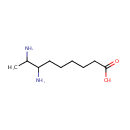
7,8-Diaminononanoate (PAMDB000957)
| Record Information | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Version | 1.0 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Update Date | 1/22/2018 11:54:54 AM | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Metabolite ID | PAMDB000957 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Identification | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Name: | 7,8-Diaminononanoate | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Description: | 7,8-diaminononanoate (or DAPA) is an intermediate in biotin biosynthesis. It is a substrate for Adenosylmethionine-8-amino-7-oxononanoate aminotransferase (or bioA). This enzyme catalyzes the transfer of the alpha-amino group from S-adenosyl-L-methionine (SAM) to 7-keto-8-aminopelargonic acid (KAPA) to form 7,8-diaminopelargonic acid (DAPA). The reaction is S-adenosyl-L-methionine + 8-amino-7-oxononanoate = S-adenosyl-4-methylthio-2-oxobutanoate + 7,8-diaminononanoate. DAPA is a simple intercalator, much like the widely studied 9-aminoacridine. (PMID 16180206; 16984394) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Structure | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Synonyms: |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Chemical Formula: | C9H19N2O2 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Average Molecular Weight: | 187.264 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Monoisotopic Molecular Weight: | 187.14520144 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| InChI Key: | KCEGBPIYGIWCDH-UHFFFAOYSA-M | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| InChI: | InChI=1S/C9H20N2O2/c1-7(10)8(11)5-3-2-4-6-9(12)13/h7-8H,2-6,10-11H2,1H3,(H,12,13)/p-1 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| CAS number: | 21738-21-6 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| IUPAC Name: | 7,8-diaminononanoic acid | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Traditional IUPAC Name: | 7,8-diaminopelargonic acid | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| SMILES: | CC(N)C(N)CCCCCC([O-])=O | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Chemical Taxonomy | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Taxonomy Description | This compound belongs to the class of organic compounds known as medium-chain fatty acids. These are fatty acids with an aliphatic tail that contains between 4 and 12 carbon atoms. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Kingdom | Organic compounds | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Super Class | Lipids and lipid-like molecules | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Class | Fatty Acyls | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Sub Class | Fatty acids and conjugates | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Direct Parent | Medium-chain fatty acids | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Alternative Parents | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Substituents |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Molecular Framework | Aliphatic acyclic compounds | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| External Descriptors | Not Available | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Physical Properties | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| State: | Not Available | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Charge: | 1 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Melting point: | Not Available | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Experimental Properties: |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Predicted Properties |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Biological Properties | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Cellular Locations: | Cytoplasm | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Reactions: | 8-Amino-7-oxononanoate + S-Adenosylmethionine <> S-Adenosyl-4-methylthio-2-oxobutanoate + 7,8-Diaminononanoate Adenosine triphosphate + 7,8-Diaminononanoate + Carbon dioxide <> ADP + Phosphate + Dethiobiotin Carbon dioxide + 7,8-Diaminononanoate + Adenosine triphosphate > Hydrogen ion + Dethiobiotin + Phosphate + ADP Adenosine triphosphate + 7,8-Diaminononanoate + Carbon dioxide > ADP + Inorganic phosphate + Dethiobiotin 8-Amino-7-oxononanoate + S-adenosyl-L-methionine > a sulfurated [sulfur carrier] + 7,8-Diaminononanoate + 7,8-Diaminononanoate 7,8-Diaminononanoate + Adenosine triphosphate + Carbon dioxide + 7,8-Diaminononanoate > Dethiobiotin + Adenosine diphosphate + Phosphate + ADP | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Pathways: | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Spectra | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Spectra: |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| References | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| References: |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Synthesis Reference: | Not Available | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Material Safety Data Sheet (MSDS) | Not Available | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Links | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| External Links: |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||