|
Record Information |
|---|
| Version |
1.0 |
|---|
| Update Date |
1/22/2018 11:54:54 AM |
|---|
|
Metabolite ID | PAMDB000971 |
|---|
|
Identification |
|---|
| Name: |
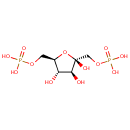
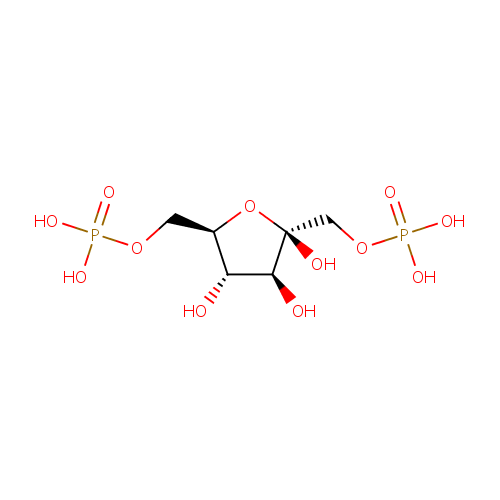
beta-D-Fructose 1,6-bisphosphate |
|---|
| Description: | Beta-D-fructose 1,6-bisphosphate is a member of the chemical class known as Pentoses. These are monosaccharides in which the carbohydrate moiety contains five carbon atoms. The hydrolysis of fructose 1,6-bisphosphate to fructose 6-phosphate is a key reaction of carbohydrate metabolism. (PMID 3008716) Fructose-1,6-bisphosphate (F-1,6-P2) is an allosteric activator of two key enzymes of glycolysis: phosphofructokinase and pyruvate kinase. (PMID 18025560) In gluconeogenesis, fructose 6-phosphate is formed from fructose 1,6-bisphosphate, and if fructose 1,6-bisphosphate were reformed by the phosphofructokinase reaction there would be a "gluconeogenic futile cycle". (PMID 6217196) Fructose-1,6-bisphosphate (FBP) aldolase is an essential glycolytic enzyme that reversibly cleaves its ketohexose substrate into triose phosphates. (PMID 14699122) Fructose 1-phosphate is a metabolite that plays a regulatory role in metabolism and is best measured using an assay based on its conversion to fructose 1,6-bisphosphate by a bacterial fructose-1-phosphate kinase (Fru1PK). (PMID 10833389) For growth, the assimilated fructose is sequentially phosphorylated by ATP and (i) manno(fructo)kinase, to form fructose 6-phosphate, and (ii) phosphofructokinase, to form fructose 1,6-bisphosphate, which is a member of central routes of glycolysis and gluconeogenesis. (PMID 17159144) |
|---|
|
Structure |
|
|---|
| Synonyms: | - β-D-fructose-1,6-diphosphate
- β-D-fructose-1,6-diphosphoric acid
- 1,6-Di-O-phosphono-b-D-fructofuranose
- 1,6-Di-O-phosphono-beta-D-fructofuranose
- 1,6-Di-O-phosphono-β-D-fructofuranose
- 6055-82-9 (Calcium[1:2] salt)
- b Fructose 1,6-diphosphate
- b Fructose 1,6-diphosphoric acid
- b-D-Fructofuranose 1,6-bis(dihydrogen phosphate)
- b-D-Fructofuranose 1,6-bis(dihydrogen phosphoric acid)
- b-D-Fructofuranose 1,6-bisphosphate
- b-D-Fructofuranose 1,6-bisphosphoric acid
- b-D-Fructofuranose, 1,6-bis(dihydrogen phosphate)
- b-D-Fructofuranose, 1,6-bis(dihydrogen phosphoric acid)
- b-D-Fructose 1,6-bisphosphate
- b-D-Fructose 1,6-bisphosphoric acid
- b-D-Fructose-1,6-diphosphate
- b-D-Fructose-1,6-diphosphoric acid
- Beta Fructose 1,6-diphosphate
- beta Fructose 1,6-diphosphoric acid
- Beta-D-Fructofuranose 1,6-bis(dihydrogen phosphate)
- beta-D-Fructofuranose 1,6-bis(dihydrogen phosphoric acid)
- Beta-D-Fructofuranose 1,6-bisphosphate
- beta-D-Fructofuranose 1,6-bisphosphoric acid
- Beta-D-Fructofuranose, 1,6-bis(dihydrogen phosphate)
- beta-D-Fructofuranose, 1,6-bis(dihydrogen phosphoric acid)
- beta-D-Fructose 1,6-bisphosphoric acid
- Beta-D-Fructose-1,6-diphosphate
- beta-D-Fructose-1,6-diphosphoric acid
- BFP
- D-Arabino-2-Hexulose-1,6-bis(dihydrogenphosphat)
- D-Fructofuranose, 1,6-bis(dihydrogen phosphate)
- D-Fructofuranose, 1,6-bis(dihydrogen phosphoric acid)
- D-Fructose 1,6-bis(dihydrogen phosphate)
- D-Fructose 1,6-bis(dihydrogen phosphoric acid)
- D-Fructose, 1,6-bis(dihydrogen phosphate)
- D-Fructose, 1,6-bis(dihydrogen phosphoric acid)
- D-Fructose-1,6-bis(dihydrogenphosphat)
- D-Fructose-1,6-bisphosphate
- D-Fructose-1,6-bisphosphoric acid
- D-Fructose-1,6-diphosphate
- D-Fructose-1,6-diphosphoric acid
- FBP
- Fructose 1,6-bisphosphate
- Fructose 1,6-bisphosphoric acid
- Fructose 1,6-diphosphate
- Fructose 1,6-diphosphoric acid
- Fructose-1,6-biphosphate
- Fructose-1,6-biphosphoric acid
- Fructose-1,6-bisphosphate
- Fructose-1,6-bisphosphoric acid
- Fructose-1,6-diphosphate
- Fructose-1,6-diphosphoric acid
- Harden-young-ester
- β Fructose 1,6-diphosphate
- β Fructose 1,6-diphosphoric acid
- β-D-Fructofuranose 1,6-bis(dihydrogen phosphate)
- β-D-Fructofuranose 1,6-bis(dihydrogen phosphoric acid)
- β-D-Fructofuranose 1,6-bisphosphate
- β-D-Fructofuranose 1,6-bisphosphoric acid
- β-D-Fructofuranose, 1,6-bis(dihydrogen phosphate)
- β-D-Fructofuranose, 1,6-bis(dihydrogen phosphoric acid)
- β-D-Fructose 1,6-bisphosphate
- β-D-Fructose 1,6-bisphosphoric acid
- β-D-Fructose-1,6-diphosphate
- β-D-Fructose-1,6-diphosphoric acid
|
|---|
|
Chemical Formula: |
C6H14O12P2 |
|---|
| Average Molecular Weight: |
340.1157 |
|---|
| Monoisotopic Molecular
Weight: |
339.996048936 |
|---|
| InChI Key: |
RNBGYGVWRKECFJ-ARQDHWQXSA-N |
|---|
| InChI: | InChI=1S/C6H14O12P2/c7-4-3(1-16-19(10,11)12)18-6(9,5(4)8)2-17-20(13,14)15/h3-5,7-9H,1-2H2,(H2,10,11,12)(H2,13,14,15)/t3-,4-,5+,6-/m1/s1 |
|---|
| CAS
number: |
125740-83-2 |
|---|
| IUPAC Name: | {[(2R,3S,4S,5R)-2,3,4-trihydroxy-5-[(phosphonooxy)methyl]oxolan-2-yl]methoxy}phosphonic acid |
|---|
|
Traditional IUPAC Name: |
β fructose 1,6-diphosphate |
|---|
| SMILES: | O[C@H]1[C@H](O)[C@@](O)(COP(O)(O)=O)O[C@@H]1COP(O)(O)=O |
|---|
|
Chemical Taxonomy |
|---|
|
Taxonomy Description | This compound belongs to the class of organic compounds known as c-glycosyl compounds. These are glycoside in which a sugar group is bonded through one carbon to another group via a C-glycosidic bond. |
|---|
|
Kingdom |
Organic compounds |
|---|
| Super Class | Organooxygen compounds |
|---|
|
Class |
Carbohydrates and carbohydrate conjugates |
|---|
| Sub Class | Glycosyl compounds |
|---|
|
Direct Parent |
C-glycosyl compounds |
|---|
| Alternative Parents |
|
|---|
| Substituents |
- C-glycosyl compound
- Monosaccharide phosphate
- Monoalkyl phosphate
- Alkyl phosphate
- Phosphoric acid ester
- Organic phosphoric acid derivative
- Organic phosphate
- Monosaccharide
- Oxolane
- Secondary alcohol
- Polyol
- Hemiacetal
- 1,2-diol
- Oxacycle
- Organoheterocyclic compound
- Hydrocarbon derivative
- Alcohol
- Aliphatic heteromonocyclic compound
|
|---|
| Molecular Framework |
Aliphatic heteromonocyclic compounds |
|---|
| External Descriptors |
|
|---|
|
Physical Properties |
|---|
| State: |
Not Available |
|---|
| Charge: | -4 |
|---|
|
Melting point: |
Not Available |
|---|
| Experimental Properties: |
|
|---|
| Predicted Properties |
|
|---|
|
Biological Properties |
|---|
| Cellular Locations: |
Cytoplasm |
|---|
| Reactions: | |
|---|
|
Pathways: |
- Fructose and mannose metabolism pae00051
- Glycolysis / Gluconeogenesis pae00010
- Microbial metabolism in diverse environments pae01120
- Pentose phosphate pathway pae00030
|
|---|
|
Spectra |
|---|
| Spectra: |
|
|---|
|
References |
|---|
| References: |
- Bennett, B. D., Kimball, E. H., Gao, M., Osterhout, R., Van Dien, S. J., Rabinowitz, J. D. (2009). "Absolute metabolite concentrations and implied enzyme active site occupancy in Escherichia coli." Nat Chem Biol 5:593-599. Pubmed: 19561621
- Buchholz, A., Takors, R., Wandrey, C. (2001). "Quantification of intracellular metabolites in Escherichia coli K12 using liquid chromatographic-electrospray ionization tandem mass spectrometric techniques." Anal Biochem 295:129-137. Pubmed: 11488613
- Daldal, F., Fraenkel, D. G. (1983). "Assessment of a futile cycle involving reconversion of fructose 6-phosphate to fructose 1,6-bisphosphate during gluconeogenic growth of Escherichia coli." J Bacteriol 153:390-394. Pubmed: 6217196
- Izard, T., Sygusch, J. (2004). "Induced fit movements and metal cofactor selectivity of class II aldolases: structure of Thermus aquaticus fructose-1,6-bisphosphate aldolase." J Biol Chem 279:11825-11833. Pubmed: 14699122
- Kanehisa, M., Goto, S., Sato, Y., Furumichi, M., Tanabe, M. (2012). "KEGG for integration and interpretation of large-scale molecular data sets." Nucleic Acids Res 40:D109-D114. Pubmed: 22080510
- Keseler, I. M., Collado-Vides, J., Santos-Zavaleta, A., Peralta-Gil, M., Gama-Castro, S., Muniz-Rascado, L., Bonavides-Martinez, C., Paley, S., Krummenacker, M., Altman, T., Kaipa, P., Spaulding, A., Pacheco, J., Latendresse, M., Fulcher, C., Sarker, M., Shearer, A. G., Mackie, A., Paulsen, I., Gunsalus, R. P., Karp, P. D. (2011). "EcoCyc: a comprehensive database of Escherichia coli biology." Nucleic Acids Res 39:D583-D590. Pubmed: 21097882
- Kornberg, H., Lourenco, C. (2006). "A route for fructose utilization by Escherichia coli involving the fucose regulon." Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 103:19496-19499. Pubmed: 17159144
- Nghiem, N. P., Cofer, T. M. (2007). "Effect of a nonmetabolizable analog of fructose-1,6-bisphosphate on glycolysis and ethanol production in strains of Saccharomyces cerevisiae and Escherichia coli." Appl Biochem Biotechnol 141:335-347. Pubmed: 18025560
- Park, C., Park, C., Lee, Y., Lee, S.Y., Oh, H.B., Lee, J. (2011) Determination of the Intracellular Concentration of Metabolites in Escherichia coli Collected during the Exponential and Stationary Growth Phases using Liquid Chromatography-Mass Spectrometry. Bull Korean Chem. Soc. 32: 524-530.
- Peng, L., Arauzo-Bravo, M. J., Shimizu, K. (2004). "Metabolic flux analysis for a ppc mutant Escherichia coli based on 13C-labelling experiments together with enzyme activity assays and intracellular metabolite measurements." FEMS Microbiol Lett 235:17-23. Pubmed: 15158257
- Veiga-da-Cunha, M., Hoyoux, A., Van Schaftingen, E. (2000). "Overexpression and purification of fructose-1-phosphate kinase from Escherichia coli: application to the assay of fructose 1-phosphate." Protein Expr Purif 19:48-52. Pubmed: 10833389
|
|---|
| Synthesis Reference: |
Not Available |
|---|
| Material Safety Data Sheet (MSDS) |
Not Available |
|---|
|
Links |
|---|
| External Links: |
|
|---|