dimethoxybenzene
- Dimethoxybenzene
- Monoterpenoid
- Monocyclic monoterpenoid
- Methoxyphenol
- Aromatic monoterpenoid
- Hydroxyquinol derivative
- Methoxybenzene
- Phenol ether
- O-cresol
- M-cresol
- Hydroquinone
- Anisole
- Toluene
- Phenol
- Alkyl aryl ether
- Benzenoid
- Monocyclic benzene moiety
- Ether
- Hydrocarbon derivative
- Organooxygen compound
- Aromatic homomonocyclic compound
|
|---|
| Molecular Framework |
Aromatic homomonocyclic compounds |
|---|
| External Descriptors |
Not Available |
|---|
|
Physical Properties |
|---|
| State: |
Not Available |
|---|
| Charge: | Not Available |
|---|
|
Melting point: |
Not Available |
|---|
| Experimental Properties: |
|
|---|
| Predicted Properties |
|
|---|
|
Biological Properties |
|---|
| Cellular Locations: |
Cytoplasm |
|---|
| Reactions: | |
|---|
|
Pathways: |
Not Available |
|---|
|
Spectra |
|---|
| Spectra: |
|
|---|
|
References |
|---|
| References: |
- Winder, C. L., Dunn, W. B., Schuler, S., Broadhurst, D., Jarvis, R., Stephens, G. M., Goodacre, R. (2008). "Global metabolic profiling of Escherichia coli cultures: an evaluation of methods for quenching and extraction of intracellular metabolites." Anal Chem 80:2939-2948. Pubmed: 18331064
|
|---|
| Synthesis Reference: |
Not Available |
|---|
| Material Safety Data Sheet (MSDS) |
Not Available |
|---|
|
Links |
|---|
| External Links: |
| Resource | Link |
|---|
| CHEBI ID | Not Available | | HMDB ID | HMDB01304 | | Pubchem Compound ID | 5280344 | | Kegg ID | C00390 | | ChemSpider ID | 4444052 | | Wikipedia ID | Not Available | | BioCyc ID | Not Available |
|
|---|