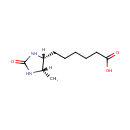
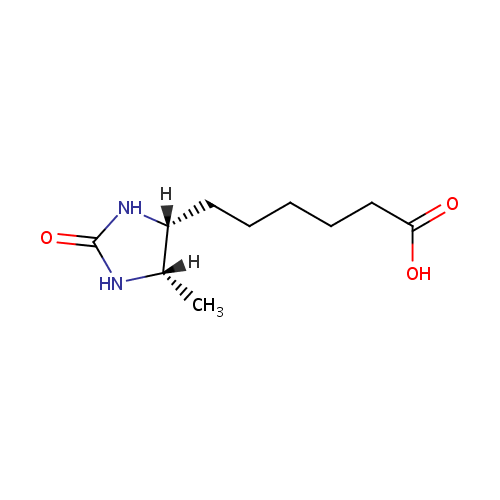
Dethiobiotin (PAMDB000517)
| Record Information | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Version | 1.0 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Update Date | 1/22/2018 11:54:54 AM | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Metabolite ID | PAMDB000517 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Identification | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Name: | Dethiobiotin | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Description: | Dethiobiotin is a synthetic metabolite that mimic the effects of biotin on gene expression and thus have biotin-like activities. It is an intermediate in biotin metabolism, and converted to biotin via biotin synthase (EC:2.8.1.6). (KEGG) Biotin serves as a coenzyme for carboxylases such as propionyl-CoA carboxylase. (PMID 12730407) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Structure | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Synonyms: |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Chemical Formula: | C10H18N2O3 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Average Molecular Weight: | 214.2615 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Monoisotopic Molecular Weight: | 214.131742452 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| InChI Key: | AUTOLBMXDDTRRT-JGVFFNPUSA-N | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| InChI: | InChI=1S/C10H18N2O3/c1-7-8(12-10(15)11-7)5-3-2-4-6-9(13)14/h7-8H,2-6H2,1H3,(H,13,14)(H2,11,12,15)/t7-,8+/m0/s1 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| CAS number: | 533-48-2 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| IUPAC Name: | 6-[(4R,5S)-5-methyl-2-oxoimidazolidin-4-yl]hexanoic acid | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Traditional IUPAC Name: | (4R,5S)-dethiobiotin | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| SMILES: | [H][C@@]1(C)NC(=O)N[C@]1([H])CCCCCC(O)=O | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Chemical Taxonomy | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Taxonomy Description | This compound belongs to the class of organic compounds known as medium-chain fatty acids. These are fatty acids with an aliphatic tail that contains between 4 and 12 carbon atoms. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Kingdom | Organic compounds | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Super Class | Lipids and lipid-like molecules | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Class | Fatty Acyls | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Sub Class | Fatty acids and conjugates | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Direct Parent | Medium-chain fatty acids | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Alternative Parents | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Substituents |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Molecular Framework | Aliphatic heteromonocyclic compounds | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| External Descriptors |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Physical Properties | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| State: | Solid | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Charge: | -1 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Melting point: | 157 °C | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Experimental Properties: |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Predicted Properties |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Biological Properties | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Cellular Locations: | Cytoplasm | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Reactions: | [2Fe-2S] iron-sulfur cluster + S-Adenosylmethionine + Dethiobiotin > [2Fe-1S] desulfurated iron-sulfur cluster + Biotin + 5'-Deoxyadenosine + Hydrogen ion + L-Methionine Dethiobiotin + Sulfur donor + 2 S-Adenosylmethionine + 2 e- + 2 Hydrogen ion <> Biotin +2 L-Methionine +2 5'-Deoxyadenosine Adenosine triphosphate + 7,8-Diaminononanoate + Carbon dioxide <> ADP + Phosphate + Dethiobiotin <i>S</i>-sulfanyl-[acceptor] + Dethiobiotin + S-Adenosylmethionine > an unsulfurated sulfur acceptor + Biotin + 5'-Deoxyadenosine + L-Methionine + Hydrogen ion Carbon dioxide + 7,8-Diaminononanoate + Adenosine triphosphate > Hydrogen ion + Dethiobiotin + Phosphate + ADP Adenosine triphosphate + 7,8-Diaminononanoate + Carbon dioxide > ADP + Inorganic phosphate + Dethiobiotin 7,8-Diaminononanoate + Adenosine triphosphate + Carbon dioxide + 7,8-Diaminononanoate > Dethiobiotin + Adenosine diphosphate + Phosphate + ADP Dethiobiotin + 2 S-adenosyl-L-methionine + 2 Hydrogen ion + a sulfurated [sulfur carrier] > Biotin +2 L-Methionine +2 5'-Deoxyadenosine | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Pathways: | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Spectra | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Spectra: |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| References | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| References: |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Synthesis Reference: | Kuzuhara, Hiroyoshi; Ohrui, Hiroshi; Emoto, Sakae. Syntheses with azido sugars. II. Conversion of D-glucose to (+)-dethiobiotin. Agricultural and Biological Chemistry (1971), 35(1), 8-17. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Material Safety Data Sheet (MSDS) | Download (PDF) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Links | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| External Links: |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||