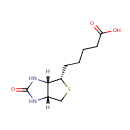
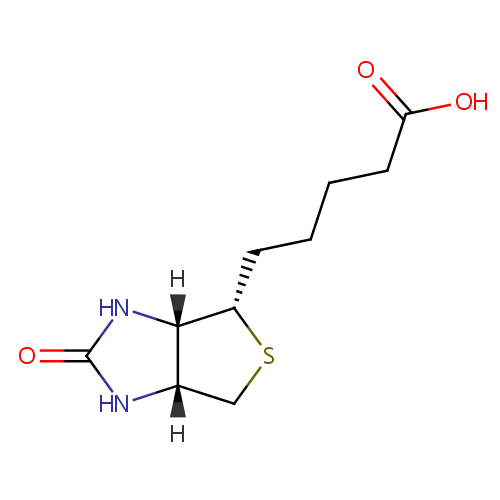
Biotin (PAMDB000008)
| Record Information | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Version | 1.0 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Update Date | 1/22/2018 11:54:54 AM | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Metabolite ID | PAMDB000008 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Identification | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Name: | Biotin | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Description: | Biotin is an enzyme co-factor present in minute amounts in every living cell. Biotin is also known as vitamin H or B7 or coenzyme R. It occurs mainly bound to proteins or polypeptides. The utilization of biotin for covalent attachment to carboxylases and its reutilization through the release of carboxylase biotin after proteolytic degradation constitutes the 'biotin cycle'. Biotin acts as a carboxyl carrier in carboxylation reactions. The biotin moiety is covalently bound to the epsilon amino group of a Lysine residue in each of these carboxylases in a domain 60-80 amino acids long. The domain is structurally similar among carboxylases from bacteria to mammals. The biotin moiety is covalently bound to the epsilon amino group of a Lys residue in carboxylases in a domain 60-80 amino acids long. The domain is structurally similar among carboxylases from bacteria to mammals. Posttranscriptional events related to ribosomal activity and protein folding may further contribute to effects of biotin on gene expression. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Structure | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Synonyms: |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Chemical Formula: | C10H16N2O3S | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Average Molecular Weight: | 244.311 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Monoisotopic Molecular Weight: | 244.088163078 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| InChI Key: | YBJHBAHKTGYVGT-ZKWXMUAHSA-N | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| InChI: | InChI=1S/C10H16N2O3S/c13-8(14)4-2-1-3-7-9-6(5-16-7)11-10(15)12-9/h6-7,9H,1-5H2,(H,13,14)(H2,11,12,15)/t6-,7-,9-/m0/s1 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| CAS number: | 58-85-5 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| IUPAC Name: | 5-[(3aS,4S,6aR)-2-oxo-hexahydro-1H-thieno[3,4-d]imidazolidin-4-yl]pentanoic acid | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Traditional IUPAC Name: | biotin | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| SMILES: | [H][C@]12CS[C@@H](CCCCC(O)=O)[C@@]1([H])NC(=O)N2 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Chemical Taxonomy | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Taxonomy Description | This compound belongs to the class of organic compounds known as biotin and derivatives. These are organic compounds containing a ureido (tetrahydroimidizalone) ring fused with a tetrahydrothiophene ring. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Kingdom | Organic compounds | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Super Class | Organoheterocyclic compounds | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Class | Biotin and derivatives | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Sub Class | Not Available | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Direct Parent | Biotin and derivatives | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Alternative Parents |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Substituents |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Molecular Framework | Aliphatic heteropolycyclic compounds | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| External Descriptors |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Physical Properties | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| State: | Solid | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Charge: | -1 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Melting point: | 232 °C | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Experimental Properties: |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Predicted Properties |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Biological Properties | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Cellular Locations: | Cytoplasm | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Reactions: | [2Fe-2S] iron-sulfur cluster + S-Adenosylmethionine + Dethiobiotin > [2Fe-1S] desulfurated iron-sulfur cluster + Biotin + 5'-Deoxyadenosine + Hydrogen ion + L-Methionine D-Biotin D-sulfoxide + Hydrogen ion + NADH > Biotin + Water + NAD D-Biotin D-sulfoxide + Hydrogen ion + NADPH > Biotin + Water + NADP Adenosine triphosphate + Biotin <> Pyrophosphate + Biotinyl-5'-AMP Dethiobiotin + Sulfur donor + 2 S-Adenosylmethionine + 2 e- + 2 Hydrogen ion <> Biotin +2 L-Methionine +2 5'-Deoxyadenosine <i>S</i>-sulfanyl-[acceptor] + Dethiobiotin + S-Adenosylmethionine > an unsulfurated sulfur acceptor + Biotin + 5'-Deoxyadenosine + L-Methionine + Hydrogen ion Benzo[a]pyrene-4,5-oxide + Red-Thioredoxin Biotin + Water + Ox-Thioredoxin Adenosine triphosphate + Biotin + apo-[acetyl-CoA:carbon-dioxide ligase (ADP-forming)] > Adenosine monophosphate + Pyrophosphate + [acetyl-CoA:carbon-dioxide ligase (ADP-forming)] Adenosine triphosphate + Biotin > Biotinyl-5'-AMP + Pyrophosphate Biocytin + Water > Biotin + L-Lysine + L-Lysine Dethiobiotin + 2 S-adenosyl-L-methionine + 2 Hydrogen ion + a sulfurated [sulfur carrier] > Biotin +2 L-Methionine +2 5'-Deoxyadenosine Biotin Sulfoxide > Biotin Biotin + Adenosine triphosphate > diphosphate + Biotinyl-5'-AMP + Pyrophosphate | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Pathways: | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Spectra | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Spectra: | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| References | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| References: |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Synthesis Reference: | Corey, E. J.; Mehrotra, Mukund M. A simple and enantioselective synthesis of (+)-biotin. Tetrahedron Letters (1988), 29(1), 57-60. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Material Safety Data Sheet (MSDS) | Download (PDF) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Links | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| External Links: |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Enzymes
- General function:
- Involved in biotin-[acetyl-CoA-carboxylase] ligase activity
- Specific function:
- BirA acts both as a biotin-operon repressor and as the enzyme that synthesizes the corepressor, acetyl-CoA:carbon-dioxide ligase. This protein also activates biotin to form biotinyl-5'- adenylate and transfers the biotin moiety to biotin-accepting proteins
- Gene Name:
- birA
- Locus Tag:
- PA4280
- Molecular weight:
- 34 kDa
Reactions
| ATP + biotin + apo-[acetyl-CoA:carbon-dioxide ligase (ADP-forming)] = AMP + diphosphate + [acetyl-CoA:carbon-dioxide ligase (ADP-forming)]. |
- General function:
- Involved in catalytic activity
- Specific function:
- Catalyzes the conversion of dethiobiotin (DTB) to biotin by the insertion of a sulfur atom into dethiobiotin via a radical- based mechanism
- Gene Name:
- bioB
- Locus Tag:
- PA0500
- Molecular weight:
- 39.1 kDa
Reactions
| Dethiobiotin + sulfur + 2 S-adenosyl-L-methionine = biotin + 2 L-methionine + 2 5'-deoxyadenosine. |