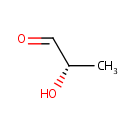
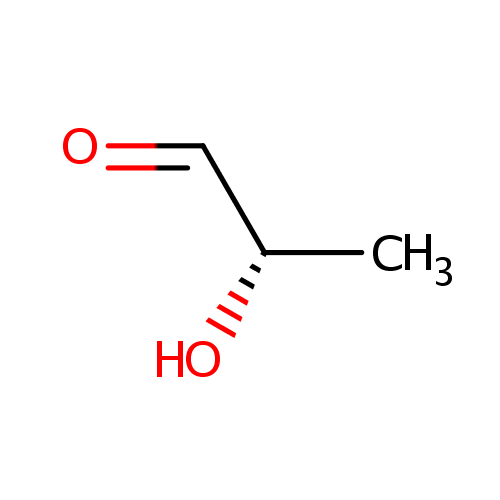
Lactaldehyde (PAMDB000476)
| Record Information | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Version | 1.0 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Update Date | 1/22/2018 11:54:54 AM | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Metabolite ID | PAMDB000476 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Identification | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Name: | Lactaldehyde | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Description: | L-lactaldehyde is an intermediate metabolite in the pyruvate metabolism pathway. L-lactaldehyde is irreversibly produced from pyruvaldehyde via the enzyme aldehyde reductase (EC:1.1.1.21) which is then irreversibly converted to propylene glycol via aldehyde reductase (EC:1.1.1.21). | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Structure | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Synonyms: |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Chemical Formula: | C3H6O2 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Average Molecular Weight: | 74.079 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Monoisotopic Molecular Weight: | 74.036779433 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| InChI Key: | BSABBBMNWQWLLU-UHFFFAOYSA-N | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| InChI: | InChI=1S/C3H6O2/c1-3(5)2-4/h2-3,5H,1H3 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| CAS number: | 598-35-6 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| IUPAC Name: | (2S)-2-hydroxypropanal | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Traditional IUPAC Name: | L-lactaldehyde | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| SMILES: | [H]C(=O)C(C)O | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Chemical Taxonomy | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Taxonomy Description | This compound belongs to the class of organic compounds known as alpha-hydroxyaldehydes. These are organic compounds containing an aldehyde substituted with a hydroxyl group on the adjacent carbon. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Kingdom | Organic compounds | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Super Class | Organooxygen compounds | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Class | Carbonyl compounds | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Sub Class | Aldehydes | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Direct Parent | Alpha-hydroxyaldehydes | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Alternative Parents | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Substituents |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Molecular Framework | Aliphatic acyclic compounds | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| External Descriptors |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Physical Properties | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| State: | Solid | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Charge: | 0 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Melting point: | Not Available | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Experimental Properties: |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Predicted Properties |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Biological Properties | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Cellular Locations: | Cytoplasm | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Reactions: | L-Fuculose 1-phosphate <> Dihydroxyacetone phosphate + Lactaldehyde + (S)-Lactaldehyde Water + Lactaldehyde + NAD + (S)-Lactaldehyde <>2 Hydrogen ion + L-Lactic acid + NADH Hydrogen ion + Lactaldehyde + NADH <> (S)-Propane-1,2-diol + NAD L-Rhamnulose 1-phosphate <> Dihydroxyacetone phosphate + Lactaldehyde + (S)-Lactaldehyde Lactaldehyde + NAD + Water <> L-Lactic acid + NADH + Hydrogen ion Propylene glycol + NAD <> Lactaldehyde + NADH + Hydrogen ion 2-Dehydro-3-deoxy-L-rhamnonate <> Lactaldehyde + Pyruvic acid + (S)-Lactaldehyde L-Fuculose 1-phosphate <> Dihydroxyacetone phosphate + Lactaldehyde L-Rhamnulose 1-phosphate <> Dihydroxyacetone phosphate + Lactaldehyde Lactaldehyde + NADP < Pyruvaldehyde + NADPH + Hydrogen ion 2-keto-3-deoxy-L-rhamnonate Pyruvic acid + Lactaldehyde Lactaldehyde + NAD + Water > L-Lactic acid + NADH (S)-Propane-1,2-diol + NAD > Lactaldehyde + NADH L-rhamnulose 1-phosphate + L-Rhamnulose 1-phosphate > Dihydroxyacetone phosphate + (S)-lactaldehyde + Lactaldehyde L-fuculose 1-phosphate + L-Fuculose 1-phosphate > Dihydroxyacetone phosphate + (S)-lactaldehyde + Lactaldehyde NAD + Water + (S)-lactaldehyde + Lactaldehyde > NADH +2 Hydrogen ion + L-Lactic acid + L-Lactic acid (S)-lactaldehyde + NADH + Hydrogen ion + Lactaldehyde > NAD + Propylene glycol | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Pathways: | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Spectra | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Spectra: |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| References | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| References: |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Synthesis Reference: | Kranz, Cyrill. Synthesis of Lactic Aldehyde. Chemicke Listy pro Vedu a Prumysl (1912), 5 323-7. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Material Safety Data Sheet (MSDS) | Not Available | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Links | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| External Links: |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Enzymes
- General function:
- Involved in oxidoreductase activity
- Specific function:
- Catalyzes the reduction of 2,5-diketo-D-gluconic acid (25DKG) to 2-keto-L-gulonic acid (2KLG)
- Gene Name:
- dkgB
- Locus Tag:
- PA4167
- Molecular weight:
- 29.5 kDa
Reactions
| 2-dehydro-D-gluconate + NADP(+) = 2,5-didehydro-D-gluconate + NADPH. |
- General function:
- Involved in carbon-carbon lyase activity
- Specific function:
- Catalyzes the reversible retro-aldol cleavage of 2-keto- 3-deoxy-L-rhamnonate (KDR) to pyruvate and lactaldehyde. 2-keto-3- deoxy-L-mannonate, 2-keto-3-deoxy-L-lyxonate and 4-hydroxy-2- ketoheptane-1,7-dioate (HKHD) are also reasonably good substrates, although 2-keto-3-deoxy-L-rhamnonate is likely to be the physiological substrate
- Gene Name:
- rhmA
- Locus Tag:
- PA4128
- Molecular weight:
- 28.2 kDa
Reactions
| 2-dehydro-3-deoxy-L-rhamnonate = pyruvate + (R)-lactaldehyde. |