|
Record Information |
|---|
| Version |
1.0 |
|---|
| Update Date |
1/22/2018 11:54:54 AM |
|---|
|
Metabolite ID | PAMDB001300 |
|---|
|
Identification |
|---|
| Name: |
UDP-N-Acetylmuramyl-L-Ala |
|---|
| Description: | UDP-n-acetylmuramyl-L-Ala is a precursor to peptidoglycan synthesis. UDP-N-acetylmuramoyl-L-alanine (UDP-MurNAc-L-Ala), which is the nucleotide substrate of the D-glutamic-acid-adding enzyme (the murD gene product) catalyzes key steps in the pathway for peptidoglycan synthesis. (PMID 8098327) MurD (UDP-N-acetylmuramoyl-L-alanine:D-glutamate ligase) is the second enzyme in the series of Mur ligases, and it catalyzes the addition of D-glutamic acid (D-Glu) to the cytoplasmic intermediate UDP-N-acetylmuramoyl-L-alanine (UMA). (PMID 19007109) The peptidoglycan synthesis pathway starts at the cytoplasm, where in six steps the peptidoglycan precursor a UDP-N-acetylmuramoyl-pentapeptide is synthesized. This precursor is then attached to the memberane acceptor all-trans-undecaprenyl phosphate, generating a N-acetylmuramoyl-pentapeptide-diphosphoundecaprenol, also known as lipid I. Another transferase then adds UDP-N-acetyl-D-glucosamine, yielding the complete monomeric unit a lipid II, also known as lipid II. This final lipid intermediate is transferred through the membrane. The peptidoglycan monomers are then polymerized on the outside surface by glycosyltransferases, which form the linear glycan chains, and transpeptidases, which catalyze the formation of peptide crosslinks. |
|---|
|
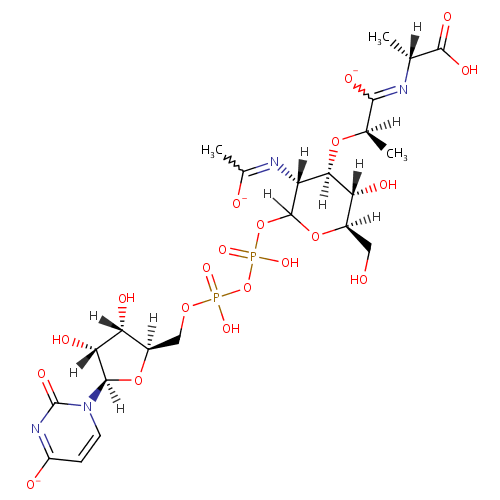
Structure |
|
|---|
| Synonyms: | - UDP-N-acetylmuramoyl-L-alanine
- UDP-N-Acetylmuramoyl-L-alanine
|
|---|
|
Chemical Formula: |
C23H33N4O20P2 |
|---|
| Average Molecular Weight: |
747.4704 |
|---|
| Monoisotopic Molecular
Weight: |
747.11633754 |
|---|
| InChI Key: |
NTMMCWJNQNKACG-JKXSCJIPSA-K |
|---|
| InChI: | InChI=1S/C23H36N4O20P2/c1-8(21(35)36)24-19(34)9(2)43-18-14(25-10(3)29)22(45-11(6-28)16(18)32)46-49(40,41)47-48(38,39)42-7-12-15(31)17(33)20(44-12)27-5-4-13(30)26-23(27)37/h4-5,8-9,11-12,14-18,20,22,28,31-33H,6-7H2,1-3H3,(H,24,34)(H,25,29)(H,35,36)(H,38,39)(H,40,41)(H,26,30,37)/p-3/t8-,9-,11-,12-,14-,15-,16-,17-,18-,20-,22?/m1/s1 |
|---|
| CAS
number: |
Not Available |
|---|
| IUPAC Name: | (2R)-N-[(1R)-1-carboxyethyl]-2-{[(3R,4R,5S,6R)-2-({[({[(2R,3S,4R,5R)-3,4-dihydroxy-5-(4-oxido-2-oxo-1,2-dihydropyrimidin-1-yl)oxolan-2-yl]methoxy}(hydroxy)phosphoryl)oxy](hydroxy)phosphoryl}oxy)-5-hydroxy-6-(hydroxymethyl)-3-[(1-oxidoethylidene)amino]oxan-4-yl]oxy}propanecarboximidate |
|---|
|
Traditional IUPAC Name: |
(2R)-N-[(1R)-1-carboxyethyl]-2-{[(3R,4R,5S,6R)-2-[({[(2R,3S,4R,5R)-3,4-dihydroxy-5-(4-oxido-2-oxopyrimidin-1-yl)oxolan-2-yl]methoxy(hydroxy)phosphoryl}oxy(hydroxy)phosphoryl)oxy]-5-hydroxy-6-(hydroxymethyl)-3-[(1-oxidoethylidene)amino]oxan-4-yl]oxy}propanecarboximidate |
|---|
| SMILES: | [H][C@](C)(O[C@@]1([H])[C@]([H])(O)[C@@]([H])(CO)OC([H])(OP(O)(=O)OP(O)(=O)OC[C@@]2([H])O[C@@]([H])(N3C=CC([O-])=NC3=O)[C@]([H])(O)[C@]2([H])O)[C@]1([H])N=C(C)[O-])C([O-])=N[C@]([H])(C)C(O)=O |
|---|
|
Chemical Taxonomy |
|---|
|
Taxonomy Description | This compound belongs to the class of organic compounds known as pyrimidine nucleotide sugars. These are pyrimidine nucleotides bound to a saccharide derivative through the terminal phosphate group. |
|---|
|
Kingdom |
Organic compounds |
|---|
| Super Class | Nucleosides, nucleotides, and analogues |
|---|
|
Class |
Pyrimidine nucleotides |
|---|
| Sub Class | Pyrimidine nucleotide sugars |
|---|
|
Direct Parent |
Pyrimidine nucleotide sugars |
|---|
| Alternative Parents |
|
|---|
| Substituents |
- Pyrimidine nucleotide sugar
- Pyrimidine ribonucleoside diphosphate
- N-acyl-alpha-hexosamine
- N-acyl-alpha amino acid or derivatives
- Glucosamine
- Amino sugar
- N-glycosyl compound
- Glycosyl compound
- Organic pyrophosphate
- Monosaccharide phosphate
- Alpha-amino acid or derivatives
- Monoalkyl phosphate
- Amino saccharide
- Pyrimidone
- Alkyl phosphate
- Pyrimidine
- Phosphoric acid ester
- Oxane
- Organic phosphoric acid derivative
- Organic phosphate
- Monosaccharide
- Hydropyrimidine
- Saccharide
- Heteroaromatic compound
- Oxolane
- Secondary alcohol
- 1,2-diol
- Oxacycle
- Azacycle
- Organoheterocyclic compound
- Monocarboxylic acid or derivatives
- Ether
- Dialkyl ether
- Carboxylic acid
- Carboxylic acid derivative
- Carboximidic acid derivative
- Carboximidic acid
- Hydrocarbon derivative
- Primary alcohol
- Organooxygen compound
- Organonitrogen compound
- Carbonyl group
- Alcohol
- Organic anion
- Aromatic heteromonocyclic compound
|
|---|
| Molecular Framework |
Aromatic heteromonocyclic compounds |
|---|
| External Descriptors |
Not Available |
|---|
|
Physical Properties |
|---|
| State: |
Not Available |
|---|
| Charge: | -2 |
|---|
|
Melting point: |
Not Available |
|---|
| Experimental Properties: |
|
|---|
| Predicted Properties |
|
|---|
|
Biological Properties |
|---|
| Cellular Locations: |
Cytoplasm |
|---|
| Reactions: | |
|---|
|
Pathways: |
Not Available |
|---|
|
Spectra |
|---|
| Spectra: |
|
|---|
|
References |
|---|
| References: |
- Humljan, J., Kotnik, M., Contreras-Martel, C., Blanot, D., Urleb, U., Dessen, A., Solmajer, T., Gobec, S. (2008). "Novel naphthalene-N-sulfonyl-D-glutamic acid derivatives as inhibitors of MurD, a key peptidoglycan biosynthesis enzyme." J Med Chem 51:7486-7494. Pubmed: 19007109
- Keseler, I. M., Collado-Vides, J., Santos-Zavaleta, A., Peralta-Gil, M., Gama-Castro, S., Muniz-Rascado, L., Bonavides-Martinez, C., Paley, S., Krummenacker, M., Altman, T., Kaipa, P., Spaulding, A., Pacheco, J., Latendresse, M., Fulcher, C., Sarker, M., Shearer, A. G., Mackie, A., Paulsen, I., Gunsalus, R. P., Karp, P. D. (2011). "EcoCyc: a comprehensive database of Escherichia coli biology." Nucleic Acids Res 39:D583-D590. Pubmed: 21097882
|
|---|
| Synthesis Reference: |
Not Available |
|---|
| Material Safety Data Sheet (MSDS) |
Not Available |
|---|
|
Links |
|---|
| External Links: |
| Resource | Link |
|---|
| CHEBI ID | Not Available | | HMDB ID | Not Available | | Pubchem Compound ID | 25246252 | | Kegg ID | Not Available | | ChemSpider ID | Not Available | | Wikipedia ID | Not Available | | BioCyc ID | CPD0-1456 | | EcoCyc ID | CPD0-1456 |
|
|---|