|
Record Information |
|---|
| Version |
1.0 |
|---|
| Update Date |
1/22/2018 11:54:54 AM |
|---|
|
Metabolite ID | PAMDB000745 |
|---|
|
Identification |
|---|
| Name: |
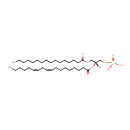
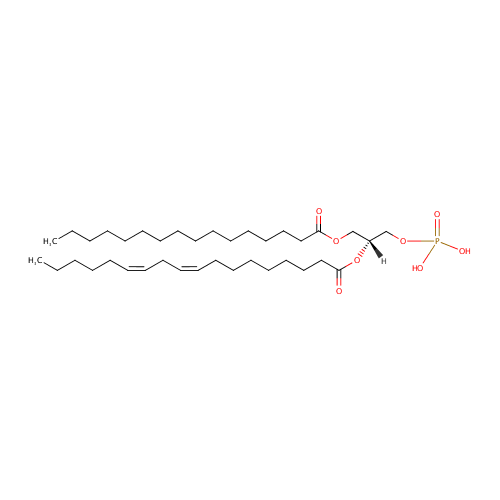
PA(16:0/18:2(9Z,12Z)) |
|---|
| Description: | PA(16:0/18:2(9Z,12Z)) is a phosphatidic acid. It is a glycerophospholipid in which a phosphate moiety occupies a glycerol substitution site. As is the case with diacylglycerols, phosphatidic acids can have many different combinations of fatty acids of varying lengths and saturation attached at the C-1 and C-2 positions. Fatty acids containing 16, 18 and 20 carbons are the most common. PA(16:0/18:2(9Z,12Z)), in particular, consists of one chain of palmitic acid at the C-1 position and one chain of linoleic acid at the C-2 position. Phosphatidic acids are quite rare but are extremely important as intermediates in the biosynthesis of triacylglycerols and phospholipids. PAs are biologically active lipids that can stimulate a large range of responses in many different cell types. Diacylglycerols (DAGs) can be converted to PAs by DAG kinases. Phospholipase Ds (PLDs), which catalyze the conversion of glycerolphospholipids, particularly phosphatidylcholine, to PAs and the conversion of N-arachidonoyl-phosphatidylethanolamine (NAPE) to anandamide and PAs are activated by several inflammatory mediators including bradykinin, ATP and glutamate. PAs activate downstream signaling pathways such as PKCs and mitogen-activated protein kinases (MAPKs). Circumstantial evidence that PAs are converted to DAGs. (PMID: 12618218, 16185776). |
|---|
|
Structure |
|
|---|
| Synonyms: | - 1-Hexadecanoyl-2-(9Z,12Z-octadecadienoyl)-sn-phosphatidate
- 1-Hexadecanoyl-2-(9Z,12Z-octadecadienoyl)-sn-phosphatidic acid
- 1-Palmitoyl-2-linoleoyl-sn-glycero-3-phosphate
- 1-Palmitoyl-2-linoleoyl-sn-glycero-3-phosphoric acid
- A 1,2-diacylglycerol-3-phosphate
- a 1,2-Diacylglycerol-3-phosphoric acid
- A 3-sn-phosphatidate
- a 3-sn-Phosphatidate
- a 3-sn-Phosphatidic acid
- A diacyl-glycerol-3p
- A diacyl-glycerol-p
- A diacylglycerol-3-phosphate
- a Diacylglycerol-3-phosphoric acid
- A phosphatidate
- A phosphatidic acid
- A phosphatidylglycerol
- An L-phosphatidate
- An L-phosphatidic acid
- DGP
- Diacylglycerol phosphate
- Diacylglycerol phosphoric acid
- PA(16:0/18:2)
- PA(16:0/18:2n6)
- PA(16:0/18:2w6)
- PA(34:2)
- Phosphatidate(16:0/18:2)
- Phosphatidate(16:0/18:2n6)
- Phosphatidate(16:0/18:2w6)
- Phosphatidate(34:2)
- Phosphatidic acid(16:0/18:2)
- Phosphatidic acid(16:0/18:2n6)
- Phosphatidic acid(16:0/18:2w6)
- Phosphatidic acid(34:2)
|
|---|
|
Chemical Formula: |
C37H69O8P |
|---|
| Average Molecular Weight: |
672.9127 |
|---|
| Monoisotopic Molecular
Weight: |
672.473005696 |
|---|
| InChI Key: |
YQMUIZXKIKXZHD-UMKNCJEQSA-N |
|---|
| InChI: | InChI=1S/C37H69O8P/c1-3-5-7-9-11-13-15-17-18-20-22-24-26-28-30-32-37(39)45-35(34-44-46(40,41)42)33-43-36(38)31-29-27-25-23-21-19-16-14-12-10-8-6-4-2/h11,13,17-18,35H,3-10,12,14-16,19-34H2,1-2H3,(H2,40,41,42)/b13-11-,18-17-/t35-/m1/s1 |
|---|
| CAS
number: |
Not Available |
|---|
| IUPAC Name: | [(2R)-3-(hexadecanoyloxy)-2-[(9Z,12Z)-octadeca-9,12-dienoyloxy]propoxy]phosphonic acid |
|---|
|
Traditional IUPAC Name: |
(2R)-3-(hexadecanoyloxy)-2-[(9Z,12Z)-octadeca-9,12-dienoyloxy]propoxyphosphonic acid |
|---|
| SMILES: | CCCCCCCCCCCCCCCC(=O)OC[C@]([H])(COP(O)(=O)O)OC(=O)CCCCCCC\C=C/C\C=C/CCCCC |
|---|
|
Chemical Taxonomy |
|---|
|
Taxonomy Description | This compound belongs to the class of organic compounds known as 1,2-diacylglycerol-3-phosphates. These are glycerol-3-phosphates in which the glycerol moiety is bonded to two aliphatic chains through ester linkages. |
|---|
|
Kingdom |
Organic compounds |
|---|
| Super Class | Lipids and lipid-like molecules |
|---|
|
Class |
Glycerophospholipids |
|---|
| Sub Class | Glycerophosphates |
|---|
|
Direct Parent |
1,2-diacylglycerol-3-phosphates |
|---|
| Alternative Parents |
|
|---|
| Substituents |
- 1,2-diacylglycerol-3-phosphate
- Monoalkyl phosphate
- Fatty acid ester
- Fatty acyl
- Alkyl phosphate
- Phosphoric acid ester
- Organic phosphoric acid derivative
- Organic phosphate
- Dicarboxylic acid or derivatives
- Carboxylic acid ester
- Carboxylic acid derivative
- Hydrocarbon derivative
- Organooxygen compound
- Carbonyl group
- Aliphatic acyclic compound
|
|---|
| Molecular Framework |
Aliphatic acyclic compounds |
|---|
| External Descriptors |
|
|---|
|
Physical Properties |
|---|
| State: |
Solid |
|---|
| Charge: | -2 |
|---|
|
Melting point: |
Not Available |
|---|
| Experimental Properties: |
|
|---|
| Predicted Properties |
|
|---|
|
Biological Properties |
|---|
| Cellular Locations: |
Membrane |
|---|
| Reactions: | |
|---|
|
Pathways: |
|
|---|
|
Spectra |
|---|
| Spectra: |
|
|---|
|
References |
|---|
| References: |
- Kanehisa, M., Goto, S., Sato, Y., Furumichi, M., Tanabe, M. (2012). "KEGG for integration and interpretation of large-scale molecular data sets." Nucleic Acids Res 40:D109-D114. Pubmed: 22080510
- Keseler, I. M., Collado-Vides, J., Santos-Zavaleta, A., Peralta-Gil, M., Gama-Castro, S., Muniz-Rascado, L., Bonavides-Martinez, C., Paley, S., Krummenacker, M., Altman, T., Kaipa, P., Spaulding, A., Pacheco, J., Latendresse, M., Fulcher, C., Sarker, M., Shearer, A. G., Mackie, A., Paulsen, I., Gunsalus, R. P., Karp, P. D. (2011). "EcoCyc: a comprehensive database of Escherichia coli biology." Nucleic Acids Res 39:D583-D590. Pubmed: 21097882
- Niedernberg, A., Tunaru, S., Blaukat, A., Ardati, A., Kostenis, E. (2003). "Sphingosine 1-phosphate and dioleoylphosphatidic acid are low affinity agonists for the orphan receptor GPR63." Cell Signal 15:435-446. Pubmed: 12618218
- Park KA, Vasko MR: Lipid mediators of sensitivity in sensory neurons. Trends Pharmacol Sci. 2005 Nov;26(11):571-7. Epub 2005 Sep 26. Pubmed: 16185776
- Yurtsever D. (2007). Fatty acid methyl ester profiling of Enterococcus and Esherichia coli for microbial source tracking. M.sc. Thesis. Villanova University: U.S.A
|
|---|
| Synthesis Reference: |
Not Available |
|---|
| Material Safety Data Sheet (MSDS) |
Not Available |
|---|
|
Links |
|---|
| External Links: |
|
|---|