|
Record Information |
|---|
| Version |
1.0 |
|---|
| Update Date |
1/22/2018 11:54:54 AM |
|---|
|
Metabolite ID | PAMDB000508 |
|---|
|
Identification |
|---|
| Name: |
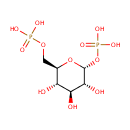
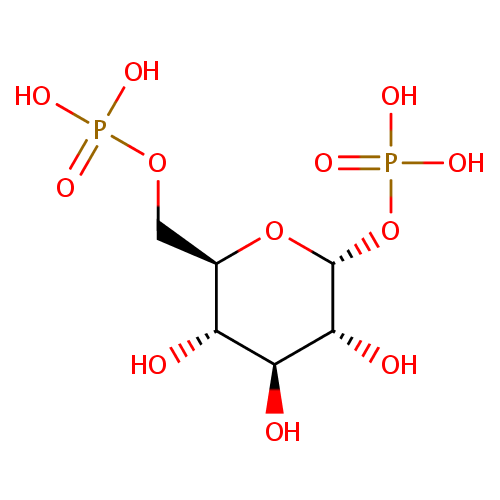
alpha-D-Glucose 1,6-bisphosphate |
|---|
| Description: | Alpha-D-glucose 1,6-bisphosphate is considered to be a major regulator of carbohydrate metabolism. Glucose 1,6-diphosphate (G 1,6-P2) have been recognized as a regulatory signal implicated in the control of metabolism, oxygen affinity of red cells and other cellular functions. G 1,6-P2 is a potent allosteric activator of phosphofructokinase. |
|---|
|
Structure |
|
|---|
| Synonyms: | - α-D-glucopyranose, 1,6-bis(dihydrogen phosphate)
- α-D-glucopyranose, 1,6-bis(dihydrogen phosphoric acid)
- α-D-glucose-1,6-P2
- α-D-glucose-1,6-P2
- a-D-1,6-Bis(dihydrogen phosphate) glucopyranose
- a-D-1,6-Bis(dihydrogen phosphoric acid) glucopyranose
- a-D-Glucopyranose, 1,6-bis(dihydrogen phosphate)
- a-D-Glucopyranose, 1,6-bis(dihydrogen phosphoric acid)
- A-D-Glucose 1,6-bis(dihydrogen phosphate)
- a-D-Glucose 1,6-bis(dihydrogen phosphoric acid)
- A-D-Glucose 1,6-bisphosphate
- a-D-Glucose 1,6-bisphosphoric acid
- A-D-Glucose 1,6-diphosphate
- a-D-Glucose 1,6-diphosphoric acid
- a-D-Glucose-1,6-P2
- a-delta-1,6-Bis(dihydrogen phosphate) glucopyranose
- a-delta-1,6-Bis(dihydrogen phosphoric acid) glucopyranose
- a-delta-Glucose 1,6-bis(dihydrogen phosphate)
- a-delta-Glucose 1,6-bis(dihydrogen phosphoric acid)
- a-delta-Glucose 1,6-bisphosphate
- a-delta-Glucose 1,6-bisphosphoric acid
- a-delta-Glucose 1,6-diphosphate
- a-delta-Glucose 1,6-diphosphoric acid
- a-δ-1,6-Bis(dihydrogen phosphate) glucopyranose
- a-δ-1,6-Bis(dihydrogen phosphoric acid) glucopyranose
- a-δ-Glucose 1,6-bis(dihydrogen phosphate)
- a-δ-Glucose 1,6-bis(dihydrogen phosphoric acid)
- a-δ-Glucose 1,6-bisphosphate
- a-δ-Glucose 1,6-bisphosphoric acid
- a-δ-Glucose 1,6-diphosphate
- a-δ-Glucose 1,6-diphosphoric acid
- Alpha-D-1,6-Bis(dihydrogen phosphate) Glucopyranose
- alpha-D-1,6-Bis(dihydrogen phosphoric acid) glucopyranose
- Alpha-D-Glucopyranose, 1,6-bis(dihydrogen phosphate)
- alpha-D-Glucopyranose, 1,6-bis(dihydrogen phosphoric acid)
- Alpha-D-Glucose 1,6-bis(dihydrogen phosphate)
- alpha-D-Glucose 1,6-bis(dihydrogen phosphoric acid)
- Alpha-D-Glucose 1,6-bisphosphate
- alpha-D-Glucose 1,6-bisphosphoric acid
- Alpha-D-Glucose 1,6-diphosphate
- alpha-D-Glucose 1,6-diphosphoric acid
- Alpha-D-Glucose-1,6-P2
- Alpha-delta-1,6-Bis(dihydrogen phosphate) Glucopyranose
- alpha-delta-1,6-Bis(dihydrogen phosphoric acid) glucopyranose
- Alpha-delta-Glucose 1,6-bis(dihydrogen phosphate)
- alpha-delta-Glucose 1,6-bis(dihydrogen phosphoric acid)
- Alpha-delta-Glucose 1,6-bisphosphate
- alpha-delta-Glucose 1,6-bisphosphoric acid
- Alpha-delta-Glucose 1,6-diphosphate
- alpha-delta-Glucose 1,6-diphosphoric acid
- D-Glucose 1,6-biphosphate
- D-Glucose 1,6-biphosphoric acid
- D-Glucose 1,6-bisphosphate
- D-Glucose 1,6-bisphosphoric acid
- D-Glucose 1,6-diphosphate
- D-Glucose 1,6-diphosphoric acid
- Delta-Glucose 1,6-diphosphate
- delta-Glucose 1,6-diphosphoric acid
- Glucose 1,6-bisphosphate
- Glucose 1,6-bisphosphoric acid
- Glucose 1,6-diphosphate
- Glucose 1,6-diphosphoric acid
- Glucose-1,6-bisphosphate
- Glucose-1,6-bisphosphoric acid
- Glucose-1,6-diphosphate
- Glucose-1,6-diphosphoric acid
- α-D-1,6-Bis(dihydrogen phosphate) glucopyranose
- α-D-1,6-Bis(dihydrogen phosphoric acid) glucopyranose
- α-D-Glucopyranose, 1,6-bis(dihydrogen phosphate)
- α-D-Glucopyranose, 1,6-bis(dihydrogen phosphoric acid)
- α-D-Glucose 1,6-bis(dihydrogen phosphate)
- α-D-Glucose 1,6-bis(dihydrogen phosphoric acid)
- α-D-Glucose 1,6-bisphosphate
- α-D-Glucose 1,6-bisphosphoric acid
- α-D-Glucose 1,6-diphosphate
- α-D-Glucose 1,6-diphosphoric acid
- α-D-Glucose-1,6-P2
- α-δ-1,6-Bis(dihydrogen phosphate) glucopyranose
- α-δ-1,6-Bis(dihydrogen phosphoric acid) glucopyranose
- α-δ-Glucose 1,6-bis(dihydrogen phosphate)
- α-δ-Glucose 1,6-bis(dihydrogen phosphoric acid)
- α-δ-Glucose 1,6-bisphosphate
- α-δ-Glucose 1,6-bisphosphoric acid
- α-δ-Glucose 1,6-diphosphate
- α-δ-Glucose 1,6-diphosphoric acid
- δ-Glucose 1,6-diphosphate
- δ-Glucose 1,6-diphosphoric acid
|
|---|
|
Chemical Formula: |
C6H14O12P2 |
|---|
| Average Molecular Weight: |
340.1157 |
|---|
| Monoisotopic Molecular
Weight: |
339.996048936 |
|---|
| InChI Key: |
RWHOZGRAXYWRNX-VFUOTHLCSA-N |
|---|
| InChI: | InChI=1S/C6H14O12P2/c7-3-2(1-16-19(10,11)12)17-6(5(9)4(3)8)18-20(13,14)15/h2-9H,1H2,(H2,10,11,12)(H2,13,14,15)/t2-,3-,4+,5-,6-/m1/s1 |
|---|
| CAS
number: |
10139-18-1 |
|---|
| IUPAC Name: | {[(2R,3S,4S,5R,6R)-3,4,5-trihydroxy-6-(phosphonooxy)oxan-2-yl]methoxy}phosphonic acid |
|---|
|
Traditional IUPAC Name: |
glucose 1,6-bisphosphate |
|---|
| SMILES: | O[C@H]1[C@H](O)[C@@H](COP(O)(O)=O)O[C@H](OP(O)(O)=O)[C@@H]1O |
|---|
|
Chemical Taxonomy |
|---|
|
Taxonomy Description | This compound belongs to the class of organic compounds known as monosaccharide phosphates. These are monosaccharides comprising a phosphated group linked to the carbohydrate unit. |
|---|
|
Kingdom |
Organic compounds |
|---|
| Super Class | Organooxygen compounds |
|---|
|
Class |
Carbohydrates and carbohydrate conjugates |
|---|
| Sub Class | Monosaccharides |
|---|
|
Direct Parent |
Monosaccharide phosphates |
|---|
| Alternative Parents |
|
|---|
| Substituents |
- Monosaccharide phosphate
- Monoalkyl phosphate
- Alkyl phosphate
- Phosphoric acid ester
- Oxane
- Organic phosphoric acid derivative
- Organic phosphate
- Secondary alcohol
- Polyol
- 1,2-diol
- Oxacycle
- Organoheterocyclic compound
- Hydrocarbon derivative
- Alcohol
- Aliphatic heteromonocyclic compound
|
|---|
| Molecular Framework |
Aliphatic heteromonocyclic compounds |
|---|
| External Descriptors |
|
|---|
|
Physical Properties |
|---|
| State: |
Solid |
|---|
| Charge: | -4 |
|---|
|
Melting point: |
Not Available |
|---|
| Experimental Properties: |
|
|---|
| Predicted Properties |
|
|---|
|
Biological Properties |
|---|
| Cellular Locations: |
Cytoplasm |
|---|
| Reactions: | |
|---|
|
Pathways: |
|
|---|
|
Spectra |
|---|
| Spectra: |
|
|---|
|
References |
|---|
| References: |
- Cadefau JA, Andres V, Carreras J, Vernet M, Grau JM, Urbano-Marquez A, Cusso R: Glucose 1,6-bisphosphate and fructose 2,6-bisphosphate in muscle from healthy humans and chronic alcoholic patients. Alcohol Alcohol. 1992 May;27(3):253-6. Pubmed: 1449560
- Kanehisa, M., Goto, S., Sato, Y., Furumichi, M., Tanabe, M. (2012). "KEGG for integration and interpretation of large-scale molecular data sets." Nucleic Acids Res 40:D109-D114. Pubmed: 22080510
- Katz A, Sahlin K, Broberg S: Regulation of glucose utilization in human skeletal muscle during moderate dynamic exercise. Am J Physiol. 1991 Mar;260(3 Pt 1):E411-5. Pubmed: 2003594
- Katz A: G-1,6-P2, glycolysis, and energy metabolism during circulatory occlusion in human skeletal muscle. Am J Physiol. 1988 Aug;255(2 Pt 1):C140-4. Pubmed: 3407759
- van der Werf, M. J., Overkamp, K. M., Muilwijk, B., Coulier, L., Hankemeier, T. (2007). "Microbial metabolomics: toward a platform with full metabolome coverage." Anal Biochem 370:17-25. Pubmed: 17765195
- Yamada Y, Kono N, Nakajima H, Shimizu T, Kiyokawa H, Kawachi M, Ono A, Nishimura T, Kuwajima M, Tarui S: Low glucose-1, 6-bisphosphate and high fructose-2, 6-bisphosphate concentrations in muscles of patients with glycogenosis types VII and V. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1991 Apr 15;176(1):7-10. Pubmed: 2018547
|
|---|
| Synthesis Reference: |
Not Available |
|---|
| Material Safety Data Sheet (MSDS) |
Not Available |
|---|
|
Links |
|---|
| External Links: |
|
|---|