|
Record Information |
|---|
| Version |
1.0 |
|---|
| Update Date |
1/22/2018 11:54:54 AM |
|---|
|
Metabolite ID | PAMDB000445 |
|---|
|
Identification |
|---|
| Name: |
(S)-b-aminoisobutyric acid |
|---|
| Description: | Beta-Aminoisobutyric acid is a non-protein amino acid originating from the catabolism of thymine and valine. Beta-Aminoisobutyric acid occurs in two isomeric forms. The S-enantiomer of beta-Aminoisobutyric acid is predominantly derived from the catabolism of valine. It has been suggested that an altered homoeostasis of b-alanine underlies some of the abnormalities with a dihydropyrimidine dehydrogenase (DPD). DPD constitutes the first step of the pyrimidine degradation pathway, in which the pyrimidine bases uracil and thymine are catabolized to b-alanine and the R-enantiomer of beta-Aminoisobutyric acid respectively. In normal situation with an intact pyrimidine degradation pathway, R-methylmalonic acid semialdehyde can be synthesized directly from the catabolism of thymine. Hence, there might be less cross-over between the valine and thymine pathway, allowing the conversion of S-methylmalonic acid semialdehyde into S-beta-Aminoisobutyric acid and the subsequent accumulation of S-beta-Aminoisobutyric acid. (PMID: 14705962, 14292857, 14453202) |
|---|
|
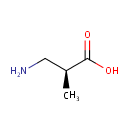
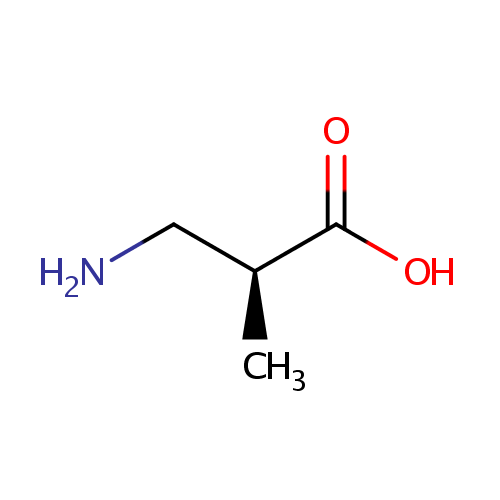
Structure |
|
|---|
| Synonyms: | - (+)-a-Methyl-b-alanine
- (+)-alpha-Methyl-beta-alanine
- (+)-b-Aminoisobutyrate
- (+)-b-Aminoisobutyric acid
- (+)-beta-Aminoisobutyrate
- (+)-beta-Aminoisobutyric acid
- (+)-α-Methyl-β-alanine
- (+)-β-Aminoisobutyrate
- (+)-β-Aminoisobutyric acid
- (S)-3-amino-2-methyl-Propanoate
- (S)-3-amino-2-methyl-Propanoic acid
- (S)-3-Amino-2-methylpropanoate
- (S)-3-Amino-2-methylpropanoic acid
- (S)-3-Amino-isobutanoate
- (S)-3-Amino-isobutanoic acid
- (S)-3-Amino-isobutyrate
- (S)-3-Amino-isobutyric acid
- (S)-b-Aminoisobutyrate
- (S)-b-Aminoisobutyric acid
- (S)-beta-Aminoisobutyrate
- (S)-beta-Aminoisobutyric acid
- (S)-β-Aminoisobutyrate
- (S)-β-Aminoisobutyric acid
- L-2-Methyl-b-Alanine
- L-2-Methyl-beta-Alanine
- L-2-Methyl-β-alanine
- L-3-Amino-2-methylpropanoate
- L-3-Amino-2-methylpropanoic acid
- L-3-Amino-2-methylpropionate
- L-3-Amino-2-methylpropionic acid
- L-3-Amino-isobutanoate
- L-3-Amino-isobutanoic acid
- L-3-Amino-isobutyrate
- L-3-Amino-isobutyric acid
- L-b-Aminoisobutyrate
- L-b-Aminoisobutyric acid
- L-beta-Aminoisobutyrate
- L-beta-Aminoisobutyric acid
- L-β-Aminoisobutyrate
- L-β-Aminoisobutyric acid
- S-b-Aminoisobutyrate
- S-b-Aminoisobutyric acid
- S-beta-Aminoisobutyrate
- S-beta-Aminoisobutyric acid
- S-β-Aminoisobutyrate
- S-β-Aminoisobutyric acid
|
|---|
|
Chemical Formula: |
C4H9NO2 |
|---|
| Average Molecular Weight: |
103.1198 |
|---|
| Monoisotopic Molecular
Weight: |
103.063328537 |
|---|
| InChI Key: |
QCHPKSFMDHPSNR-VKHMYHEASA-N |
|---|
| InChI: | InChI=1S/C4H9NO2/c1-3(2-5)4(6)7/h3H,2,5H2,1H3,(H,6,7)/t3-/m0/s1 |
|---|
| CAS
number: |
4249-19-8 |
|---|
| IUPAC Name: | (2S)-3-amino-2-methylpropanoic acid |
|---|
|
Traditional IUPAC Name: |
(+)-α-methyl-β-alanine |
|---|
| SMILES: | C[C@@H](CN)C(O)=O |
|---|
|
Chemical Taxonomy |
|---|
|
Taxonomy Description | This compound belongs to the class of organic compounds known as beta amino acids and derivatives. These are amino acids having a (-NH2) group attached to the beta carbon atom. |
|---|
|
Kingdom |
Organic compounds |
|---|
| Super Class | Organic acids and derivatives |
|---|
|
Class |
Carboxylic acids and derivatives |
|---|
| Sub Class | Amino acids, peptides, and analogues |
|---|
|
Direct Parent |
Beta amino acids and derivatives |
|---|
| Alternative Parents |
|
|---|
| Substituents |
- Beta amino acid or derivatives
- Monocarboxylic acid or derivatives
- Carboxylic acid
- Hydrocarbon derivative
- Primary amine
- Organooxygen compound
- Organonitrogen compound
- Primary aliphatic amine
- Carbonyl group
- Amine
- Aliphatic acyclic compound
|
|---|
| Molecular Framework |
Aliphatic acyclic compounds |
|---|
| External Descriptors |
|
|---|
|
Physical Properties |
|---|
| State: |
Solid |
|---|
| Charge: | 0 |
|---|
|
Melting point: |
175-177 °C |
|---|
| Experimental Properties: |
|
|---|
| Predicted Properties |
|
|---|
|
Biological Properties |
|---|
| Cellular Locations: |
Cytoplasm |
|---|
| Reactions: | |
|---|
|
Pathways: |
- Valine, leucine and isoleucine degradation pae00280
|
|---|
|
Spectra |
|---|
| Spectra: |
|
|---|
|
References |
|---|
| References: |
- KAKIMOTO Y, ARMSTRONG MD: The preparation and isolation of D-(-)-beta-aminoisobutyric acid. J Biol Chem. 1961 Dec;236:3283-6. Pubmed: 14453202
- KAKIMOTO Y, KANAZAWA A, SANO I: IDENTIFICATION OF D(-)-BETA-AMINOISOBUTYRIC ACID IN HUMAN LIVER. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1965 Feb 15;97:376-7. Pubmed: 14292857
- Kanehisa, M., Goto, S., Sato, Y., Furumichi, M., Tanabe, M. (2012). "KEGG for integration and interpretation of large-scale molecular data sets." Nucleic Acids Res 40:D109-D114. Pubmed: 22080510
- Roe CR, Struys E, Kok RM, Roe DS, Harris RA, Jakobs C: Methylmalonic semialdehyde dehydrogenase deficiency: psychomotor delay and methylmalonic aciduria without metabolic decompensation. Mol Genet Metab. 1998 Sep;65(1):35-43. Pubmed: 9787093
- Van Kuilenburg, A. B., Stroomer, A. E., Van Lenthe, H., Abeling, N. G., Van Gennip, A. H. (2004). "New insights in dihydropyrimidine dehydrogenase deficiency: a pivotal role for beta-aminoisobutyric acid?" Biochem J 379:119-124. Pubmed: 14705962
|
|---|
| Synthesis Reference: |
Alauddin, Mian M.; Fissekis, John D.; Conti, Peter S. a-Alkylation of amino acid derivatives: synthesis and chiral resolution of [11C]b-aminoisobutyric acid. Nuclear Medicine and Biology (1997), 24(8), 771-775. |
|---|
| Material Safety Data Sheet (MSDS) |
Not Available |
|---|
|
Links |
|---|
| External Links: |
|
|---|