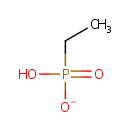
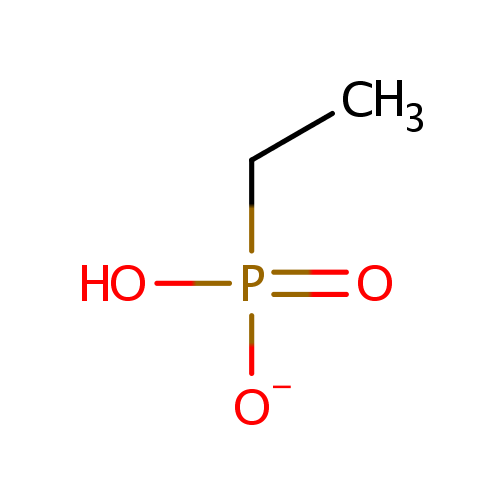
Ethylphosphonate (PAMDB001161)
| Record Information | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Version | 1.0 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Update Date | 1/22/2018 11:54:54 AM | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Metabolite ID | PAMDB001161 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Identification | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Name: | Ethylphosphonate | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Description: | Ethylphosphonate is a member of the chemical class known as Organic Phosphonic Acids and Derivatives. These are organic compounds containing phosphonic acid or a derivative thereof. phosphonoacetaldehyde is catalyzed by phosphonoacetaldehyde hydrolase. This is the first nucleic sequence report of the phosphonoacetaldehyde hydrolase, an enzyme involved in the carbon-phosphorus bond cleavage. (PMID 9332393). Phosphonates (Pn) are a large class of organophosphorus molecules that have direct carbon-phosphorus (C-P) bonds in place of the carbon-oxygen-phosphorus ester bond. In bacteria two pathways exist for Pn breakdown for use as a P source: the phosphonatase and C-P lyase pathways. These pathways differ both in regard to their substrate specificity and their cleavage mechanism. The phosphonatase pathway acts on the natural Pn alpha-aminoethylphosphonate (AEPn). In a two-step process it leads to cleavage of the C-P bond by a hydrolysis reaction requiring an adjacent carbonyl group. In contrast the C-P lyase pathway has a broad substrate specificity. It leads to cleavage of substituted Pn (such as AEPn) as well as unsubstituted Pn by a mechanism involving redox or radical chemistry. Due to its broad substrate specificity, the C-P lyase pathway is generally thought to be responsible for the breakdown of Pn herbicides (such as glyphosate) by bacteria. | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Structure | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Synonyms: |
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Chemical Formula: | C2H6O3P | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Average Molecular Weight: | 109.041 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Monoisotopic Molecular Weight: | 109.00545557 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| InChI Key: | GATNOFPXSDHULC-UHFFFAOYSA-M | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| InChI: | InChI=1S/C2H7O3P/c1-2-6(3,4)5/h2H2,1H3,(H2,3,4,5)/p-1 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| CAS number: | 6779-09-5 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| IUPAC Name: | hydrogen ethylphosphonate | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Traditional IUPAC Name: | hydrogen ethylphosphonate | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| SMILES: | CCP(O)([O-])=O | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Chemical Taxonomy | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Taxonomy Description | This compound belongs to the class of organic compounds known as organic phosphonic acids. These are organic compounds containing phosphonic acid. | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Kingdom | Organic compounds | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Super Class | Organophosphorus compounds | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Class | Organic phosphonic acids and derivatives | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Sub Class | Organic phosphonic acids | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Direct Parent | Organic phosphonic acids | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Alternative Parents | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Substituents |
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Molecular Framework | Aliphatic acyclic compounds | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| External Descriptors |
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Physical Properties | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| State: | Not Available | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Charge: | -1 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Melting point: | Not Available | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Experimental Properties: |
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Predicted Properties |
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Biological Properties | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Cellular Locations: | Cytoplasm | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Reactions: | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Pathways: | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Spectra | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Spectra: |
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| References | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| References: |
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Synthesis Reference: | Not Available | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Material Safety Data Sheet (MSDS) | Not Available | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Links | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| External Links: |
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Transporters
- General function:
- Involved in transporter activity
- Specific function:
- Part of the binding-protein-dependent transport system for phosphonates; probably responsible for the translocation of the substrate across the membrane
- Gene Name:
- phnE
- Locus Tag:
- PA3382
- Molecular weight:
- 28.4 kDa