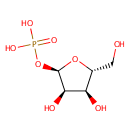
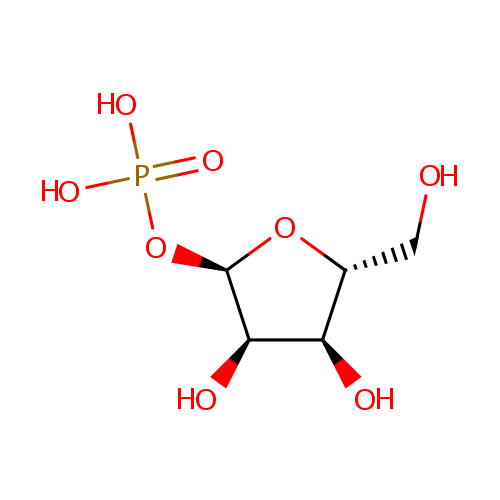
Ribose-1-phosphate (PAMDB000637)
| Record Information | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Version | 1.0 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Update Date | 1/22/2018 11:54:54 AM | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Metabolite ID | PAMDB000637 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Identification | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Name: | Ribose-1-phosphate | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Description: | Ribose 1-phosphate is an intermediate in the metabolism of Pyrimidine and the metabolism of Nicotinate and nicotinamide. It is a substrate for Uridine phosphorylase 2, Phosphoglucomutase, Purine nucleoside phosphorylase and Uridine phosphorylase 1. Ribose 1-phosphate can be formed from guanosine through the action of purine nucleoside phosphorylase. Ribose 1-phosphate can also act as a ribose donor in the synthesis of xanthosine as catalyzed by the same enzyme (purine nucleoside phosphorylase). The presence of guanase, which irreversibly converts guanine to xanthine, affects the overall process of guanosine transformation. The activated ribose moiety in Ribose 1-phosphate which stems from the catabolism of purine nucleosides can be transferred to uracil and, in the presence of ATP, used for the synthesis of pyrimidine nucleotides; therefore, purine nucleosides can act as ribose donors for the salvage of pyrimidine bases. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Structure | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Synonyms: |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Chemical Formula: | C5H11O8P | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Average Molecular Weight: | 230.1098 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Monoisotopic Molecular Weight: | 230.01915384 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| InChI Key: | YXJDFQJKERBOBM-TXICZTDVSA-N | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| InChI: | InChI=1S/C5H11O8P/c6-1-2-3(7)4(8)5(12-2)13-14(9,10)11/h2-8H,1H2,(H2,9,10,11)/t2-,3-,4-,5-/m1/s1 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| CAS number: | 14075-00-4 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| IUPAC Name: | {[(2R,3R,4S,5R)-3,4-dihydroxy-5-(hydroxymethyl)oxolan-2-yl]oxy}phosphonic acid | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Traditional IUPAC Name: | ribose 1-phosphate | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| SMILES: | OC[C@H]1O[C@H](OP(O)(O)=O)[C@H](O)[C@@H]1O | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Chemical Taxonomy | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Taxonomy Description | This compound belongs to the class of organic compounds known as monoalkyl phosphates. These are organic compounds containing a phosphate group that is linked to exactly one alkyl chain. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Kingdom | Organic compounds | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Super Class | Organophosphorus compounds | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Class | Organic phosphoric acids and derivatives | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Sub Class | Phosphate esters | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Direct Parent | Monoalkyl phosphates | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Alternative Parents | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Substituents |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Molecular Framework | Aliphatic heteromonocyclic compounds | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| External Descriptors |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Physical Properties | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| State: | Solid | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Charge: | -2 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Melting point: | Not Available | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Experimental Properties: |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Predicted Properties |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Biological Properties | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Cellular Locations: | Cytoplasm | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Reactions: | Guanosine + Phosphate <> Guanine + Ribose-1-phosphate Inosine + Phosphate <> Hypoxanthine + Ribose-1-phosphate Ribose-1-phosphate <> D-Ribose-5-phosphate Phosphate + Xanthosine <> Ribose-1-phosphate + Xanthine Phosphate + Uridine <> Ribose-1-phosphate + Uracil Adenosine + Phosphate <> Adenine + Ribose-1-phosphate alpha-D-Ribose 1-phosphate + Ribose-1-phosphate <> D-Ribose-5-phosphate Uridine + Phosphate <> Uracil + alpha-D-Ribose 1-phosphate + Ribose-1-phosphate Ribose-1-phosphate + Adenosine triphosphate > Hydrogen ion + Ribose 1,5-bisphosphate + ADP a purine ribonucleoside + Phosphate <> a purine base + Ribose-1-phosphate Purine nucleoside + Inorganic phosphate > Purine + Ribose-1-phosphate Uridine + Inorganic phosphate > Uracil + Ribose-1-phosphate Purine nucleoside + Phosphate + Purine deoxyribonucleoside <> Purine + Ribose-1-phosphate + Deoxyribose 1-phosphate | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Pathways: | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Spectra | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Spectra: |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| References | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| References: |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Synthesis Reference: | Tochikura, Tatsurokuro; Sakai, Takuo; Ogata, Koichi. Ribose 1-phosphate production by fermentation. Jpn. Tokkyo Koho (1969), 3 pp. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Material Safety Data Sheet (MSDS) | Not Available | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Links | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| External Links: |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Enzymes
- General function:
- Involved in intramolecular transferase activity, phosphotransferases
- Specific function:
- This enzyme participates in both the breakdown and synthesis of glucose
- Gene Name:
- pgm
- Locus Tag:
- PA5131
- Molecular weight:
- 55.6 kDa
Reactions
| Alpha-D-glucose 1-phosphate = alpha-D-glucose 6-phosphate. |