|
Record Information |
|---|
| Version |
1.0 |
|---|
| Update Date |
1/22/2018 11:54:54 AM |
|---|
|
Metabolite ID | PAMDB000442 |
|---|
|
Identification |
|---|
| Name: |
Coproporphyrinogen I |
|---|
| Description: | Coproporphyrinogen is formed by Uroporphyrinogen decarboxylase from Uroporphyrinogen by decarboxylation of 4 acetates. |
|---|
|
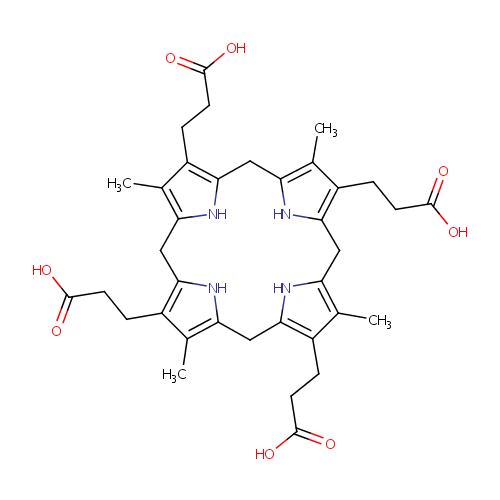
Structure |
|
|---|
| Synonyms: | - 3,8,13,18-Tetramethyl-5,10,15,20,22,24-hexahydroporphyrin-2,7,12,17-tetrapropanoate
- 3,8,13,18-Tetramethyl-5,10,15,20,22,24-hexahydroporphyrin-2,7,12,17-tetrapropanoic acid
|
|---|
|
Chemical Formula: |
C36H44N4O8 |
|---|
| Average Molecular Weight: |
660.7566 |
|---|
| Monoisotopic Molecular
Weight: |
660.315914404 |
|---|
| InChI Key: |
WIUGGJKHYQIGNH-UHFFFAOYSA-N |
|---|
| InChI: | InChI=1S/C36H44N4O8/c1-17-21(5-9-33(41)42)29-14-26-19(3)23(7-11-35(45)46)31(39-26)16-28-20(4)24(8-12-36(47)48)32(40-28)15-27-18(2)22(6-10-34(43)44)30(38-27)13-25(17)37-29/h37-40H,5-16H2,1-4H3,(H,41,42)(H,43,44)(H,45,46)(H,47,48) |
|---|
| CAS
number: |
31110-56-2 |
|---|
| IUPAC Name: | 3-[9,14,19-tris(2-carboxyethyl)-5,10,15,20-tetramethyl-21,22,23,24-tetraazapentacyclo[16.2.1.1?,??1????.1??,???tetracosa-1(20),3,5,8,10,13,15,18-octaen-4-yl]propanoic acid |
|---|
|
Traditional IUPAC Name: |
coproporphyrinogen I |
|---|
| SMILES: | CC1=C2CC3=C(CCC(O)=O)C(C)=C(CC4=C(CCC(O)=O)C(C)=C(CC5=C(CCC(O)=O)C(C)=C(CC(N2)=C1CCC(O)=O)N5)N4)N3 |
|---|
|
Chemical Taxonomy |
|---|
|
Taxonomy Description | This compound belongs to the class of organic compounds known as porphyrins. These are compounds containing a fundamental skeleton of four pyrrole nuclei united through the alpha-positions by four methine groups to form a macrocyclic structure. |
|---|
|
Kingdom |
Organic compounds |
|---|
| Super Class | Organoheterocyclic compounds |
|---|
|
Class |
Tetrapyrroles and derivatives |
|---|
| Sub Class | Porphyrins |
|---|
|
Direct Parent |
Porphyrins |
|---|
| Alternative Parents |
|
|---|
| Substituents |
- Porphyrin
- Tetracarboxylic acid or derivatives
- Substituted pyrrole
- Heteroaromatic compound
- Pyrrole
- Azacycle
- Carboxylic acid
- Carboxylic acid derivative
- Hydrocarbon derivative
- Organooxygen compound
- Organonitrogen compound
- Carbonyl group
- Aromatic heteropolycyclic compound
|
|---|
| Molecular Framework |
Aromatic heteropolycyclic compounds |
|---|
| External Descriptors |
|
|---|
|
Physical Properties |
|---|
| State: |
Solid |
|---|
| Charge: | -4 |
|---|
|
Melting point: |
171 - 174 °C |
|---|
| Experimental Properties: |
|
|---|
| Predicted Properties |
|
|---|
|
Biological Properties |
|---|
| Cellular Locations: |
Membrane |
|---|
| Reactions: | |
|---|
|
Pathways: |
- Porphyrin and chlorophyll metabolism pae00860
|
|---|
|
Spectra |
|---|
| Spectra: |
|
|---|
|
References |
|---|
| References: |
- Beukeveld GJ, In 't Veld G, Havinga R, Groen AK, Wolthers BG, Kuipers F: Relationship between biliary lipid and protoporphyrin secretion; potential role of mdr2 P-glycoprotein in hepatobiliary organic anion transport. J Hepatol. 1996 Mar;24(3):343-52. Pubmed: 8778203
- Cornford P: Transformation of porphobilinogen into porphyrins by preparations from human erythrocytes. Biochem J. 1964 Apr;91(1):64-73. Pubmed: 5833390
- Ding Y, Lin B, Huie CW: Binding studies of porphyrins to human serum albumin using affinity capillary electrophoresis. Electrophoresis. 2001 Jul;22(11):2210-6. Pubmed: 11504054
- Gorchein A, Guo R, Lim CK, Raimundo A, Pullon HW, Bellingham AJ: Porphyrins in urine, plasma, erythrocytes, bile and faeces in a case of congenital erythropoietic porphyria (Gunther's disease) treated with blood transfusion and iron chelation: lack of benefit from oral charcoal. Biomed Chromatogr. 1998 Nov-Dec;12(6):350-6. Pubmed: 9861496
- Kanehisa, M., Goto, S., Sato, Y., Furumichi, M., Tanabe, M. (2012). "KEGG for integration and interpretation of large-scale molecular data sets." Nucleic Acids Res 40:D109-D114. Pubmed: 22080510
- Mel'nikova YaI, Kravchuk ZI, Preygerzon VA, Martsev SP: Functional activation of antibodies on modification with Pd(II) coproporphyrin I N-Hydroxysuccinimide ester. Biochemistry (Mosc). 1997 Aug;62(8):924-7. Pubmed: 9360305
- Pannier E, Viot G, Aubry MC, Grange G, Tantau J, Fallet-Bianco C, Muller F, Cabrol D: Congenital erythropoietic porphyria (Gunther's disease): two cases with very early prenatal manifestation and cystic hygroma. Prenat Diagn. 2003 Jan;23(1):25-30. Pubmed: 12533808
- Pinelli A, Mussini C, Bertolini B, Buratti M, Trivulzio S: Increased excretion of urine coproporphyrins during daunorubicin administration in patients affected by acute myelogenous leukemia. Pharmacol Res. 2003 Nov;48(5):515-8. Pubmed: 12967599
- Sakai T, Niinuma Y, Yanagihara S, Ushio K: Liquid-chromatographic separation and determination of coproporphyrins I and III in urine. Clin Chem. 1983 Feb;29(2):350-3. Pubmed: 6821943
|
|---|
| Synthesis Reference: |
Not Available |
|---|
| Material Safety Data Sheet (MSDS) |
Not Available |
|---|
|
Links |
|---|
| External Links: |
|
|---|