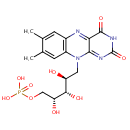
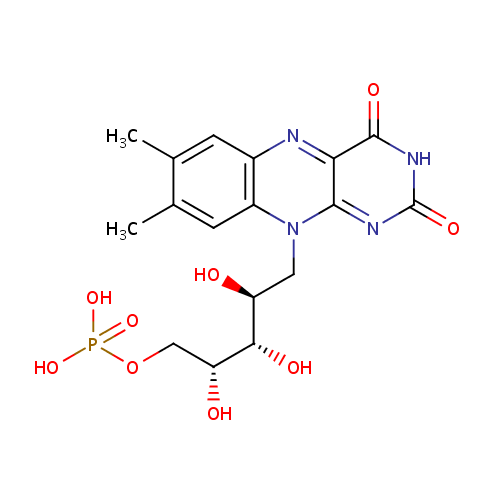
Flavin Mononucleotide (PAMDB000408)
| Record Information | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Version | 1.0 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Update Date | 1/22/2018 12:54:54 PM | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Metabolite ID | PAMDB000408 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Identification | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Name: | Flavin Mononucleotide | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Description: | FMN is coenzyme for a number of oxidative enzymes including NADH dehydrogenase. It is the principal form in which riboflavin is found in cells. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Structure | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Synonyms: |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Chemical Formula: | C17H21N4O9P | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Average Molecular Weight: | 456.3438 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Monoisotopic Molecular Weight: | 456.104614802 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| InChI Key: | FVTCRASFADXXNN-SCRDCRAPSA-N | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| InChI: | InChI=1S/C17H21N4O9P/c1-7-3-9-10(4-8(7)2)21(15-13(18-9)16(25)20-17(26)19-15)5-11(22)14(24)12(23)6-30-31(27,28)29/h3-4,11-12,14,22-24H,5-6H2,1-2H3,(H,20,25,26)(H2,27,28,29)/t11-,12+,14-/m0/s1 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| CAS number: | 146-17-8 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| IUPAC Name: | {[(2R,3S,4S)-5-{7,8-dimethyl-2,4-dioxo-2H,3H,4H,10H-benzo[g]pteridin-10-yl}-2,3,4-trihydroxypentyl]oxy}phosphonic acid | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Traditional IUPAC Name: | riboflavin 5'-phosphate | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| SMILES: | CC1=CC2=C(C=C1C)N(C[C@H](O)[C@H](O)[C@H](O)COP(O)(O)=O)C1=NC(=O)NC(=O)C1=N2 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Chemical Taxonomy | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Taxonomy Description | This compound belongs to the class of organic compounds known as flavin nucleotides. These are nucleotides containing a flavin moiety. Flavin is a compound that contains the tricyclic isoalloxazine ring system, which bears 2 oxo groups at the 2- and 4-positions. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Kingdom | Organic compounds | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Super Class | Nucleosides, nucleotides, and analogues | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Class | Flavin nucleotides | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Sub Class | Not Available | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Direct Parent | Flavin nucleotides | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Alternative Parents | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Substituents |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Molecular Framework | Aromatic heteropolycyclic compounds | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| External Descriptors |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Physical Properties | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| State: | Solid | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Charge: | -3 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Melting point: | 290 °C | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Experimental Properties: |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Predicted Properties |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Biological Properties | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Cellular Locations: | Cytoplasm | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Reactions: | Flavin Mononucleotide + Hydrogen ion + NADH > FMNH + NAD Flavin Mononucleotide + Hydrogen ion + NADPH <> FMNH + NADP Adenosine triphosphate + Riboflavin <> ADP + Flavin Mononucleotide + Hydrogen ion Adenosine triphosphate + Flavin Mononucleotide + Hydrogen ion > FAD + Pyrophosphate FMNH + Oxygen + Sulfoacetate > Flavin Mononucleotide + Glyoxylic acid + Hydrogen ion + Water + Sulfite FMNH + Isethionic acid + Oxygen > Flavin Mononucleotide + Glycolaldehyde + Hydrogen ion + Water + Sulfite FMNH + Methanesulfonate + Oxygen > Formaldehyde + Flavin Mononucleotide + Hydrogen ion + Water + Sulfite Butanesulfonate + FMNH + Oxygen > Butanal + Flavin Mononucleotide + Hydrogen ion + Water + Sulfite Ethanesulfonate + FMNH + Oxygen > Acetaldehyde + Flavin Mononucleotide + Hydrogen ion + Water + Sulfite 2 Ferroxamine + FMNH >2 Iron +2 ferroxamine minus Fe(3) + Flavin Mononucleotide +2 Hydrogen ion Adenosine triphosphate + Flavin Mononucleotide <> Pyrophosphate + FAD Adenosine triphosphate + Riboflavin <> ADP + Flavin Mononucleotide Uracil + FMNH + Oxygen <> Ureidoacrylate peracid + Flavin Mononucleotide NAD(P)<sup>+</sup> + FMNH <> NAD(P)H + Flavin Mononucleotide + Hydrogen ion Thymine + Oxygen + FMNH > (<i>Z</i>)-2-methylureidoacrylate peracid + Flavin Mononucleotide + Hydrogen ion an alkanesulfonate + Oxygen + FMNH > an aldehyde + Sulfite + Water + Flavin Mononucleotide + Hydrogen ion Flavin Mononucleotide + Water > Riboflavin + Phosphate Uracil + Oxygen + FMNH > Hydrogen ion + Ureidoacrylate peracid + Flavin Mononucleotide Uracil + FMNH(2) + Oxygen > Ureidoacrylate peracid + Flavin Mononucleotide + Water More...Thymine + FMNH(2) + Oxygen > (Z)-2-Methyl-ureidoacrylate peracid + Flavin Mononucleotide + Water FMNH(2) + NAD > Flavin Mononucleotide + NADH An alkanesufonate (R-CH(2)-SO(3)H) + FMNH(2) + Oxygen > an aldehyde (R-CHO) + Flavin Mononucleotide + Sulfite + Water FMNH(2) + NADP > Flavin Mononucleotide + NADPH Alkanesulfonate + FMNH + Oxygen <> Aldehyde + Flavin Mononucleotide + Sulfite + Water Uracil + FMNH + Oxygen + Thymine <> Ureidoacrylate peracid + Flavin Mononucleotide + (Z)-2-Methyl-ureidoacrylate peracid alkylsulfonate + FMNH2 + Oxygen > Betaine aldehyde + Sulfite + Flavin Mononucleotide + Water +2 Hydrogen ion + Sulfite Butanesulfonate + Oxygen + FMNH2 > Hydrogen ion + Water + Sulfite + Flavin Mononucleotide + Betaine aldehyde + Sulfite Oxygen + FMNH2 + 3-(N-morpholino)propanesulfonate > Sulfite + Water + Hydrogen ion + Flavin Mononucleotide + Betaine aldehyde + Sulfite ethanesulfonate + Oxygen + FMNH2 > Hydrogen ion + Water + Flavin Mononucleotide + Sulfite + Betaine aldehyde + Sulfite isethionate + Oxygen + FMNH2 > Betaine aldehyde + Flavin Mononucleotide + Hydrogen ion + Water + Sulfite + Sulfite Oxygen + methanesulfonate + FMNH2 + Methanesulfonate > Hydrogen ion + Water + Flavin Mononucleotide + Sulfite + Betaine aldehyde + Sulfite | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Pathways: | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Spectra | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Spectra: |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| References | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| References: |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Synthesis Reference: | Ono, Shigeru; Hirano, Hiroko; Sato, Yoshiyuki. Formation of flavin adenine dinucleotide and flavin mononucleotide by lens homogenate. Experimental Eye Research (1982), 34(2), 297-301. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Material Safety Data Sheet (MSDS) | Download (PDF) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Links | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| External Links: |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||