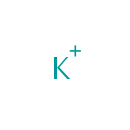Potassium (PAMDB000632)
| Record Information | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Version | 1.0 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Update Date | 1/22/2018 11:54:54 AM | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Metabolite ID | PAMDB000632 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Identification | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
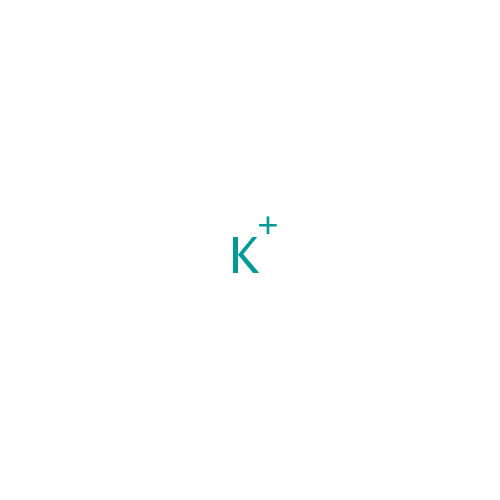
| Name: | Potassium | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Description: | Potassium is an essential electrolyte and part of many minerals. Potassium ion is a major intracellular cation in bacteria, plants and animals. It is necessary for the function of all living cells. There are a number of of potassium transport systems that regulate the intracellular potassium concentration. | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Structure | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Synonyms: |
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Chemical Formula: | K | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Average Molecular Weight: | 39.0983 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Monoisotopic Molecular Weight: | 38.963706861 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| InChI Key: | NPYPAHLBTDXSSS-UHFFFAOYSA-N | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| InChI: | InChI=1S/K/q+1 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| CAS number: | 7440-09-7 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| IUPAC Name: | potassium(1+) ion | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Traditional IUPAC Name: | potassium(1+) ion | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| SMILES: | [K+] | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Chemical Taxonomy | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Taxonomy Description | This compound belongs to the class of inorganic compounds known as homogeneous alkali metal compounds. These are inorganic compounds containing only metal atoms,with the largest atom being a alkali metal atom. | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Kingdom | Inorganic compounds | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Super Class | Homogeneous metal compounds | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Class | Homogeneous alkali metal compounds | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Sub Class | Not Available | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Direct Parent | Homogeneous alkali metal compounds | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Alternative Parents | Not Available | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Substituents |
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Molecular Framework | Acyclic compounds | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| External Descriptors |
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Physical Properties | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| State: | Solid | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Charge: | 1 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Melting point: | 63.2 °C | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Experimental Properties: |
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Predicted Properties |
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Biological Properties | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Cellular Locations: | Cytoplasm | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Reactions: | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Pathways: | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Spectra | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Spectra: |
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| References | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| References: |
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Synthesis Reference: | Alberti, Augusto. Recovering potassium salts from the refuse liquor of the manufacture of tartaric acid. (1910), US 957295 19100510 CAN 4:13164 AN 1910:13164 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Material Safety Data Sheet (MSDS) | Download (PDF) | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Links | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| External Links: |
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Enzymes
- General function:
- Involved in potassium-transporting ATPase activity
- Specific function:
- One of the components of the high-affinity ATP-driven potassium transport (or KDP) system, which catalyzes the hydrolysis of ATP coupled with the exchange of hydrogen and potassium ions
- Gene Name:
- kdpA
- Locus Tag:
- PA1633
- Molecular weight:
- 59.9 kDa
Reactions
| ATP + H(2)O + K(+)(Out) = ADP + phosphate + K(+)(In). |
- General function:
- Involved in nucleotide binding
- Specific function:
- One of the components of the high-affinity ATP-driven potassium transport (or KDP) system, which catalyzes the hydrolysis of ATP coupled with the exchange of hydrogen and potassium ions
- Gene Name:
- kdpB
- Locus Tag:
- PA1634
- Molecular weight:
- 73 kDa
Reactions
| ATP + H(2)O + K(+)(Out) = ADP + phosphate + K(+)(In). |
- General function:
- Involved in potassium-transporting ATPase activity
- Specific function:
- One of the components of the high-affinity ATP-driven potassium transport (or KDP) system, which catalyzes the hydrolysis of ATP coupled with the exchange of hydrogen and potassium ions. The C subunit may be involved in assembly of the KDP complex
- Gene Name:
- kdpC
- Locus Tag:
- PA1635
- Molecular weight:
- 19.3 kDa
Reactions
| ATP + H(2)O + K(+)(Out) = ADP + phosphate + K(+)(In). |
- General function:
- Not Available
- Specific function:
- Specific function unknown
- Gene Name:
- kdpF
- Locus Tag:
- PA1632
- Molecular weight:
- 3.2 kDa
Transporters
- General function:
- Involved in potassium-transporting ATPase activity
- Specific function:
- One of the components of the high-affinity ATP-driven potassium transport (or KDP) system, which catalyzes the hydrolysis of ATP coupled with the exchange of hydrogen and potassium ions
- Gene Name:
- kdpA
- Locus Tag:
- PA1633
- Molecular weight:
- 59.9 kDa
Reactions
| ATP + H(2)O + K(+)(Out) = ADP + phosphate + K(+)(In). |
- General function:
- Involved in nucleotide binding
- Specific function:
- One of the components of the high-affinity ATP-driven potassium transport (or KDP) system, which catalyzes the hydrolysis of ATP coupled with the exchange of hydrogen and potassium ions
- Gene Name:
- kdpB
- Locus Tag:
- PA1634
- Molecular weight:
- 73 kDa
Reactions
| ATP + H(2)O + K(+)(Out) = ADP + phosphate + K(+)(In). |
- General function:
- Involved in potassium-transporting ATPase activity
- Specific function:
- One of the components of the high-affinity ATP-driven potassium transport (or KDP) system, which catalyzes the hydrolysis of ATP coupled with the exchange of hydrogen and potassium ions. The C subunit may be involved in assembly of the KDP complex
- Gene Name:
- kdpC
- Locus Tag:
- PA1635
- Molecular weight:
- 19.3 kDa
Reactions
| ATP + H(2)O + K(+)(Out) = ADP + phosphate + K(+)(In). |
- General function:
- Involved in potassium ion transmembrane transporter activity
- Specific function:
- Responsible for the low-affinity transport of potassium into the cell, with the probable concomitant uptake of protons (symport system). Can also transport cesium
- Gene Name:
- kup
- Locus Tag:
- PA0917
- Molecular weight:
- 68.7 kDa
- General function:
- Involved in cation transmembrane transporter activity
- Specific function:
- Part of the constitutive potassium transport systems trkG and trkH. May regulate the transport activity of trkG and trkH systems. Binds to NAD+ and NADH
- Gene Name:
- trkA
- Locus Tag:
- PA0016
- Molecular weight:
- 49.9 kDa
- General function:
- Involved in cation transmembrane transporter activity
- Specific function:
- Low-affinity potassium transport system. Interacts with trk system potassium uptake protein trkA and requires trkE for transport activity
- Gene Name:
- trkH
- Locus Tag:
- PA3210
- Molecular weight:
- 52.6 kDa
- General function:
- Involved in solute:hydrogen antiporter activity
- Specific function:
- Transport system that facilitates potassium-efflux, possibly by potassium-proton antiport
- Gene Name:
- kefB
- Locus Tag:
- PA1207
- Molecular weight:
- 66.3 kDa
- General function:
- Not Available
- Specific function:
- Specific function unknown
- Gene Name:
- kdpF
- Locus Tag:
- PA1632
- Molecular weight:
- 3.2 kDa