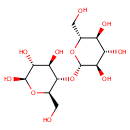
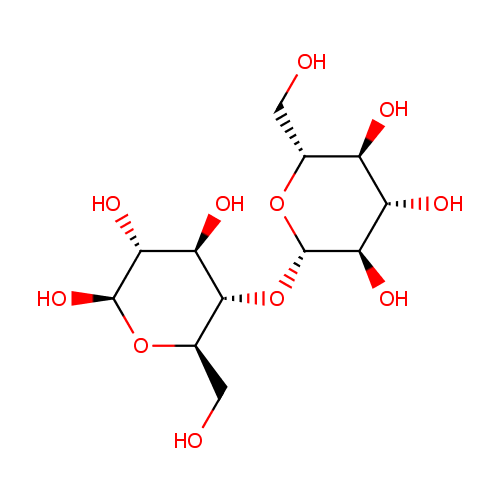
| References: |
- Cain WJ, Millar JS, Himebauch AS, Tietge UJ, Maugeais C, Usher D, Rader DJ: Lipoprotein [a] is cleared from the plasma primarily by the liver in a process mediated by apolipoprotein [a]. J Lipid Res. 2005 Dec;46(12):2681-91. Epub 2005 Sep 8. Pubmed: 16150825
- Calero M, Ghiso J: Radiolabeling of amyloid-beta peptides. Methods Mol Biol. 2005;299:325-48. Pubmed: 15980615
- Cobden I, Hamilton I, Rothwell J, Axon AT: Cellobiose/mannitol test: physiological properties of probe molecules and influence of extraneous factors. Clin Chim Acta. 1985 May 15;148(1):53-62. Pubmed: 3924445
- Garcia-Martos P, Garcia-Agudo L, Ruiz-Aragon J, Saldarreaga A, Marin P: [Carbohydrate assimilation by clinical and environmental Rhodotorula glutinis strains] Rev Iberoam Micol. 2004 Jun;21(2):90-2. Pubmed: 15538836
- Hu WL, Chindemi PA, Regoeczi E: In vivo behaviour of rat transferrin bearing a hybrid glycan and its interaction with macrophages. Biochem Cell Biol. 1992 Aug;70(8):636-42. Pubmed: 1476702
- Johansson AG, Sundqvist T, Skogh T: IgG immune complex binding to and activation of liver cells. An in vitro study with IgG immune complexes, Kupffer cells, sinusoidal endothelial cells and hepatocytes. Int Arch Allergy Immunol. 2000 Apr;121(4):329-36. Pubmed: 10828724
- Juby LD, Rothwell J, Axon AT: Cellobiose/mannitol sugar test--a sensitive tubeless test for coeliac disease: results on 1010 unselected patients. Gut. 1989 Apr;30(4):476-80. Pubmed: 2497056
- Kaczmarczyk A, Blom AM, Alston-Smith J, Sjoquist M, Fries E: Plasma bikunin: half-life and tissue uptake. Mol Cell Biochem. 2005 Mar;271(1-2):61-7. Pubmed: 15881656
- Kanehisa, M., Goto, S., Sato, Y., Furumichi, M., Tanabe, M. (2012). "KEGG for integration and interpretation of large-scale molecular data sets." Nucleic Acids Res 40:D109-D114. Pubmed: 22080510
- Keseler, I. M., Collado-Vides, J., Santos-Zavaleta, A., Peralta-Gil, M., Gama-Castro, S., Muniz-Rascado, L., Bonavides-Martinez, C., Paley, S., Krummenacker, M., Altman, T., Kaipa, P., Spaulding, A., Pacheco, J., Latendresse, M., Fulcher, C., Sarker, M., Shearer, A. G., Mackie, A., Paulsen, I., Gunsalus, R. P., Karp, P. D. (2011). "EcoCyc: a comprehensive database of Escherichia coli biology." Nucleic Acids Res 39:D583-D590. Pubmed: 21097882
- Matsuura Y: Degradation of konjac glucomannan by enzymes in human feces and formation of short-chain fatty acids by intestinal anaerobic bacteria. J Nutr Sci Vitaminol (Tokyo). 1998 Jun;44(3):423-36. Pubmed: 9742462
- Morita T, Ozawa M, Ito H, Kimio S, Kiriyama S: Cellobiose is extensively digested in the small intestine by beta-galactosidase in rats. Nutrition. 2008 Nov-Dec;24(11-12):1199-204. Epub 2008 Aug 26. Pubmed: 18752931
- Nakamura S, Oku T, Ichinose M: Bioavailability of cellobiose by tolerance test and breath hydrogen excretion in humans. Nutrition. 2004 Nov-Dec;20(11-12):979-83. Pubmed: 15561487
- Potier M, Dallaire L, Melancon SB: Occurrence and properties of fetal intestinal glycosidases (disaccharidases) in human amniotic fluid. Biol Neonate. 1975;27(3-4):141-52. Pubmed: 241430
- Sakamoto M, Huang Y, Umeda M, Ishikawa I, Benno Y: Prevotella multiformis sp. nov., isolated from human subgingival plaque. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol. 2005 Mar;55(Pt 2):815-9. Pubmed: 15774668
- van der Werf, M. J., Overkamp, K. M., Muilwijk, B., Coulier, L., Hankemeier, T. (2007). "Microbial metabolomics: toward a platform with full metabolome coverage." Anal Biochem 370:17-25. Pubmed: 17765195
- Welcker K, Martin A, Kolle P, Siebeck M, Gross M: Increased intestinal permeability in patients with inflammatory bowel disease. Eur J Med Res. 2004 Oct 29;9(10):456-60. Pubmed: 15546811
- Winder, C. L., Dunn, W. B., Schuler, S., Broadhurst, D., Jarvis, R., Stephens, G. M., Goodacre, R. (2008). "Global metabolic profiling of Escherichia coli cultures: an evaluation of methods for quenching and extraction of intracellular metabolites." Anal Chem 80:2939-2948. Pubmed: 18331064
|
|---|